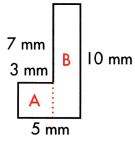
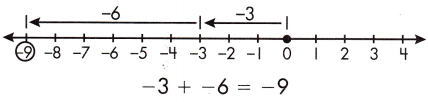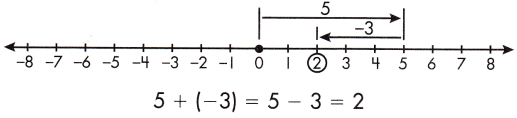This handy Spectrum Math Grade 7 Answer Key Chapter 1 Lesson 1.5 Adding Integers provides detailed answers for the workbook questions.
Spectrum Math Grade 7 Chapter 1 Lesson 1.5 Adding Integers Answers Key
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
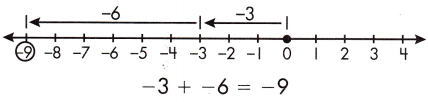
To find the sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
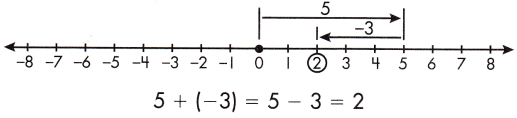
Add.
Question 1.
a. 3 + 4 _____
Answer: 7
3 + 4 = 7
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 3 and 4 both are positive integers. Hence their sum is also positive.
b. -3 + (-4) _____
Answer: -7
-3 + (-4) = -3 – 4 = -7
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, -3 and -4 both are negative integers. Hence their sum is also negative.
c. 3 + (-4) _____
Answer: -1
3 + (-4) =3 – 4= -1
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 3 is a positive integer and -4 is a negative integer. And 4 is greater than 3. Hence their sum is also negative.
d. -3 + 4 _____
Answer: 1
-3 + 4 = 1
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, -3 is a negative integer and 4 is a positive integer. And 4 is greater than 3. Hence their sum is also positive.
Question 2.
a. -3 + (-3) ____
Answer: -6
-3 + (-3) = -3 – 3 = -6
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, -3 and -3 both are negative integers. Hence their sum is also negative.
b. 3 + (-3) _____
Answer: 0
3 + (-3) =3 – 3= 0
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 3 is a positive integer and -3 is a negative integer. Hence their sum is zero.
c. -3 + 3 _____
Answer: 0
-3 + 3= 0
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 3 is a positive integer and -3 is a negative integer. Hence their sum is zero.
d. 3 + 3 ____
Answer: 6
3 + 3 = 6
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 3 and 3 both are positive integers. Hence their sum is also positive.
Question 3.
a. 5 + (-1) ____
Answer: 4
5 + (-1) =5 – 1= 4
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 5 is a positive integer and -1 is a negative integer. And 5 is greater than 1. Hence their sum is also positive.
b. -5 + 1 ____
Answer: -4
-5 + 1 = -4
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 1 is a positive integer and -5 is a negative integer. And 5 is greater than 1. Hence their sum is also negative.
c. -5 + (-1) ____
Answer: -6
-5 + (-1) = -5 – 1 = -6
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, -5 and -1 both are negative integers. Hence their sum is also negative.
d. 5 + 1 ____
Answer: 6
5 + 1 = 6
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 5 and 1 both are positive integers. Hence their sum is also positive.
Question 4.
a. -7 + 3 ____
Answer: -4
-7 + 3 = -4
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 3 is a positive integer and -7 is a negative integer. And 7 is greater than 3. Hence their sum is also negative.
b. -7 + (-3) _____
Answer: -10
-7 + (-3) = -7- 3 = -10
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, -7 and -3 both are negative integers. Hence their sum is also negative.
c. 7 + (-3) _____
Answer: 4
7 + (-3) = 7 – 3 = 4
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 7 is a positive integer and -3 is a negative integer. And 7 is greater than 3. Hence their sum is also positive.
d. 7 + 3 _____
Answer: 10
7 + 3 = 10
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 7 and 3 both are positive integers. Hence their sum is also positive.
Question 5.
a. 4 + 7 ____
Answer: 11
4 + 7 = 11
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 4 and 7 both are positive integers. Hence their sum is also positive.
b. 4 + (-7) _____
Answer: -3
4 + (-7) = 4 – 7 = -3
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 4 is a positive integer and -7 is a negative integer. And 7 is greater than 4. Hence their sum is also negative.
c. -4 + (7) ____
Answer: 3
-4 + (7) = -4 + 7 = 3
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 7 is a positive integer and -4 is a negative integer. And 7 is greater than 4. Hence their sum is also positive.
d. -4 + (-7) _____
Answer: -11
-4 + (-7) = -4 – 7 = -11
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, -7 and -4 both are negative integers. Hence their sum is also negative.
Question 6.
a. 8 + (-8) _____
Answer: 0
8 + (-8) = 8 – 8= 0
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 8 is a positive integer and -8 is a negative integer. Hence their sum is zero.
b. -8 + (-8) ______
Answer: -16
-8 + (-8) = -8 – 8 = -16
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, -8 and -8 both are negative integers. Hence their sum is also negative.
c. 8 + 8 ____
Answer: 16
8 + 8 = 16
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 8 and 8 both are positive integers. Hence their sum is also positive.
d. -8 + 8 _____
Answer: 0
-8 + 8= 0
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 8 is a positive integer and -8 is a negative integer. Hence their sum is zero.
Question 7.
a. -3 + 0 _____
Answer: -3
-3 + 0= -3
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, -3 is a negative integer and 0 is neither a positive number nor a negative number. Hence their sum is also negative.
b. 3 + 0 ____
Answer: 3
3 + 0 = 3
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 3 is a positive integer and 0 is neither a positive number nor a negative number. Hence their sum is also positive.
c. -5 + (-6) _____
Answer: -11
-5 + (-6) =-5 – 6 = -11
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, -5 and -6 both are negative integers. Hence their sum is also negative.
d. -5 + 6 ____
Answer: 1
-5 + 6 = 1
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 6 is a positive integer and -5 is a negative integer. And 6 is greater than 5. Hence their sum is also positive.
Question 8.
a. 5 + (-6) _____
Answer: -1
5 + (-6) = 5 – 6 = -1
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 5 is a positive integer and -6 is a negative integer. And 6 is greater than 5. Hence their sum is also negative.
b. 5 + 6 ____
Answer: 11
5 + 6 = 11
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 5 and 6 both are positive integers. Hence their sum is also positive.
c. -8 + 0 ____
Answer: -8
-8 + 0 = -8
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, -8 is a negative integer and 0 is neither a positive number nor a negative number. Hence their sum is also negative.
d. 8 + 0 ____
Answer: 8
8 + 0 = 8
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 8 and 0 both are positive integers. Hence their sum is also positive.
Question 9.
a. -3 + 6 ____
Answer: 3
-3 + 6 = 3
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 6 is a positive integer and -3 is a negative integer. And 6 is greater than 3. Hence their sum is also positive.
b. -3 + (-6) ____
Answer: -9
-3 + (-6) = -3 – 6 = -9
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, -3 and -6 both are negative integers. Hence their sum is also negative.
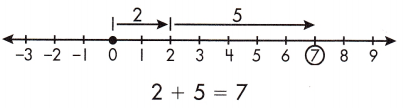
c. 3 + 6 ____
Answer: 9
3 + 6 = 9
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 3 and 6 both are positive integers. Hence their sum is also positive.
d. 3 + (-6) _____
Answer: -3
3 + (-6) = 3 – 6 = -3
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 3 is a positive integer and -6 is a negative integer. And 6 is greater than 3. Hence their sum is also negative.
Question 10.
a. -6 + (-4) ______
Answer: -10
-6 + (-4) = -6 – 4 = -10
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, -4 and -6 both are negative integers. Hence their sum is also negative.
b. -6 + 4 ____
Answer: -2
-6 + 4 = -2
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 4 is a positive integer and -6 is a negative integer. And 6 is greater than 4. Hence their sum is also negative.
c. 6 + (-4) _____
Answer: 2
6 + (-4) = 6 – 4 = 2
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 6 is a positive integer and -4 is a negative integer. And 6 is greater than 4. Hence their sum is also positive.
d. 6 + 4 ____
Answer: 10
6 + 4 = 10
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 6 and 4 both are positive integers. Hence their sum is also positive.
Adding Integers
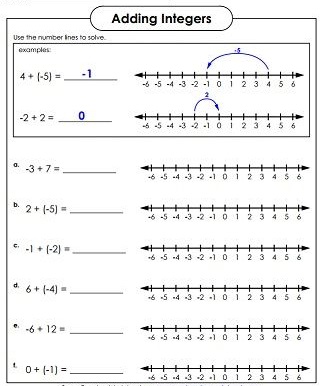
To find the sum of two integers with different signs, find their absolute values. Remember, absolute value is the distance (in units) that a number is from 0, expressed as a positive quantity. Subtract the lesser number from the greater number. Absolute value is written as |n|.
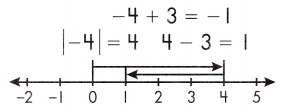
4 > 3, so the sum is negative
The sum has the same sign as the integer with the larger absolute value.
Add.
Question 1.
a. 6 + 2 = ____
Answer: 8
6 + 2 = 8
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 6 and 2 both are positive integers. Hence their sum is also positive.
b. 9 + (-4) = ____
Answer: 5
9 + (-4) = 9 – 4 = 5
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 9 is a positive integer and -4 is a negative integer. And 9 is greater than 4. Hence their sum is also positive.
c. 7 + (-9) = ____
Answer: -2
7 + (-9) = 7 – 9 = -2
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 7 is a positive integer and -9 is a negative integer. And 9 is greater than 7. Hence their sum is also negative.
Question 2.
a. -4 + 7 = ____
Answer: 3
-4 + 7 = 3
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 7 is a positive integer and -4 is a negative integer. And 7 is greater than 4. Hence their sum is also positive.
b. -3 + (-6) = ____
Answer: -9
-3 + (-6) = -3 – 6 = -9
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, -3 and -6 both are negative integers. Hence their sum is also negative.
c. -12 + 11 = ____
Answer: -1
-12 + 11 = -1
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 11 is a positive integer and -12 is a negative integer. And 12 is greater than 11. Hence their sum is also negative.
Question 3.
a. -16 + 0 = ____
Answer: -16
-16 + 0 = -16
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, -16 is a negative integer and 0 is neither a positive number nor a negative number. Hence their sum is also negative.
b. 13 + (-24) = ____
Answer: -11
13 + (-24) = 13 – 24 = -11
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 13 is a positive integer and -24 is a negative integer. And 24 is greater than 13. Hence their sum is also negative.
c. -6 + 8 = ____
Answer: 2
-6 + 8 = 2
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 8 is a positive integer and -6 is a negative integer. And 8 is greater than 6. Hence their sum is also positive.
Question 4.
a. 0 + (-9) = ____
Answer: -9
0 + (-9) = 0 – 9= -9
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, -9 is a negative integer and 0 is neither a positive number nor a negative number. Hence their sum is also negative.
b. -1 + 2 = ____
Answer: 1
-1 + 2 = 1
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 2 is a positive integer and -1 is a negative integer. And 2 is greater than 1. Hence their sum is also positive.
c. 1 + (-2) = ____
Answer: -1
1 + (-2) = -1
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 1 is a positive integer and -2 is a negative integer. And 2 is greater than 1. Hence their sum is also negative.
Question 5.
a. -4 + 4 = ____
Answer: 0
-4 + 4= 0
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 4 is a positive integer and -4 is a negative integer. Hence their sum is zero.
b. 3 + (-6) = ____
Answer: -3
3 + (-6) = 3 – 6= -3
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, -6 is a negative integer and 3 is a positive integer. And 6 is greater than 3. Hence their sum is also negative.
c. 7 + (-17) = ____
Answer: -10
7 + (-17) = 7 – 17= -10
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, -17 is a negative integer and 7 is a positive integer. And 17 is greater than 7. Hence their sum is also negative.
Question 6.
a. -45 + 21 = ____
Answer: -24
-45 + 21 = -24
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, -45 is a negative integer and 21 is a positive integer. And 45 is greater than 21. Hence their sum is also negative.
b. 41 + 44 = ____
Answer: 85
41 + 44 = 85
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 41 and 44 both are positive integers. Hence their sum is also positive.
c. 33 + 25 = ____
Answer: 58
33 + 25 = 58
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 33 and 25 both are positive integers. Hence their sum is also positive.
Question 7.
a. 27 + (-39) = ____
Answer: -12
27 + (-39) = 27 – 39 = -12
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, -39 is a negative integer and 27 is a positive integer. And 39 is greater than 27. Hence their sum is also negative.
b. 20 + 1 = ___
Answer: 21
20 + 1 = 21
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 20 and 1 both are positive integers. Hence their sum is also positive.
c. 3 + (-3) = ____
Answer: 0
3 + (-3) =3 – 3= 0
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 3 is a positive integer and -3 is a negative integer. Hence their sum is zero.
Question 8.
a. -12 + (-12) = ____
Answer: -24
-12 + (-12) = -12 – 12 = -24
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, -12 and -12 both are negative integers. Hence their sum is also negative.
b. 35 + (-26) = ____
Answer: 9
35 + (-26) = 35 – 26 = 9
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, -26 is a negative integer and 35 is a positive integer. And 35 is greater than 26. Hence their sum is also positive.
c. -22 + 16 = ____
Answer: 6
-22 + 16 = 6
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, -22 is a negative integer and 16 is a positive integer. And 22 is greater than 16. Hence their sum is also negative.
Question 9.
a. 31 + 17 = ___
Answer: 48
31 + 17 = 48
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 31 and 17 both are positive integers. Hence their sum is also positive.
b. -9 + (-6) = ____
Answer: -15
-9 + (-6) = -15
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, -9 and -6 both are negative integers. Hence their sum is also negative.
c. -47 + 36 = _____
Answer: 11
-47 + 36 = 11
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, -47 is a negative integer and 36 is a positive integer. And 47 is greater than 36. Hence their sum is also negative.
Question 10.
a. 4 + 5 = ____
Answer: 9
4 + 5 = 9
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, 4 and 5 both are positive integers. Hence their sum is also positive.
b. -43 + 35 = ___
Answer: -8
-43 + 35 = -8
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, -43 is a negative integer and 35 is a positive integer. And 43 is greater than 35. Hence their sum is also negative.
c. 24 + (-33) = ____
Answer: -9
24 + (-33) = 24 – 33 = -9
The sum of two positive integers is a positive integer.
The sum of two negative integers is a negative integer.
The sum of two integers with opposite signs, subtract the digit of lesser value from the digit of greater value and keep the sign of the greater digit.
Therefore, -33 is a negative integer and 24 is a positive integer. And 33 is greater than 24. Hence their sum is also negative.