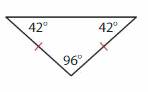
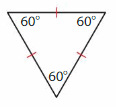
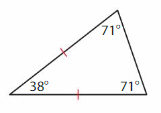
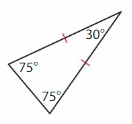
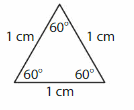
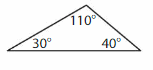
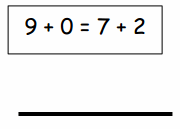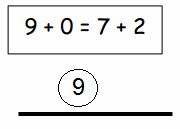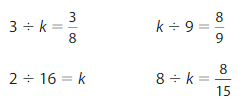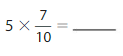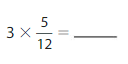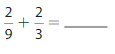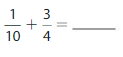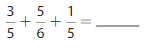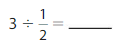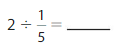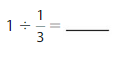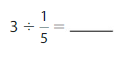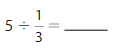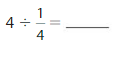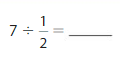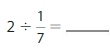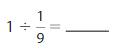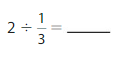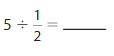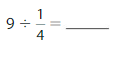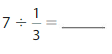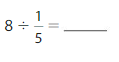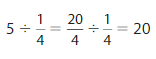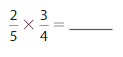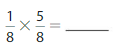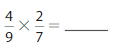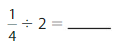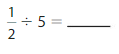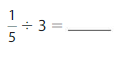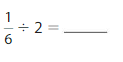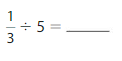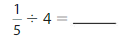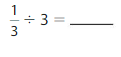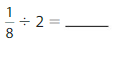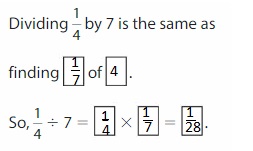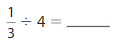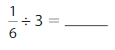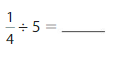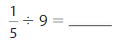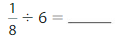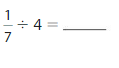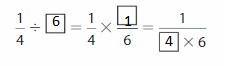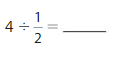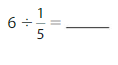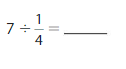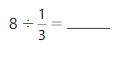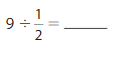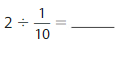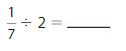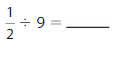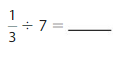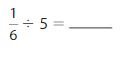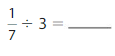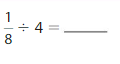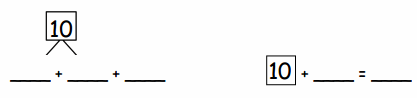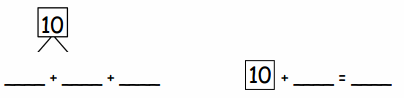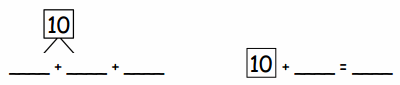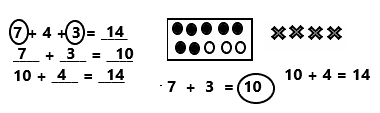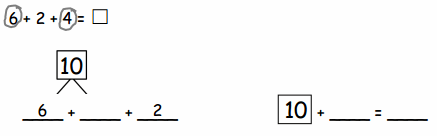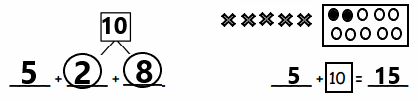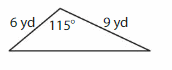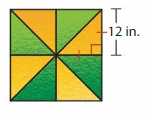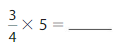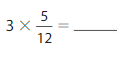Download the Big Ideas Math Book Answer Key Grade 5 Chapter 10 Divide Fractions free of cost and kick start your preparation immediately. You will get the necessary skill set needed to solve the problems related to fractions here. Access Detailed Solutions to all the problems and learn how to solve related problems when you encounter them during your exams. Seek Homework Help needed by accessing the Big Ideas Math Answers Grade 5 Chapter 10 Divide Fractions.
Big Ideas Math Book Answer Key Grade 5 Chapter 10 Divide Fractions
Cross Check the Solutions from our Big Ideas Math Answers Grade 5 Chapter 10 Divide Fractions and understand the areas you are facing difficulty. Score higher grades in your exams and refer to Big Ideas Math Book Solution Key Grade 5 Chapter 10 Divide Fractions to have strong command over fractions.
Lesson: 1 Interpret Fractions as Division

Lesson: 2 Mixed Numbers as Quotients
Lesson: 3 Divide Whole Numbers by Unit Fractions

Lesson: 4 Divide Unit Fractions by Whole Numbers
Lesson: 5 Problem Solving: Fraction Division
Chapter: 10 – Divide Fractions
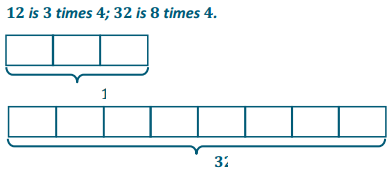
Lesson 10.1 Interpret Fractions as Division
Explore and Grow`
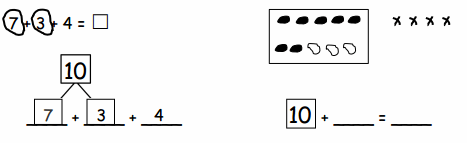
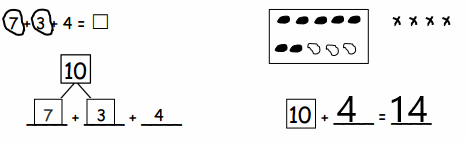
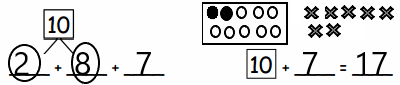
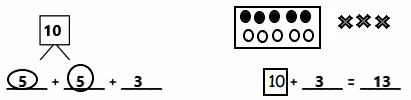
You share 4 sheets of construction paper equally among 8 people. Write a division expression that represents the situation. What fraction of a sheet of paper does each person get? Use a model to support your answer?
Answer:
The division expression that represents the fraction of a sheet of paper does each person get is:
4 ÷ 8 = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation:
It is given that you have 4 sheets of construction paper equally among 8 people.
Hence,
The division expression that represents the fraction of a sheet of paper is:
( The number of sheets of construction paper ) ÷ ( The number of people )
= 4 ÷ 8
= \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the fraction of a sheet of paper does each person get is: \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Structure
How can you check your answer using multiplication?
Answer: We can check the answer by using the partial products method or by using the simplification method.
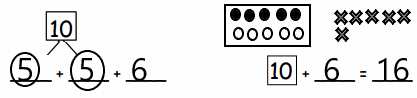
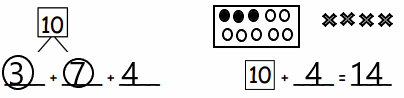
Think and Grow: Divide Whole Numbers
You can use models to divide whole numbers that have a fraction as the quotient.
Answer: 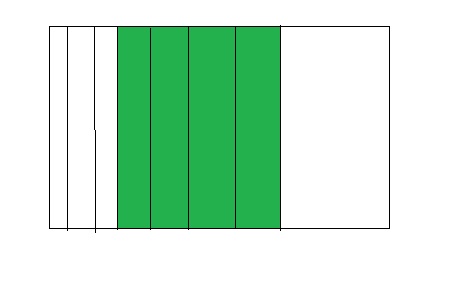
From the above model,
The number of colored parts is: 4
The total number of parts are: 8
So,
The fraction of the colored part out of the total number of parts = 4 ÷ 8
= \(\frac{4}{8}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
In \(\frac{1}{2}\),
1 represents the quotient
2 represents the remainder
Example
Find 2 ÷ 3.
One Way: Use a tape diagram. Show 2 wholes. Divide each whole into 3 equal parts.
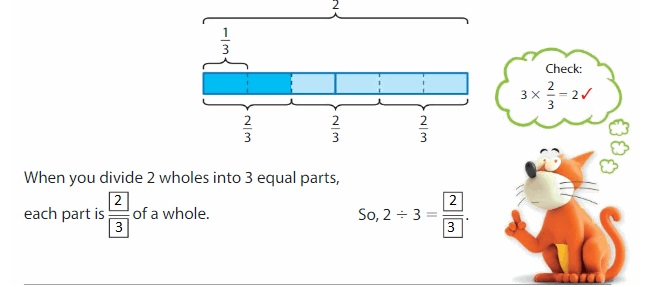
Another Way: Use an area model. Show 2 wholes. Divide each whole into 3 equal parts. Then separate the parts into 3 equal groups.

Show and Grow
Divide. Use a model to help
Question 1.
2 ÷ 4 =0.5
Answer: 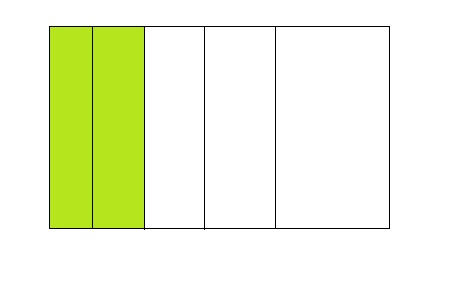
From the above model,
The number of colored parts is: 2
The number of total parts is: 4
So,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts = 2 ÷ 4
= \(\frac{2}{4}\)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\)
So,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts in the decimal form is: 0.5
Question 2.
1 ÷ 3 = 0.33
Answer: 
From the above model,
The number of colored parts is: 1
The number of total parts is: 3
So,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts = 1 ÷ 3
= \(\frac{1}{3}\)
So,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts in the decimal form is: 0.33
Apply and Grow: Practice
Divide. Use a model to help.
Question 3.
1 ÷ 8 =0.018
Answer: 
From the above model,
The number of colored parts is: 1
The number of total parts is: 8
So,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts = 1 ÷ 8
= \(\frac{1}{8}\)
So,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts in the decimal form is: 0.018
Question 4.
1 ÷ 4 =0.25
Answer: 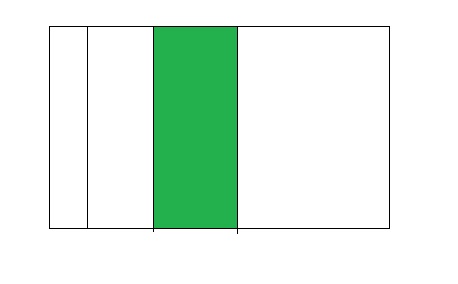
From the above model,
The number of colored parts is: 1
The number of total parts is: 4
So,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts = 1 ÷ 4
= \(\frac{1}{4}\)
So,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts in the decimal form is: 0.25
Question 5.
2 ÷ 6 =0.33
Answer: 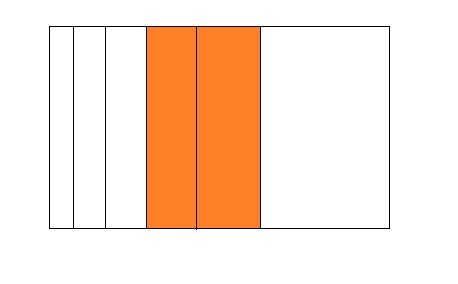
From the above model,
The number of colored parts is: 2
The number of total parts is: 6
So,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts = 2 ÷ 6
= \(\frac{2}{6}\)
= \(\frac{1}{3}\)
So,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts in the decimal form is: 0.33
Question 6.
2 ÷ 5 = 0.4
Answer: 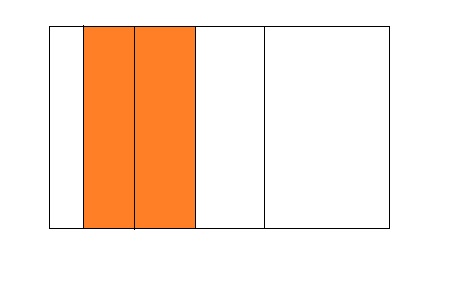
From the above model,
The number of colored parts is: 2
The number of total parts is: 5
So,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts = 2 ÷ 5
= \(\frac{2}{5}\)
So,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts in the decimal form is: 0.4
Question 7.
3 ÷ 7 = 0.42
Answer: 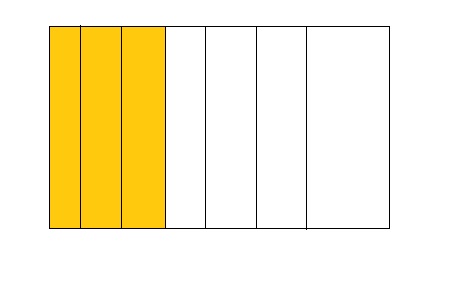
From the above model,
The number of colored parts is: 3
The number of total parts is: 7
So,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts = 3 ÷ 7
= \(\frac{3}{7}\)
So,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts in the decimal form is: 0.42
Question 8.
5 ÷ 6 = 0.83
Answer: 
From the above model,
The number of colored parts is: 5
The number of total parts is: 6
So,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts = 5 ÷ 6
= \(\frac{5}{6}\)
So,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts in the decimal form is: 0.83
Question 9.
How many 6s are in 1?
Answer: There are six \(\frac{1}{6}\)s in 1
Explanation:
The number of 6s in 1 can be obtained by dividing 1 into 6 equal parts.
So,
The figure obtained will be like;
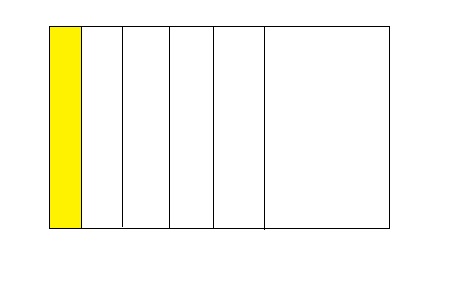
From the above model,
The number of colored parts is: 1
The number of total parts is: 6
So,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts = 1 ÷ 6
= \(\frac{1}{6}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that there are six 6s in 1
Question 10.
How many 10s are in 9?
Answer: There are 9 \(\frac{9}{10}\)s in 9
Explanation:
The model for the number of 10s in 9 are:
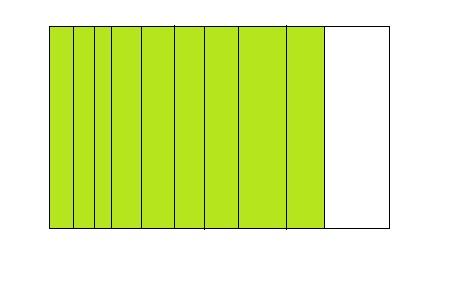
From the above model,
The number of colored parts is: 9
The number of total parts is: 10
So,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts = 9 ÷ 10
= \(\frac{9}{10}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that there are nine 9s in 10
Question 11.
Number Sense
For which equations does k = 8?
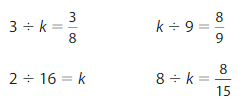
Answer: Let the equations named A), B), C), and D)
So,
The four equations are:
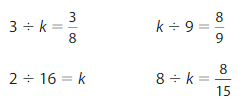
From the above equations,
The value ‘k’ must be in the numerator.
So,
In A), the value of the numerator is: 3
In B), the value of the numerator is: k
In C), the value of the numerator is: 2
In D) the value of the numerator is: 8
So,
From the above numerator values,
We can say that “k=8” holds good for Equation B)
Question 12.
Writing
Write and solve a real-life problem for 7 ÷ 12.
Answer: 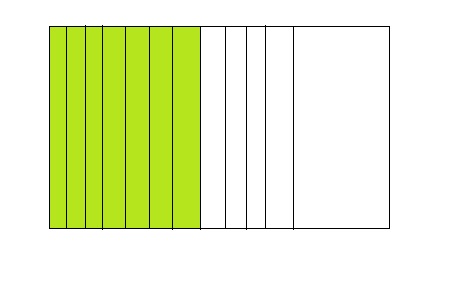
From the above model,
The number of colored parts is: 7
The number of total parts is: 12
So,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts = 7 ÷ 12
= \(\frac{7}{12}\)
Hence,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts in the decimal form is: 0.58
Think and Grow: Modeling Real Life
Example
Three fruit bars are shared equally among 4 friends. What fraction of a fruit bar does each friend get?

Divide 3 by 4 to find what fraction of a fruit bar each friend gets.
Use an area model to find 3 ÷ 4. Show 3 whole fruit bars. Divide each fruit bar into 4 equal parts. Then separate the parts into 4 equal groups.
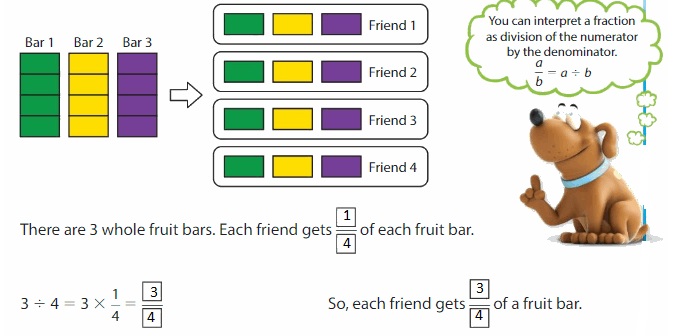
Show and Grow
Question 13.
You cut a 5-foot streamer into 6 pieces of equal size. What is the length of each piece in feet? in inches?
Answer: The length of each piece in feet is: \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Explanation:
It is given that you cut a 5-foot streamer into 6 equal pieces of equal size.
So,
The model representing the 6 equal pieces of the 5-foot streamer is:
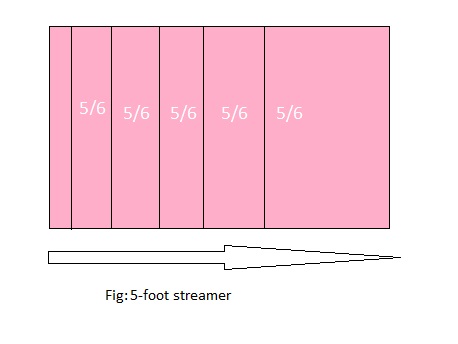
From the above model,
We can see that each part in the model represents \(\frac{5}{6}\) of each part.
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the length of each piece of a 5-foot streamer in feet is: \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Question 14.
Four circular lemon slices are shared equally among 8 glasses of water. What fraction of a lemon slice does each glass get?

Answer: The fraction of a lemon slice does each glass get is: \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation:
It is given that the four circular lemon slices are shared equally among 8 glasses of water.
So,
The model representing the portion that each glass get is:
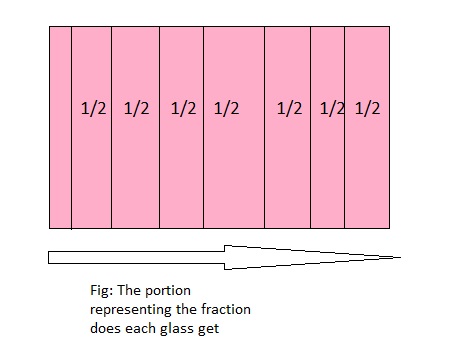
From the above model,
We can say that each part represents \(\frac{1}{2}\) part
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the portion of a lemon slice does glass get is: \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 15.
You cut a 5-foot streamer into 6 pieces of equal size. What is the length of each piece in feet? in inches?
Answer: The length of each piece in feet is: \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Explanation:
It is given that you cut a 5-foot streamer into 6 equal pieces of equal size.
So,
The model representing the 6 equal pieces of the 5-foot streamer is:

From the above model,
We can see that each part in the model represents \(\frac{5}{6}\) of each part.
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the length of each piece of a 5-foot streamer in feet is: \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Question 16.
DIG DEEPER!
A fruit drink is made using \(\frac{7}{4}\) quarts of orange juice and \(\frac{5}{4}\) quarts of pineapple juice. The drink is shared equally among 12 guests. What fraction of a quart does each guest get?
Answer: The fraction of a quart does each guest get is: \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Explanation:
It is given that a fruit drink is made using \(\frac{7}{4}\) quarts of orange juice and \(\frac{5}{4}\) quarts of pineapple juice.
So,
The total amount of fruit juice= \(\frac{7}{4}\) + \(\frac{5}{4}\)
= \(\frac{ 7 + 5}{4}\)
= \(\frac{12}{4}\)
It is also given that the drink is shared equally among 12 guests
So,
The fraction of a quart does each gust get = \(\frac{12}{4}\) ÷ 12
= \(\frac{12}{4}\) ÷ \(\frac{12}{1}\)
= \(\frac{12}{4}\) × \(\frac{1}{12}\)
= \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the fraction of a quart does each person get is: \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Interpret Fractions as Division Homework & Practice 10.1
Divide. Use a model to help.
Question 1.
1 ÷ 6 =0.16
Answer:

From the above model,
The number of colored parts is: 1
The number of total parts is: 6
So,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts = 1 ÷ 6
= \(\frac{1}{6}\)
So,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts in the decimal form is: 0.16
Question 2.
1 ÷ 7 =0.14
Answer: 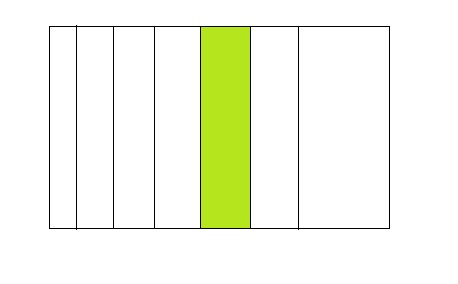
From the above model,
The number of colored parts is: 1
The number of total parts is: 7
So,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts = 1 ÷ 7
= \(\frac{1}{7}\)
So,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts in the decimal form is: 0.14
Question 3.
1 ÷ 5 = 0.20
Answer: 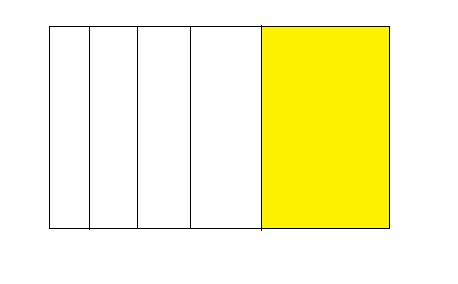
From the above model,
The number of colored parts is: 1
The number of total parts is: 5
So,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts = 1 ÷ 5
= \(\frac{1}{5}\)
So,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts in the decimal form is: 0.20
Question 4.
3 ÷ 4 = 0.75
Answer: 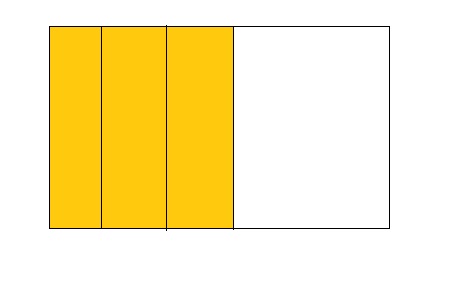
From the above model,
The number of colored parts is: 3
The number of total parts is: 4
So,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts = 3 ÷ 4
= \(\frac{3}{4}\)
So,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts in the decimal form is: 0.75
Question 5.
6 ÷ 7 = 0.85
Answer: 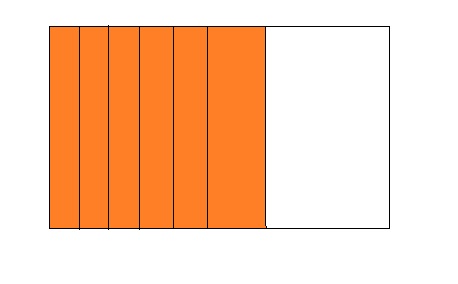
From the above model,
The number of colored parts is: 6
The number of total parts is: 7
So,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts = 6 ÷ 7
= \(\frac{6}{7}\)
So,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts in the decimal form is: 0.85
Question 6.
5 ÷ 9 = 0.55
Answer: 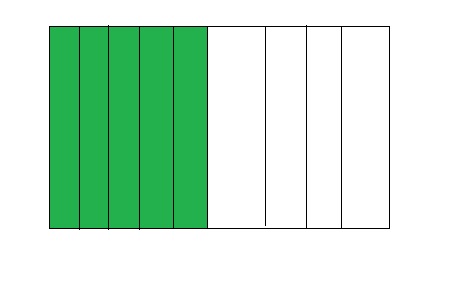
From the above model,
The number of colored parts is: 5
The number of total parts is: 9
So,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts = 5 ÷ 9
= \(\frac{5}{9}\)
So,
The fraction of the colored parts out of the total number of parts in the decimal form is: 0.55
Question 7.
YOU BE THE TEACHER
Your friend says \(\frac{5}{12}\) is equivalent to 12 ÷ 5. Is your friend correct? Explain.
Answer: No, your friend s not correct.
Explanation:
The given fraction is: \(\frac{5}{12}\)
From the given fraction,
The numerator is: 5
The denominator is: 12
We can write a fraction in the following form:
Fraction = \(\frac{Numerator}{Denominator}\)
So,
\(\frac{5}{12}\) is equivalent to 5 ÷ 12
But, according to your friend,
\(\frac{5}{12}\) is equivalent to 12 ÷ 5
Hence, from the above,
we can conclude that your friend is not correct.
Question 8.
Writing
Explain how fractions and division are related.
Question 9.
Structure
Write a division equation represented by the model.
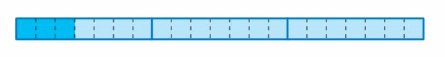
Answer:
The division equation represented by the model is: 1 ÷ 4
Explanation:
The given model is:

From the given model,
The number of shaded parts is: 1
The total number of parts are: 4
So,
The division equation can be represented as:
Division equation = (The number of shaded parts) ÷ ( The total number of parts )
= 1 ÷ 4
= \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Question 10.
Number Sense
Eight friends share multiple vegetable pizzas, and each gets \(\frac{3}{8}\) of a pizza. How many pizzas do they share?
Answer: The total number of pizzas the eight friends shared are: 3 pizzas
Explanation:
It is given that the eight friends share multiple vegetable pizzas and each gets \(\frac{3}{8}\) of a pizza.
So,
The total number of pizzas shared by the eight friends = \(\frac{3}{8}\) × 8
= \(\frac{3}{8}\) × \(\frac{8}{1}\)
= \(\frac{3 × 8}{8 × 1}\)
= \(\frac{3}{1}\)
= 3
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the total number of pizzas shared by the eight friends is: 3 pizzas
Question 11.
Modeling Real Life
Seven friends each run an equal part of a 5-kilometer relay race. What fraction of a kilometer does each friend complete?
Answer: The fraction of a kilometer does each friend complete is: \(\frac{5}{7}\) kilometer
Explanation:
It is given that there are seven friends each run an equal part of a 5-kilometer relay race.
So,
The fraction that each friend run = \(\frac{The total distance} {The number of friends}\)
= \(\frac{5}{7}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the fraction of a kilometer does each friend complete is: \(\frac{5}{7}\) kilometer
Question 12.
Modeling Real Life
A group of friends equally share 3 bags of pretzels. Each friend gets \(\frac{3}{5}\) of a bag of pretzels. How many friends are in the group?
Answer: The total number of friends in the group are: 5
Explanation:
It is given that a group of friends equally share 3 bags of pretzels and each friend gets \(\frac{3}{5}\) of a bag of pretzels.
So,
The total number of friends = \(\frac{The total number of bags}{The amount each friend gets}\)
= \(\frac{3}{1}\) × \(\frac{5}{3}\)
= \(\frac{5}{1}\)
= 5
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the total number of friends are: 5
Review & Refresh
Multiply.
Question 13.
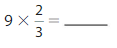
Answer: 9 × \(\frac{2}{3}\) = 6
Explanation:
The given fractions are: \(\frac{9}{1}\) and \(\frac{2}{3}\)
So,
\(\frac{9}{1}\) × \(\frac{2}{3}\)
= \(\frac{9 × 2}{1 × 3}\)
= \(\frac{6}{1}\)
= 6
Hence,
9 × \(\frac{2}{3}\) = 6
Question 14.
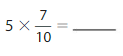
Answer: 5 × \(\frac{7}{10}\) = \(\frac{7}{2}\)
Explanation:
The given fractions are: \(\frac{5}{1}\) and \(\frac{7}{10}\)
So,
\(\frac{5}{1}\) × \(\frac{7}{10}\)
= \(\frac{5 × 7}{1 × 10}\)
= \(\frac{7}{2}\)
Hence,
5 × \(\frac{7}{10}\) = \(\frac{7}{2}\)
Question 15.
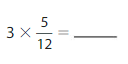
Answer: 3 × \(\frac{5}{12}\) = \(\frac{5}{4}\)
Explanation:
The given fractions are: \(\frac{3}{1}\) and \(\frac{5}{12}\)
So,
\(\frac{3}{1}\) × \(\frac{5}{12}\)
= \(\frac{3 × 5}{1 × 12}\)
= \(\frac{5}{4}\)
Hence,
3 × \(\frac{5}{12}\) = \(\frac{5}{4}\)
Lesson 10.2 Mixed Numbers as Quotients
Explore and Grow
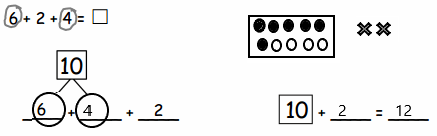
You share 6 sheets of construction paper equally among 4 people. Write a division expression that represents the situation. How much paper does each person get? Use a model to support your answer.
Answer:
The division expression representing the situation is: 6 ÷ 4
Explanation:
It s given that you have shared 6 sheets of construction paper equally among 4 people
So,
The division equation representing the sharing of construction papers is: 6 ÷ 4
Now,
6 ÷ 4 = \(\frac{6}{4}\)
So,
The above equation represents that 4 is divided into 6 parts.
So,
The model representing the situation is:
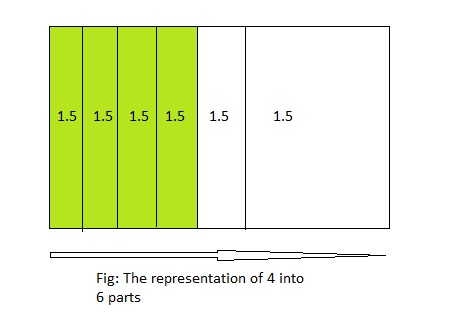
From the above model,
We can say that the amount of does each person get is: 1\(\frac{1}{2}\) or 1.5 or \(\frac{3}{2}\)
Precision
Does each person get less than or more than 1 sheet of paper? Use the dividend and divisor to explain why your answer makes sense.
Answer:
From the above problem,
We can say that each person gets more than 1 paper.
So,
The division equation of the above problem is: 6 ÷ 4
The equivalent form of 6 ÷ 4 is: \(\frac{6}{4}\)
Now,
The simplest form of \(\frac{6}{4}\) is: \(\frac{3}{2}\) ( The simplest form is the division of the numerator and the denominator with the common multiple if we can divide)
The mixed form of \(\frac{3}{2}\) is: 1\(\frac{1}{2}\)
Think and Grow: Divide Whole Numbers
You can use models to divide whole numbers that have a mixed number as the quotient.
Example
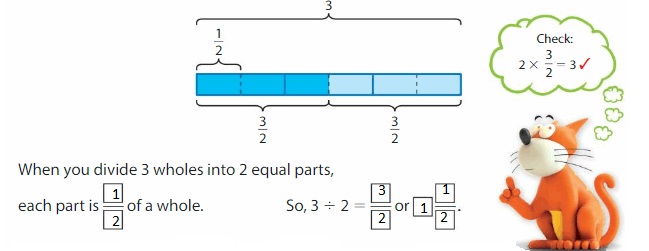
Find 3 ÷ 2.
One Way:
Use a tape diagram. Show 3 wholes. Divide each whole into 2 equal parts.
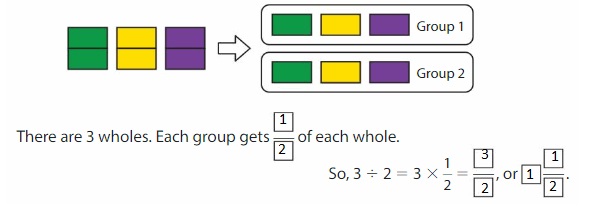
Another Way: Use an area model. Show 3 wholes. Divide each whole into 2 equal parts. Then separate the parts into 2 equal groups.
Show and Grow
Divide. Use a model to help
Question 1.
5 ÷ 3 = ___
Answer: 5 ÷ 3 = 1\(\frac{2}{3}\)
Explanation;
The given division equation is: 5 ÷ 3
The model representing the division equation is:
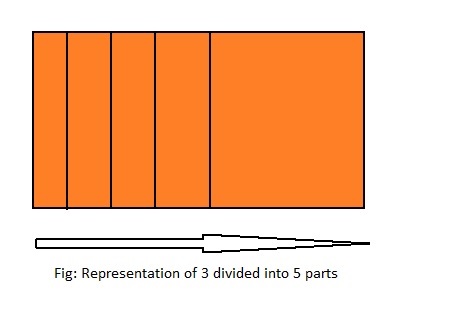
From the above model,
5 ÷ 3 = 3 ÷ 3
= 1 R 2
Hence,
We can say that each part is divided into 1\(\frac{2}{3}\) or \(\frac{5}{3}\)
Question 2.
7 ÷ 2 = ___
Answer: 7 ÷ 2 = 3\(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation;
The given division equation is: 7 ÷ 2
The model representing the division equation is:
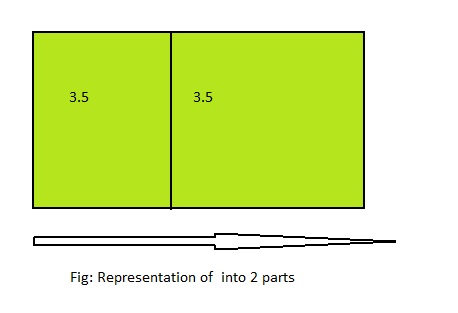
From the above model,
7 ÷ 2 = 6 ÷ 2
= 3 R 1
Hence,
We can say that each part is divided into 3\(\frac{1}{2}\) or \(\frac{7}{2}\) or 3.5
Apply and Grow: Practice
Divide. Use a model to help.
Question 3.
12 ÷ 7 = ___
Answer: 12 ÷ 7 = 1\(\frac{5}{7}\)
Explanation;
The given division equation is: 12 ÷ 7
The model representing the division equation is:
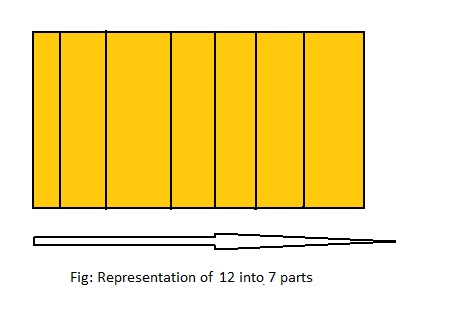
From the above model,
12 ÷ 7 = 7 ÷ 7
= 1 R 5
Hence,
We can say that each part is divided into 1\(\frac{5}{7}\) or \(\frac{12}{7}\)
Question 4.
25 ÷ 20 = ___
Answer: 25 ÷ 20 = 1\(\frac{5}{20}\) = \(\frac{5}{4}\)
Explanation;
The given division equation is: 25 ÷ 20
The model representing the division equation is:

From the above model,
25 ÷ 20 = 20 ÷ 20
= 1 R 5
Hence,
We can say that each part is divided into 1\(\frac{5}{20}\) or \(\frac{5}{4}\)
Question 5.
15 ÷ 4 = ___
Answer: 15 ÷ 4 = 3\(\frac{3}{4}\)
Explanation;
The given division equation is: 15 ÷ 4
The model representing the division equation is:
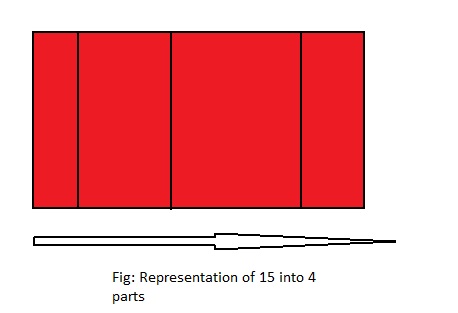
From the above model,
15 ÷ 4 = 12 ÷ 4
= 3 R 3
Hence,
We can say that each part is divided into 3\(\frac{3}{4}\) or \(\frac{15}{4}\)
Question 6.
13 ÷ 6 = ___
Answer: 13 ÷ 6 = 2\(\frac{1}{6}\)
Explanation;
The given division equation is: 13÷ 6
The model representing the division equation is:
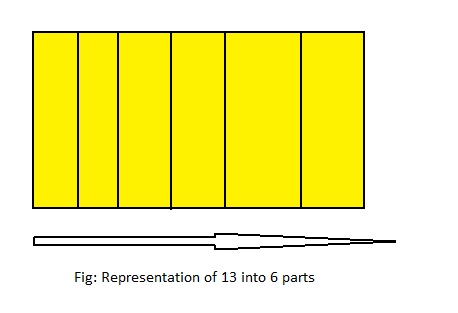
From the above model,
13 ÷ 6 = 12 ÷ 6
= 2 R 1
Hence,
We can say that each part is divided into 2\(\frac{1}{6}\) or \(\frac{13}{6}\)
Question 7.
16 ÷ 8 = ___
Answer: 16 ÷ 8 = 2
Explanation;
The given division equation is: 16÷ 8
The model representing the division equation is:
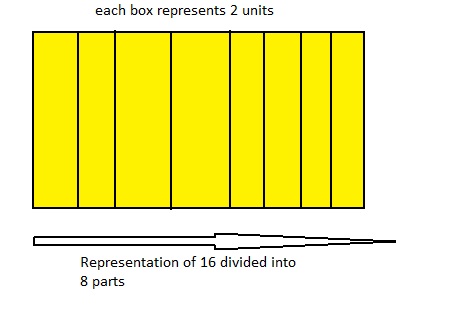
From the above model,
16 ÷ 8
= 2 R 0
Hence,
We can say that each part is divided into 2 equal parts
Question 8.
92 ÷ 50 = ___
Answer: 92 ÷ 50 = 1\(\frac{21}{25}\)
Explanation;
The given division equation is: 92÷ 50
So,
92 ÷ 50 = 50 ÷ 50
= 1 R 42
Hence,
We can say that each part is divided into 1\(\frac{42}{50}\) or 1\(\frac{21}{25}\)
Question 9.
How many 3s are in 7?
Answer: The number of 3 in 7 are: \(\frac{7}{3}\) or 2\(\frac{1}{3}\)
Explanation:
The division equation is: 7 ÷ 3
So,
The model for the given division equation is:
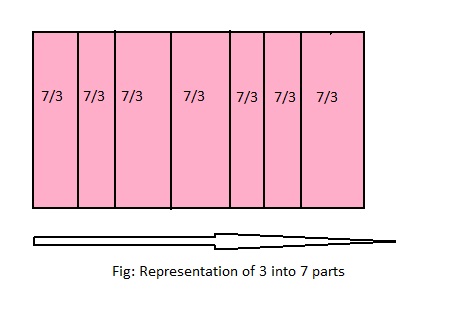
From the above model,
7 ÷ 3 = 6 ÷ 3
= 2 R 1
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that there are 2\(\frac{1}{3}\) 3s in 7
Question 10.
How many 6s are in 21?
Answer: The number of 6s in 21 are: \(\frac{21}{6}\) or 3\(\frac{3}{6}\)
Explanation:
The division equation is: 21 ÷ 6
So,
The model for the given division equation is:
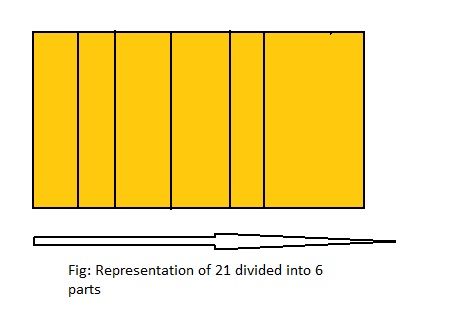
From the above model,
21 ÷ 6 = 18 ÷ 6
= 3 R 3
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that there are 3\(\frac{3}{6}\) 3s in 21
Question 11.
YOU BE THE TEACHER
Your friend says that \(\frac{35}{6}\) is equivalent to 35 ÷ 6. Is your friend correct? Explain.
Answer: Yes, your friend is correct
Explanation:
It is given that \(\frac{35}{6}\)
We know that,
The decimal equation can be converted into a fraction as \(\frac{Numerator}{Denominator}\)
So,
\(\frac{35}{6}\) = 35 ÷ 6
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that your friend is correct
Question 12.
Writing
Write and solve a real-life problem for 24 ÷ 5.
Answer: 24 ÷ 5 = 4\(\frac{4}{5}\)
Explanation;
The given division equation is: 24÷ 5
The model for the above division equation is:
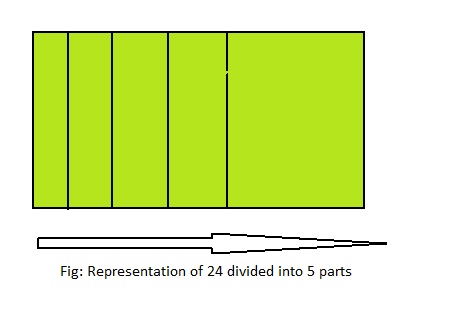
From the above model,
24 ÷ 5 = 20 ÷ 5
= 4 R 4
Hence,
We can say that each part is divided into 4\(\frac{4}{5}\)
Think and Grow: Modeling Real Life
Example
You share 7 bales of hay equally among 3 horse stalls. How many whole bales are in each stall? What fractional amount of a bale is in each stall?
Divide 7 by 3 to find how many bales of hay are in each stall. Use an area model to help.
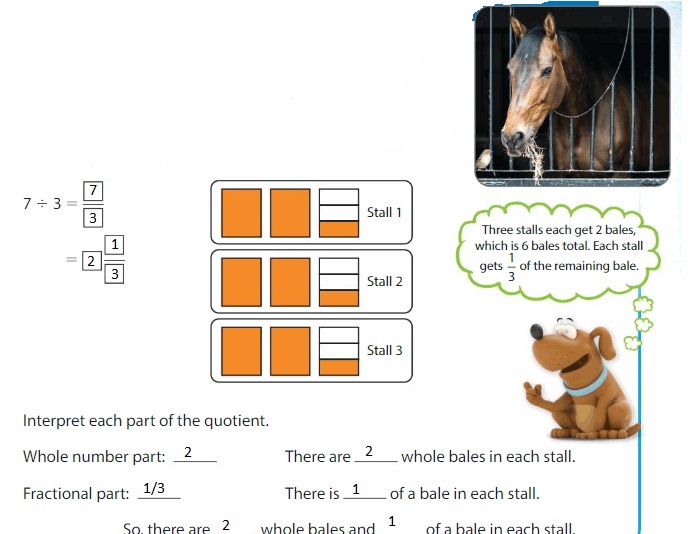
Show and Grow
Question 13.
Six muffins are shared equally among 4 friends. How many whole muffins does each friend get? What fractional amount of a muffin does each friend get?
Answer: Each friend will get 1 muffin and 2 muffins are leftovers
The fractional part of a muffin does each friend get is: \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation:
It is given that there are six muffins are shared equally among 4 friends.
So,
The number of muffins each friend get = 6 ÷ 4
= 4 ÷ 4
= 1 R 2
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that each friend gets 1 muffin each and the fraction of each muffin get is: \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 14.
A cyclist bikes 44 miles in 5 days. She bikes the same distance each day. Does she bike more than 8\(\frac{1}{2}\) miles each day? Explain.
Answer: She bikes more than 8\(\frac{1}{2}\) miles each day.
Explanation:
It is given that a cyclist bikes 44 miles in 5 days.
So,
The distance that she bikes each day = 44 ÷ 5
So,
44 ÷ 5 = 40 ÷ 5
= 8 R 4
= 8\(\frac{4}{5}\) miles
But, it is given that she bikes 8\(\frac{1}{2}\) miles each day
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that she bikes more than 8\(\frac{1}{2}\) miles each day.
Question 15.
DIG DEEPER!
At Table A, 4 students share 7 packs of clay equally. At Table B, 5 students share 8 packs of clay equally. At which table does each student get a greater amount of clay? Explain.

Answer: At Table A, each student gets a greater amount of clay.
Explanation:
It is given that at Table A, 4 students share 7 packs of clay equally.
So,
The representation of clay at table A is: \(\frac{7}{4}\)
It is also given that at Table B, 5 students share 8 packs of clay equally.
So,
The representation of clay at table B is: \(\frac{8}{5}\)
So,
For comparison, equate the denominators.
So,
Multiply the first fraction at table A by \(\frac{5}{5}\) and the fraction at table B by \(\frac{4}{4}\)
So,
\(\frac{7}{4}\) × \(\frac{5}{5}\)
= \(\frac{35}{20}\)
So,
\(\frac{8}{5}\) × \(\frac{4}{4}\)
= \(\frac{32}{20}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that at table A, the students will get more amount of clay.
Mixed Numbers as Quotients Homework & Practice 10.2
Divide. Use a model to help.
Question 1.
5 ÷ 2 = ___
Answer: 5 ÷ 2 = 2\(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation;
The given division equation is: 5 ÷ 2
The model representing the division equation is:
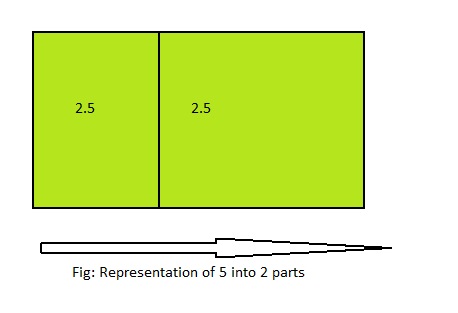
From the above model,
5 ÷ 2 = 4 ÷ 2
= 2 R 1
Hence,
We can say that 5 ÷ 2 = 2\(\frac{1}{2}\) or 2.5 or \(\frac{5}{2}\)
Question 2.
10 ÷ 7 = ___
Answer: 10 ÷ 7 = 1\(\frac{3}{7}\) = \(\frac{10}{7}\)
Explanation;
The given division equation is: 10 ÷ 7
The model representing the division equation is:
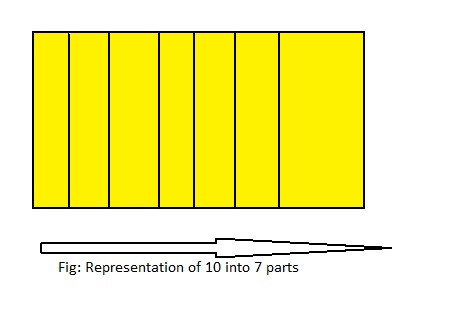
From the above model,
10 ÷ 7 = 7 ÷ 7
= 1 R 3
Hence,
We can say that 10 ÷ 7 = 1\(\frac{3}{7}\) or \(\frac{10}{7}\)
Question 3.
3 ÷ 9 = ___
Answer: 3 ÷ 9 = \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Explanation;
The given division equation is: 3 ÷ 9
The model representing the division equation is:
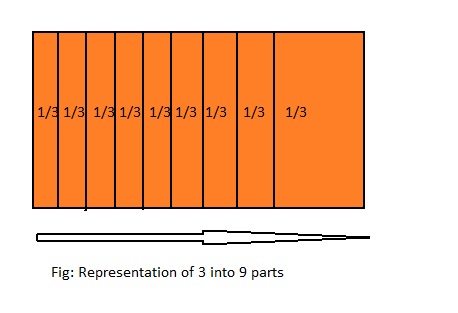
From the above model,
3 and 9 are the multiples of 3.
So,
3 ÷ 9 = \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Hence,
We can say that 3 ÷ 9 = \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Question 4.
11 ÷ 4 = ___
Answer: 11 ÷ 4 = 2\(\frac{3}{4}\)
Explanation;
The given division equation is: 11 ÷ 4
The model representing the division equation is:

From the above model,
11 ÷ 4 = 8 ÷ 4
= 2 R 3
Hence,
We can say that 11 ÷ 4 = \(\frac{11}{4}\) or 2\(\frac{3}{4}\)
Question 5.
13 ÷ 6 = ___
Answer: 13 ÷ 6 = 2\(\frac{1}{6}\)
Explanation;
The given division equation is: 13 ÷ 6
The model representing the division equation is:
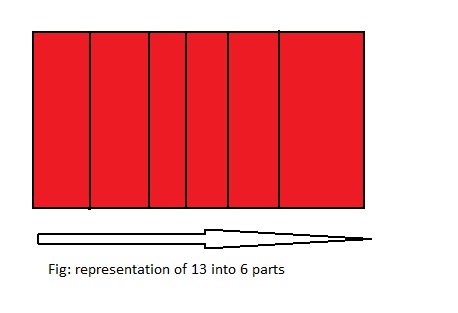
From the above model,
13 ÷ 6 = 12 ÷ 6
= 2 R 1
Hence,
We can say that 13 ÷ 6 = \(\frac{13}{6}\) or 2\(\frac{1}{6}\)
Question 6.
45 ÷ 8 = ___
Answer: 45 ÷ 8 = 5\(\frac{5}{8}\)
Explanation;
The given division equation is: 45 ÷ 8
The model representing the division equation is:
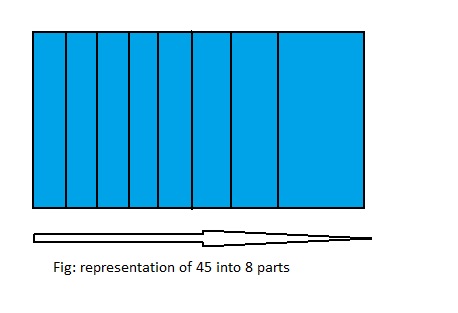
From the above model,
45 ÷ 8 = 40 ÷ 8
= 5 R 5
Hence,
We can say that 45 ÷ 8 = \(\frac{45}{8}\) or 5\(\frac{5}{8}\)
Question 7.
Number Sense
Between which two whole numbers is the quotient of 74 and 9?
Answer: The quotient of 74 and 9 is between 8 and 9
Explanation:
The given two numbers are 7 and 9
So,
By using the partial quotients method,
74 ÷ 9= 72 ÷ 9
= 8 R 2
So,
74 ÷ 9 = \(\frac{74}{9}\) or 8\(\frac{2}{9}\) or 8.3
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the quotient of 74 and 9 is between 8 and 9
Question 8.
Reasoning
Three friends want to share 22 baseball cards. For this situation, why does the quotient 7 R1 make more sense than the quotient 7\(\frac{1}{3}\)?
Answer:
It is given that three friends want to share 22 baseball cards.
So,
We have to find the number of baseball cards each friend possesses.
So,
It is sufficient to write the number of baseball cards possessed by each friend in the remainder form rather than the fraction form.
So,
The number of baseball cards possessed by each friend = \(\frac{The total number of baseball cards}{The number of friends}\)
= 22 ÷ 3
= 21 ÷ 3
= 7 R 1
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the remainder form is sufficient to find the number of baseball cars possessed by each friend rather than the fraction form.
Question 9.
DIG DEEPER!
Is \(\frac{2}{5}\) × 3 equivalent to 2 × 3 ÷ 5? Explain.
Answer: Yes, \(\frac{2}{5}\) × 3 equivalent to 2 × 3 ÷ 5
Explanation:
The given fraction and the number is: \(\frac{2}{5}\) and 3
So,
\(\frac{2}{5}\) × 3 = \(\frac{2}{5}\) × \(\frac{3}{1}\)
= \(\frac{2 × 3}{5}\)
= 2 × 3 ÷ 5
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that \(\frac{2}{5}\) × 3 equivalent to 2 × 3 ÷ 5
Question 10.
Modeling Real Life
A bag of 4 balls weighs 6 pounds. Each ball weighs the same amount. What is the weight of each ball?
Answer: The weight of each ball is: \(\frac{3}{2}\) pounds or 1.5 pounds
Explanation:
It is given that a bag of 4 balls weighs 6 pounds
So,
The weight of each ball = \(\frac{The total weight of the balls}{The number of balls}\)
= 6 ÷ 4
Since 6 and 4 are the multiples of 2, divide the two numbers by 2
So,
6 ÷ 4 = 3 ÷ 2
So,
3 ÷ 2 = 2 ÷ 2
= 1 R 1
= 1\(\frac{1}{2}\) pounds
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the weight of each ball is: 1\(\frac{1}{2}\) pounds or 1.5 pounds
Question 11.
Modeling Real Life
Zookeepers order 600 pounds of bamboo for the pandas. The bamboo lasts 7 days. How many whole pounds of bamboo do the pandas eat each day? What fractional amount of a pound do the pandas eat each day?

Answer:
The amount of bamboos the pandas eat each day is around 85 pounds
The amount of bamboos the pandas eat each day in the fraction form is: 85\(\frac{5}{7}\)
Explanation:
It is given that zookeepers order 600 pounds of bamboo for the pandas and the bamboos last 7 days for the pandas
So,
The number of bamboos the pandas eat each day = 600 ÷ 7
So,
By using the partial quotients method,
600 ÷ 7 = ( 560 + 35 ) ÷ 7
= ( 560 ÷ 7 ) + ( 35 ÷ 7 )
= 80 + 5
= 85 R 5
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that
The amount of bamboos the pandas eat each day is around 85 pounds
The amount of bamboos the pandas eat each day in the fraction form is: 85\(\frac{5}{7}\)
Question 12.
Modeling Real Life
A plumber has 20 feet of piping. He cuts the piping into 6 equal pieces. Is each piece greater than, less than, or equal to 3\(\frac{1}{2}\) feet?
Answer: Each piece is less than 3\(\frac{1}{2}\) feet
Explanation:
It is given that a plumber has 20 feet of piping and he cuts the piping into 6 equal pieces.
So,
The length of each piece = 20 ÷ 6
By using the partial quotients method,
20 ÷ 6 = 18 ÷ 6
= 3 R 2
So,
20 ÷ 6 = 3\(\frac{2}{6}\)
Now,
3\(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{7}{2}\)
3\(\frac{2}{6}\) = \(\frac{20}{6}\)
For comparison, we have to equate whether the denominators or the numerators.
So,
Multiply 3\(\frac{1}{2}\) with \(\frac{3}{3}\)
So,
3\(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{21}{6}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that each piece is less than 3\(\frac{1}{2}\) feet
Review & Refresh
Add.
Question 13.
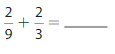
Answer: \(\frac{2}{9}\) + \(\frac{2}{3}\) = \(\frac{8}{9}\)
Explanation:
The two given fractions are: \(\frac{2}{9}\) and \(\frac{2}{3}\)
So, in addition, we have to make either the numerators or the denominators equal
So,
Multiply \(\frac{2}{3}\) with \(\frac{3}{3}\)
So,
\(\frac{2}{3}\) = \(\frac{6}{9}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that \(\frac{2}{9}\) + \(\frac{2}{3}\) = \(\frac{8}{9}\)
Question 14.
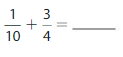
Answer: \(\frac{1}{10}\) + \(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{34}{40}\)
Explanation:
The two given fractions are: \(\frac{1}{10}\) and \(\frac{3}{4}\)
So, in addition, we have to make either the numerators or the denominators equal
So,
Multiply \(\frac{1}{10}\) with \(\frac{4}{4}\)
Multiply \(\frac{3}{4}\) with \(\frac{10}{10}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{10}\) = \(\frac{4}{40}\)
\(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{30}{40}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that \(\frac{1}{10}\) + \(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{34}{40}\)
Question 15.
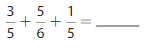
Answer: \(\frac{3}{5}\) + \(\frac{5}{6}\) + \(\frac{1}{5}\) = \(\frac{49}{30}\)
Explanation:
The three given fractions are: \(\frac{3}{5}\) , \(\frac{5}{6}\) and \(\frac{1}{5}\)
So, in addition, we have to make either the numerators or the denominators equal
So,
Multiply \(\frac{3}{5}\) with \(\frac{6}{6}\)
Multiply \(\frac{5}{6}\) with \(\frac{5}{5}\)
Multiply \(\frac{1}{5}\) with \(\frac{6}{6}\)
So,
\(\frac{3}{5}\) = \(\frac{18}{30}\)
\(\frac{5}{6}\) = \(\frac{25}{30}\)
\(\frac{1}{5}\) = \(\frac{6}{30}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that \(\frac{3}{5}\) + \(\frac{5}{6}\) +\(\frac{1}{5}\) = \(\frac{49}{30}\)
Lesson 10.3 Divide Whole Numbers by Unit Fractions
Explore and Grow
Write a real-life problem that can be represented by 6 ÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\)?
Answer:
Suppose, we have an apple and there are 6 children and we are giving each child half of the piece.
So,
Each child receives 6 ÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\) piece of the apple
What is the solution to the problem? Use a model to support your answer?
Answer:
The above problem is the division of an apple among the six children
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
The amount each child receive from an apple = 6 ÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\)
= 6 × \(\frac{2}{1}\)
= \(\frac{6}{1}\) × \(\frac{2}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 6 × 2}{1 × 1}\)
= 12
Structure
How can you check your answer using multiplication?
Answer:
We can check the answer using multiplication by the two rules regarding division and multiplication. They are:
A) a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
B) a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
Think and Grow: Divide Whole Numbers by Unit Fractions
You can use models to divide whole numbers by unit fractions.
Example
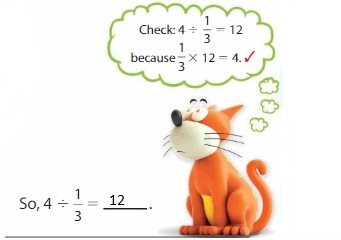
Find 4 ÷ \(\frac{1}{3}\)
One Way:
Use a tape diagram to find how many \(\frac{1}{3}\)s are in 4. There are 4 wholes.
Divide each whole into 3 equal parts. Each part is \(\frac{1}{3}\).
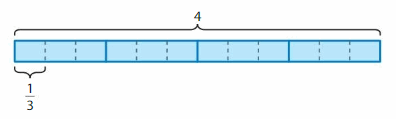
Because there are 3 one-thirds in 1 whole, there are
4 × 3 equal parts = 12 one-thirds in 4 wholes.

Show and Grow
Divide. Use a model to help
Question 1.
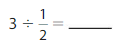
Answer: 3 ÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\) = 6
Explanation:
The given numbers are: 3 and \(\frac{1}{2}\)
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
3 ÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\) = 3 × \(\frac{2}{1}\)
= \(\frac{3}{1}\) × \(\frac{2}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 3 × 2}{1 × 1}\)
= 6
Hence,
3÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\) = 6
Question 2.
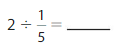
Answer: 2 ÷ \(\frac{1}{5}\) = 10
Explanation:
The given numbers are: 2 and \(\frac{1}{5}\)
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
2 ÷ \(\frac{1}{5}\) = 2 × \(\frac{5}{1}\)
= \(\frac{5}{1}\) × \(\frac{2}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 5 × 2}{1 × 1}\)
= 10
Hence,
2÷ \(\frac{1}{5}\) = 10
Apply and Grow: Practice
Divide. Use a model to help.
Question 3.
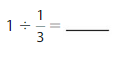
Answer: 1 ÷ \(\frac{1}{3}\) = 3
Explanation:
The given numbers are: 1 and \(\frac{1}{3}\)
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
1 ÷ \(\frac{1}{3}\) = 1 × \(\frac{3}{1}\)
= \(\frac{3}{1}\) × \(\frac{1}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 3 × 1}{1 × 1}\)
= 3
Hence,
1÷ \(\frac{1}{3}\) = 3
Question 4.
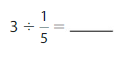
Answer: 3 ÷ \(\frac{1}{5}\) = 15
Explanation:
The given numbers are: 3 and \(\frac{1}{5}\)
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
3 ÷ \(\frac{1}{5}\) = 3 × \(\frac{5}{1}\)
= \(\frac{3}{1}\) × \(\frac{5}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 3 × 5}{1 × 1}\)
= 15
Hence,
3÷ \(\frac{1}{5}\) = 15
Question 5.
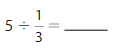
Answer: 5 ÷ \(\frac{1}{3}\) = 15
Explanation:
The given numbers are: 5 and \(\frac{1}{3}\)
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
5 ÷ \(\frac{1}{3}\) = 5 × \(\frac{3}{1}\)
= \(\frac{3}{1}\) × \(\frac{5}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 3 × 5}{1 × 1}\)
= 15
Hence,
5÷ \(\frac{1}{3}\) = 15
Question 6.
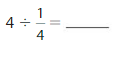
Answer: 4 ÷ \(\frac{1}{4}\) = 16
Explanation:
The given numbers are: 4 and \(\frac{1}{4}\)
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
4 ÷ \(\frac{1}{4}\) = 4 × \(\frac{4}{1}\)
= \(\frac{4}{1}\) × \(\frac{4}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 4 × 4}{1 × 1}\)
= 16
Hence,
4÷ \(\frac{1}{4}\) = 16
Question 7.
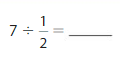
Answer: 7 ÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\) = 14
Explanation:
The given numbers are: 7 and \(\frac{1}{2}\)
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
7 ÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\) = 7 × \(\frac{2}{1}\)
= \(\frac{7}{1}\) × \(\frac{2}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 7 × 2}{1 × 1}\)
= 14
Hence,
7÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\) = 14
Question 8.
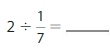
Answer: 2 ÷ \(\frac{1}{7}\) = 14
Explanation:
The given numbers are: 2 and \(\frac{1}{7}\)
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
2 ÷ \(\frac{1}{7}\) = 2 × \(\frac{7}{1}\)
= \(\frac{2}{1}\) × \(\frac{7}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 7 × 2}{1 × 1}\)
= 14
Hence,
2÷ \(\frac{1}{7}\) = 14
Question 9.
How many \(\frac{1}{4}\)s are in 5?
Answer: There are 20 \(\frac{1}{4}\)s in 5
Explanation:
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
Now,
We have to find the number of \(\frac{1}{4}\)s in 5
So,
5 ÷ \(\frac{1}{4}\) = 5 × \(\frac{4}{1}\)
= \(\frac{5}{1}\) × \(\frac{4}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 5 × 4}{1 × 1}\)
= 20
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that there are 20 \(\frac{1}{4}\)s in 5.
Question 10.
How many \(\frac{1}{6}\)s are in 2?
Answer: There are 12 \(\frac{1}{6}\)s in 2
Explanation:
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
Now,
We have to find the number of \(\frac{1}{6}\)s in 2
So,
2 ÷ \(\frac{1}{6}\) = 2 × \(\frac{6}{1}\)
= \(\frac{2}{1}\) × \(\frac{6}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 2 × 6}{1 × 1}\)
= 12
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that there are 12 \(\frac{1}{6}\)s in 2.
Question 11.
YOU BE THE TEACHER
Newton finds 6 ÷ \(\frac{1}{3}\). Is he correct? Explain.

Answer: No, Newton is not correct
Explanation:
The given division equation is: 6 ÷ \(\frac{1}{3}\)
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
6 ÷ \(\frac{1}{3}\) = 6 × \(\frac{3}{1}\)
= \(\frac{6}{1}\) × \(\frac{3}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 3 × 6}{1 × 1}\)
= 18
But, according to Newton,
6 ÷ \(\frac{1}{3}\) = 2
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that Newton is not correct.
Question 12.
Writing
Write and solve a real-life problem for 4 ÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\).
Answer:
Suppose we have 4 bags of wheat and we have to distribute the 4 bags by dividing each bag of wheat in half
So,
Each person receives 4 ÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\) bag of wheat
Now,
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
4 ÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\) = 4 × \(\frac{2}{1}\)
= \(\frac{4}{1}\) × \(\frac{2}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 4 × 2}{1 × 1}\)
= 8
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that there are 8 bags of wheat when divide the 4 bags of wheat in half.
Think and Grow: Modeling Real Life
Example
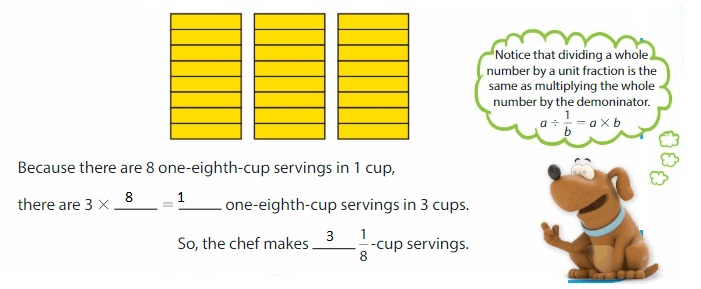
A chef makes 3 cups of salsa. A serving of salsa is \(\frac{1}{8}\) cup. How many servings does the chef make?
To find the number of servings, find the number of \(\frac{1}{8}\) cups in 3 cups.
Use an area model to find 3 ÷ \(\frac{1}{8}\). Divide each cup into 8 equal parts.

Show and Grow
Question 13.
A litter of kittens weighs a total of 2 pounds. Each newborn kitten weighs \(\frac{1}{4}\) pound. How many kittens are in the litter?
Answer: The number of kittens in the litter are: 8 kittens
Explanation:
It is given that a litter of kittens weighs a total of 2 pounds and each newborn kitten weighs \(\frac{1}{4}\) pound.
So,
The number of kittens in the litter = \(\frac{The total weight of litter}{The weight of each newborn kitten}\)
= 2 ÷ \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Now,
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
2 ÷ \(\frac{1}{4}\) = 2 × \(\frac{4}{1}\)
= \(\frac{4}{1}\) × \(\frac{2}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 4 × 2}{1 × 1}\)
= 8
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the number of kittens in the litter are: 8 kittens
Question 14.
You put signs on a walking trail that is 7 miles long. You put a sign at the start and at the end of the trail. You also put a sign every \(\frac{1}{10}\) mile. How many signs do you put on the trail?
Answer: The total number of signs you put on the trail is: 72
Explanation:
It is given that you put signs on a walking trail that is 7 miles long and you put a sign at the start and at the end of the trail.
It is also given that you put a sign every \(\frac{1}{10}\) mile.
So,
The total number of signs you put on the trail = The sign at the start of the trail + The sign at the end of the trail + The total number of signs for \(\frac{1}{10}\) mile
Now,
The total number of signs for \(\frac{1}{10}\) mile = 7 ÷ \(\frac{1}{10}\)
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
7 ÷ \(\frac{1}{10}\) = 7 × \(\frac{10}{1}\)
= \(\frac{7}{1}\) × \(\frac{10}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 7 × 10}{1 × 1}\)
= 70
So,
The total number of signs you put on the trail = 1 + 1 + 70
= 72
hence, from the above,
We can conclude that there are 72 signs that you put on the trail
Question 15.
DIG DEEPER!
You have 2 boards that are each 8 feet long. You cut \(\frac{1}{2}\)– foot pieces to make square picture frames. How many picture frames can you make?
Answer: The number of picture frames you can make is: 32
Explanation:
It is given that you have 2 boards that are each 8 feet long.
So,
The total length of 2 boards = 2 × 8 = 16 feet
It is also given that you cut \(\frac{1}{2}\)– foot pieces to make square picture frames.
So,
The total number of picture frames = \(\frac{The total length of 2 boards}{The length of each square frame}\)
= 16 ÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\)
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
16 ÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\) = 16 × \(\frac{2}{1}\)
= \(\frac{16}{1}\) × \(\frac{2}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 16 × 2}{1 × 1}\)
= 32
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that we can make 32 picture frames.
Divide Whole Numbers by Unit Fractions Homework & Practice 10.3
Divide. Use a model to help.
Question 1.
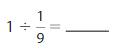
Answer: 1 ÷ \(\frac{1}{9}\) = 9
Explanation:
The given numbers are: 1 and \(\frac{1}{9}\)
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
1 ÷ \(\frac{1}{9}\) = 1 × \(\frac{9}{1}\)
= \(\frac{1}{1}\) × \(\frac{9}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 1 × 9}{1 × 1}\)
= 9
Hence,
1÷ \(\frac{1}{9}\) = 9
Question 2.
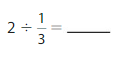
Answer: 2 ÷ \(\frac{1}{3}\) = 6
Explanation:
The given numbers are: 2 and \(\frac{1}{3}\)
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
2 ÷ \(\frac{1}{3}\) = 2 × \(\frac{3}{1}\)
= \(\frac{3}{1}\) × \(\frac{2}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 3 × 2}{1 × 1}\)
= 6
Hence,
2÷ \(\frac{1}{3}\) = 6
Question 3.
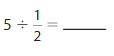
Answer: 5 ÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\) = 10
Explanation:
The given numbers are: 5 and \(\frac{1}{2}\)
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
5 ÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\) = 5 × \(\frac{2}{1}\)
= \(\frac{5}{1}\) × \(\frac{2}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 5 × 2}{1 × 1}\)
= 10
Hence,
5÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\) = 10
Divide. Use a model to help.
Question 4.
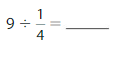
Answer: 9 ÷ \(\frac{1}{4}\) = 36
Explanation:
The given numbers are: 9 and \(\frac{1}{4}\)
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
9 ÷ \(\frac{1}{4}\) = 9 × \(\frac{4}{1}\)
= \(\frac{9}{1}\) × \(\frac{4}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 9 × 4}{1 × 1}\)
= 36
Hence,
9÷ \(\frac{1}{4}\) = 36
Question 5.
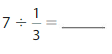
Answer: 7 ÷ \(\frac{1}{3}\) = 21
Explanation:
The given numbers are: 7 and \(\frac{1}{3}\)
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
7 ÷ \(\frac{1}{3}\) = 7 × \(\frac{3}{1}\)
= \(\frac{3}{1}\) × \(\frac{7}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 3 × 7}{1 × 1}\)
= 21
Hence,
7÷ \(\frac{1}{3}\) = 21
Question 6.
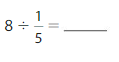
Answer: 8 ÷ \(\frac{1}{5}\) = 40
Explanation:
The given numbers are: 8 and \(\frac{1}{5}\)
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
8 ÷ \(\frac{1}{5}\) = 8 × \(\frac{5}{1}\)
= \(\frac{8}{1}\) × \(\frac{5}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 8 × 5}{1 × 1}\)
= 40
Hence,
8÷ \(\frac{1}{5}\) = 40
Question 7.
Number Sense
Explain how you can check your answer for Exercise 6.
Answer:
We can check the answer for exercise 6 by using the below model:

From the above model,
Each part represents \(\frac{8}{5}\)
So,
The total value of the 5 parts is: \(\frac{40}{5}\)
Hence,
In the above way, we can say that we check the answer
Question 8.
YOU BE THE TEACHER
Descartes finds 5 ÷ \(\frac{1}{4}\). Is he correct? Explain.
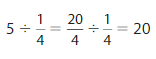
Answer: Yes, he is correct
Explanation:
We can write 5 as \(\frac{20}{4}\) or \(\frac{5}{1}\)
But, we only take \(\frac{20}{4}\) because the divided number given is 4
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{20}{4}\) ÷ \(\frac{1}{4}\)
= \(\frac{20}{4}\) × \(\frac{4}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 20 × 4}{4 × 1}\)
= 20
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that Descartes is correct.
Question 9.
Modeling Real Life
You need \(\frac{1}{2}\) pound of clay to make a pinch pot. How many pinch pots can you make with 12 pounds of clay?

Answer: You can make 24 pinch pots with 12 pounds of clay
Explanation:
It is given that you need \(\frac{1}{2}\) pound of clay to make a pinch pot.
It is also given that you have 12 pounds of clay
So,
The number of pinch pots you can make by using 12 pounds of clay = \(\frac{The total amount of clay}{The amount of clay used to make each pinch pot}\)
= 12 ÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Now,
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
12 ÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\)
= \(\frac{12}{1}\) × \(\frac{2}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 12 × 2}{4 × 1}\)
= 24
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that we can make 24 pinch pots by using 12 pounds of clay.
Question 10.
Modeling Real Life
Your art teacher has 5 yards of yellow string and 4 yards of green string. She cuts both colors \(\frac{1}{3}\)-yard pieces to hang of string into student artwork. How many pieces of student artwork can she hang?
Answer: The number of pieces of student artwork she can hang is: 27
Explanation:
It is given that your art teacher has 5 yards of yellow string and 4 yards of green string.
So,
The total number of yards of string = 5 + 4 = 9 yards of string
It is also given that she cuts both colors \(\frac{1}{3}\)-yard pieces to hang of string into student artwork.
So,
The number of pieces of student artwork she can hang = \(\frac{The total number of yards of strings}{The length of each yard f string}\)
= 9 ÷ \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Now,
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
9 ÷ \(\frac{1}{3}\)
= \(\frac{9}{1}\) × \(\frac{3}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 9 × 3}{1 × 1}\)
= 27
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that there are 27 pieces of student artwork that she can hang.
Review & Refresh
Question 11.
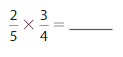
Answer: \(\frac{2}{5}\) × \(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{6}{20}\)
Explanation:
The given fractions are: \(\frac{3}{4}\) and \(\frac{2}{5}\)
So,
\(\frac{2}{5}\) × \(\frac{3}{4}\)
= \(\frac{2 × 3}{5 × 4}\)
= \(\frac{6}{20}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{2}{5}\) × \(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{6}{20}\)
Question 12.
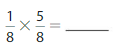
Answer: \(\frac{1}{8}\) × \(\frac{5}{8}\) = \(\frac{5}{64}\)
Explanation:
The given fractions are: \(\frac{1}{8}\) and \(\frac{5}{8}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{8}\) × \(\frac{5}{8}\)
= \(\frac{1 × 5}{8 × 8}\)
= \(\frac{5}{64}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{1}{8}\) × \(\frac{5}{8}\) = \(\frac{5}{64}\)
Question 13.
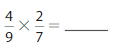
Answer: \(\frac{4}{9}\) × \(\frac{2}{7}\) = \(\frac{8}{63}\)
Explanation:
The given fractions are: \(\frac{4}{9}\) and \(\frac{2}{7}\)
So,
\(\frac{4}{9}\) × \(\frac{2}{7}\)
= \(\frac{2 × 4}{7 × 9}\)
= \(\frac{8}{63}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{4}{9}\) × \(\frac{2}{7}\) = \(\frac{8}{63}\)
Lesson 10.4 Divide Unit Fractions by Whole Numbers
Write a real-life problem that can be represented by \(\frac{1}{2}\) ÷ 3?
Answer:
Suppose we have 3 people and those 3 people each has to share \(\frac{1}{2}\) of the apple
What is the solution to the problem? Use a model to support your answer?
Answer:
The above problem is: We have to share \(\frac{1}{2}\) each for the 3 people
Now,
We know that,
\(\frac{a}{b}\) ÷ a = \(\frac{a}{b}\) × \(\frac{1}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{2}\) ÷ 3
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × \(\frac{1}{3}\)
= \(\frac{ 1 × 1}{2 × 3}\)
= \(\frac{1}{6}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{1}{6}\) is the solution to the above problem.
Precision
Is the answer greater than or less than 1? Explain?
Answer: The answer is less than 1
Explanation:
The answer for the problem is: \(\frac{1}{6}\)
So,
For the comparison of \(\frac{1}{6}\) with 1, we have to see whether the numerators or the denominators are equal or not
So, in this case, the numerators are equal
So, compare the denominators
So,
1 < 6
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that \(\frac{1}{6}\) is less than 1
Think and Grow: Divide Unit Fractions by Whole Numbers
You can use models to divide unit fractions by whole numbers.
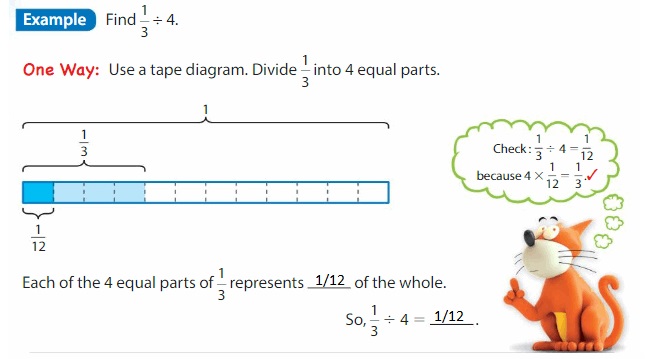
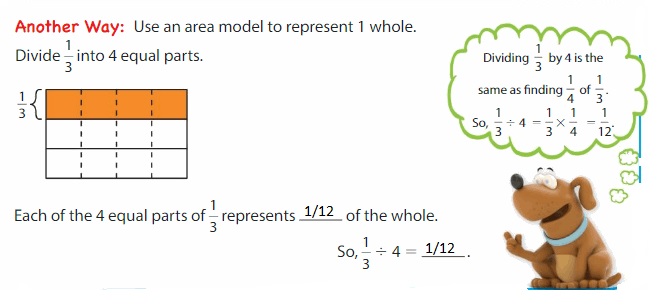
Show and Grow
Divide. Use a model to help.
Question 1.
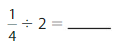
Answer: \(\frac{1}{4}\) ÷ 2 = \(\frac{1}{8}\)
Explanation:
The given numbers are: \(\frac{1}{4}\) and 2
We know that,
\(\frac{a}{b}\) ÷ a = \(\frac{a}{b}\) × \(\frac{1}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{4}\) ÷ 2
= \(\frac{1}{4}\) × \(\frac{1}{2}\)
= \(\frac{ 1 × 1}{2 × 4}\)
= \(\frac{1}{8}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{1}{4}\) ÷ 2 = \(\frac{1}{8}\)
Question 2.
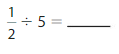
Answer: \(\frac{1}{2}\) ÷ 5 = \(\frac{1}{10}\)
Explanation:
The given numbers are: \(\frac{1}{2}\) and 5
We know that,
\(\frac{a}{b}\) ÷ a = \(\frac{a}{b}\) × \(\frac{1}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{2}\) ÷ 5
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × \(\frac{1}{5}\)
= \(\frac{ 1 × 1}{2 × 5}\)
= \(\frac{1}{10}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{1}{2}\) ÷ 5 = \(\frac{1}{10}\)
Apply and Grow: Practice
Divide. Use a model to help.
Question 3.
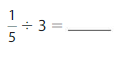
Answer: \(\frac{1}{5}\) ÷ 3 = \(\frac{1}{15}\)
Explanation:
The given numbers are: \(\frac{1}{5}\) and 3
We know that,
\(\frac{a}{b}\) ÷ a = \(\frac{a}{b}\) × \(\frac{1}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{5}\) ÷ 3
= \(\frac{1}{5}\) × \(\frac{1}{3}\)
= \(\frac{ 1 × 1}{5 × 3}\)
= \(\frac{1}{15}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{1}{5}\) ÷ 3 = \(\frac{1}{15}\)
Question 4.
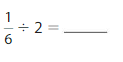
Answer: \(\frac{1}{6}\) ÷ 2 = \(\frac{1}{12}\)
Explanation:
The given numbers are: \(\frac{1}{6}\) and 2
We know that,
\(\frac{a}{b}\) ÷ a = \(\frac{a}{b}\) × \(\frac{1}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{6}\) ÷ 2
= \(\frac{1}{6}\) × \(\frac{1}{2}\)
= \(\frac{ 1 × 1}{2 × 6}\)
= \(\frac{1}{12}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{1}{6}\) ÷ 2 = \(\frac{1}{12}\)
Question 5.
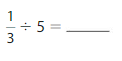
Answer: \(\frac{1}{3}\) ÷ 5 = \(\frac{1}{15}\)
Explanation:
The given numbers are: \(\frac{1}{3}\) and 5
We know that,
\(\frac{a}{b}\) ÷ a = \(\frac{a}{b}\) × \(\frac{1}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{3}\) ÷ 5
= \(\frac{1}{3}\) × \(\frac{1}{5}\)
= \(\frac{ 1 × 1}{3 × 5}\)
= \(\frac{1}{15}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{1}{3}\) ÷ 5 = \(\frac{1}{15}\)
Question 6.
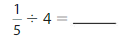
Answer: \(\frac{1}{5}\) ÷ 4 = \(\frac{1}{20}\)
Explanation:
The given numbers are: \(\frac{1}{5}\) and 4
We know that,
\(\frac{a}{b}\) ÷ a = \(\frac{a}{b}\) × \(\frac{1}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{5}\) ÷ 4
= \(\frac{1}{5}\) × \(\frac{1}{4}\)
= \(\frac{ 1 × 1}{5 × 4}\)
= \(\frac{1}{20}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{1}{5}\) ÷ 4 = \(\frac{1}{20}\)
Question 7.
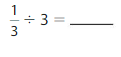
Answer: \(\frac{1}{3}\) ÷ 3 = \(\frac{1}{9}\)
Explanation:
The given numbers are: \(\frac{1}{3}\) and 3
We know that,
\(\frac{a}{b}\) ÷ a = \(\frac{a}{b}\) × \(\frac{1}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{3}\) ÷ 3
= \(\frac{1}{3}\) × \(\frac{1}{3}\)
= \(\frac{ 1 × 1}{3 × 3}\)
= \(\frac{1}{9}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{1}{3}\) ÷ 3 = \(\frac{1}{9}\)
Question 8.
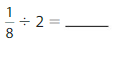
Answer: \(\frac{1}{8}\) ÷ 2 = \(\frac{1}{16}\)
Explanation:
The given numbers are: \(\frac{1}{8}\) and 2
We know that,
\(\frac{a}{b}\) ÷ a = \(\frac{a}{b}\) × \(\frac{1}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{8}\) ÷ 2
= \(\frac{1}{8}\) × \(\frac{1}{2}\)
= \(\frac{ 1 × 1}{2 × 8}\)
= \(\frac{1}{16}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{1}{8}\) ÷ 2 = \(\frac{1}{16}\)
Question 9.
How many 6s are in \(\frac{1}{2}\)?
Answer: There are \(\frac{1}{12}\) 6s in \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation:
We know that,
\(\frac{a}{b}\) ÷ a = \(\frac{a}{b}\) × \(\frac{1}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
Now,
We have to find the number of 6s in \(\frac{1}{2}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{2}\) ÷ 6
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × \(\frac{1}{6}\)
= \(\frac{ 1 × 1}{2 × 6}\)
= \(\frac{1}{12}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that there are \(\frac{1}{12}\) 6s in \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 10.
How many 2s are in \(\frac{1}{3}\) ?
Answer: There are \(\frac{1}{6}\) 2s in \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Explanation:
We know that,
\(\frac{a}{b}\) ÷ a = \(\frac{a}{b}\) × \(\frac{1}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
Now,
We have to find the number of 2s in \(\frac{1}{3}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{3}\) ÷ 2
= \(\frac{1}{3}\) × \(\frac{1}{2}\)
= \(\frac{ 1 × 1}{2 × 3}\)
= \(\frac{1}{6}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that there are \(\frac{1}{6}\) 2s in \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 11.
Writing
Write and solve a real-life problem for
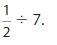
Answer:
Suppose a box has 7 chocolates. We have to divide these seven chocolates into further \(\frac{1}{2}\) parts so that the chocolates can be distributed to more people
So,
The each part of chocolate we can get = \(\frac{1}{2}\) ÷ 7
Now,
We know that,
\(\frac{a}{b}\) ÷ a = \(\frac{a}{b}\) × \(\frac{1}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{2}\) ÷ 7
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × \(\frac{1}{7}\)
= \(\frac{ 1 × 1}{2 × 7}\)
= \(\frac{1}{14}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that we can get \(\frac{1}{14}\) part of each chocolate.
Question 12.
Reasoning
Complete the statements.
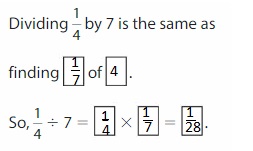
Think and Grow: Modeling Real Life
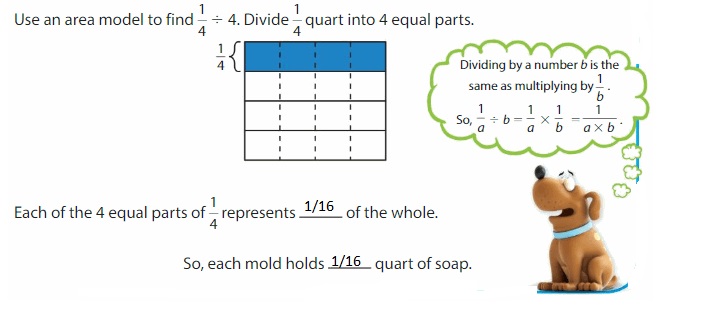
You melt \(\frac{1}{4}\) quart of soap. You pour the soap into 4 of the same-sized molds. What fraction of a quart of soap does each mold hold?
You are dividing \(\frac{1}{4}\) quart into 4 equal parts, so you need to find \(\frac{1}{4}\) ÷ 4.
Show and Grow
Question 13.
You buy \(\frac{1}{2}\) pound of grapes. You equally divide the grapes into 2 bags. What fraction of a pound of grapes do you put into each bag?
Answer: The fraction of a pound of grapes you put into each bag is: \(\frac{1}{8}\) pound
Explanation:
It is given that you buy \(\frac{1}{2}\) pound of grapes.
It is also given that you equally divide the grapes into 2 bags.
So,
The number of grapes in each bag = \(\frac{1}{2}\) ÷ 2
Now,
The fraction of pound of grapes you put into each bag = \(\frac{The number of grapes in each bag}{2}\)
= ( \(\frac{1}{2}\) ÷ 2 ) ÷ 2
Now,
We know that,
\(\frac{a}{b}\) ÷ a = \(\frac{a}{b}\) × \(\frac{1}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
( \(\frac{1}{2}\) ÷ 2 ) ÷ 2
= ( \(\frac{1}{2}\) × \(\frac{1}{2}\) ) × \(\frac{1}{2}\)
= \(\frac{ 1 × 1}{2 × 2}\) × \(\frac{1}{2}\)
= \(\frac{1}{4}\) × \(\frac{1}{2}\)
= \(\frac{ 1 × 1}{2 × 4}\)
= \(\frac{1}{8}\)
Hence, from the above
We can conclude that the fraction of pound of grapes in each bag is: \(\frac{1}{8}\) pound
Question 14.
You have \(\frac{1}{8}\) cup of red sand, \(\frac{1}{4}\) cup of blue sand, and \(\frac{1}{2}\) cup of white sand. You equally divide the sand into 3 containers. What fraction of a cup of sand do you pour into each container?
Answer: The fraction of a cup of sand you pour into each container is: \(\frac{7}{24}\)
Explanation:
It is given that you have \(\frac{1}{8}\) cup of red sand, \(\frac{1}{4}\) cup of blue sand, and \(\frac{1}{2}\) cup of white sand.
So,
The total amount of sand = \(\frac{1}{8}\) cup of red sand + \(\frac{1}{4}\) cup of blue sand + \(\frac{1}{2}\) cup of white sand
In addition, we have to see either the numerators are equal or the denominators are equal.
If the numerators are equal we have to ake the denominators also equal.
So,
\(\frac{1}{4}\) is multplied by \(\frac{2}{2}\)
\(\frac{1}{2}\) is multiplied by \(\frac{4}{4}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{4}\) = \(\frac{2}{8}\)
\(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{4}{8}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{8}\) + \(\frac{2}{8}\) + \(\frac{4}{8}\) = \(\frac{7}{8}\)
It is also given that all the sand is equally distributed into 3 containers
So,
The amount of sand in each container = \(\frac{7}{8}\) ÷ 3
Now,
We know that,
\(\frac{a}{b}\) ÷ a = \(\frac{a}{b}\) × \(\frac{1}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{7}{8}\) ÷ 3
= \(\frac{7}{8}\) × \(\frac{1}{3}\)
= \(\frac{ 7 × 1}{8 × 3}\)
= \(\frac{7}{24}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the amount of sand in each container is: \(\frac{7}{24}\) cup.
Question 15.
DIG DEEPER!
You, your friend, and your cousin share \(\frac{1}{2}\) of a vegetable pizza and \(\frac{1}{4}\) of a cheese share pizza. The pizzas are the same size. What fraction of a pizza do you get in all?
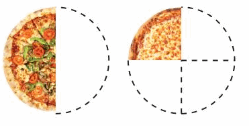
Divide. Use a model to help
Answer: The fraction of a pizza you got is: \(\frac{3}{12}\)
Explanation:
It is given that you, your friend, and your cousin share \(\frac{1}{2}\) of a vegetable pizza and \(\frac{1}{4}\) of a cheese share pizza.
So,
The total amount of pizza = \(\frac{1}{2}\) of a vegetable pizza + \(\frac{1}{4}\) of a cheese share pizza
In addition, we have to see either the numerators are equal or the denominators are equal.
If the numerators are equal we have to ake the denominators also equal.
So,
\(\frac{1}{2}\) is multplied by \(\frac{2}{2}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{2}{4}\)
So,
\(\frac{2}{4}\) + \(\frac{1}{4}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\)
So,
The fraction of pizza each get = \(\frac{The total amount of pizza}{3}\)
= \(\frac{3}{4}\) ÷ 3
Now,
We know that,
\(\frac{a}{b}\) ÷ a = \(\frac{a}{b}\) × \(\frac{1}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{3}{4}\) ÷ 3
= \(\frac{3}{4}\) × \(\frac{1}{3}\)
= \(\frac{ 3 × 1}{4 × 3}\)
= \(\frac{3}{12}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the fraction of pizza each get is: \(\frac{3}{12}\)
Divide Unit Fractions by Whole Numbers Homework & Practice 10.4
Question 1.
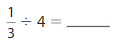
Answer: \(\frac{1}{3}\) ÷ 4 = \(\frac{1}{12}\)
Explanation:
The given numbers are: \(\frac{1}{3}\) and 4
We know that,
\(\frac{a}{b}\) ÷ a = \(\frac{a}{b}\) × \(\frac{1}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{3}\) ÷ 4
= \(\frac{1}{3}\) × \(\frac{1}{4}\)
= \(\frac{ 1 × 1}{3 × 4}\)
= \(\frac{1}{12}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{1}{3}\) ÷ 4 = \(\frac{1}{12}\)
Question 2.
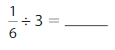
Answer: \(\frac{1}{6}\) ÷ 3 = \(\frac{1}{18}\)
Explanation:
The given numbers are: \(\frac{1}{6}\) and 3
We know that,
\(\frac{a}{b}\) ÷ a = \(\frac{a}{b}\) × \(\frac{1}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{6}\) ÷ 3
= \(\frac{1}{6}\) × \(\frac{1}{3}\)
= \(\frac{ 1 × 1}{6 × 3}\)
= \(\frac{1}{18}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{1}{6}\) ÷ 3 = \(\frac{1}{18}\)
Question 3.
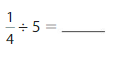
Answer: \(\frac{1}{4}\) ÷ 5 = \(\frac{1}{20}\)
Explanation:
The given numbers are: \(\frac{1}{4}\) and 5
We know that,
\(\frac{a}{b}\) ÷ a = \(\frac{a}{b}\) × \(\frac{1}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{4}\) ÷ 5
= \(\frac{1}{4}\) × \(\frac{1}{5}\)
= \(\frac{ 1 × 1}{5 × 4}\)
= \(\frac{1}{20}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{1}{4}\) ÷ 5 = \(\frac{1}{20}\)
Divide. Use a model to help.
Question 4.
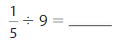
Answer: \(\frac{1}{5}\) ÷ 9 = \(\frac{1}{45}\)
Explanation:
The given numbers are: \(\frac{1}{5}\) and 9
We know that,
\(\frac{a}{b}\) ÷ a = \(\frac{a}{b}\) × \(\frac{1}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{5}\) ÷ 9
= \(\frac{1}{5}\) × \(\frac{1}{9}\)
= \(\frac{ 1 × 1}{5 × 9}\)
= \(\frac{1}{45}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{1}{5}\) ÷ 9 = \(\frac{1}{45}\)
Question 5.
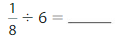
Answer: \(\frac{1}{8}\) ÷ 6 = \(\frac{1}{48}\)
Explanation:
The given numbers are: \(\frac{1}{8}\) and 6
We know that,
\(\frac{a}{b}\) ÷ a = \(\frac{a}{b}\) × \(\frac{1}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{8}\) ÷ 6
= \(\frac{1}{8}\) × \(\frac{1}{6}\)
= \(\frac{ 1 × 1}{8 × 6}\)
= \(\frac{1}{48}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{1}{8}\) ÷ 6 = \(\frac{1}{48}\)
Question 6.
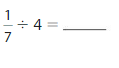
Answer: \(\frac{1}{7}\) ÷ 4 = \(\frac{1}{28}\)
Explanation:
The given numbers are: \(\frac{1}{7}\) and 4
We know that,
\(\frac{a}{b}\) ÷ a = \(\frac{a}{b}\) × \(\frac{1}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{7}\) ÷ 4
= \(\frac{1}{7}\) × \(\frac{1}{4}\)
= \(\frac{ 1 × 1}{7 × 4}\)
= \(\frac{1}{28}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{1}{7}\) ÷ 4 = \(\frac{1}{28}\)
Question 7.
YOU BE THE TEACHER
Your friend divides \(\frac{1}{3}\) by 7 to get \(\frac{1}{21}\). He checks his answer by multiplying \(\frac{1}{21}\) × \(\frac{1}{3}\). Does your friend check his answer correctly? Explain.
Answer: No, your friend does not check his answer correctly
Explanation:
It is given that your friend divides \(\frac{1}{3}\) by 7 to get \(\frac{1}{21}\).
We know that,
\(\frac{a}{b}\) ÷ a = \(\frac{a}{b}\) × \(\frac{1}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{3}\) ÷ 7
= \(\frac{1}{3}\) × \(\frac{1}{7}\)
= \(\frac{ 1 × 1}{7 × 3}\)
= \(\frac{1}{21}\)
It is also given that your friend checks his answer by multiplying \(\frac{1}{21}\) × \(\frac{1}{3}\).
Now,
\(\frac{1}{21}\) × \(\frac{1}{3}\)
= \(\frac{1 × 1}{21 × 3}\)
= \(\frac{1}{63}\)
But, your friend wanted to check whether \(\frac{1}{21}\) × \(\frac{1}{3}\) = \(\frac{1}{7}\)
But, the value becomes \(\frac{1}{63}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that your friend does not check the answer correctly.
Question 8.
Logic
Find the missing numbers.
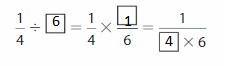
Question 9.
Modeling Real Life
You win tickets that you can exchange for prizes. You exchange \(\frac{1}{5}\) of your tickets and then divide them equally among 3 prizes. What fraction of your tickets do you spend on each prize?
Answer: The fraction of your tickets you spend on each prize is: \(\frac{1}{15}\)
Explanation:
It is given that you win tickets that you can exchange for prizes.
It is also given that you exchange \(\frac{1}{5}\) of your tickets and then divide them equally among 3 prizes
So,
The fraction of the tickets spent on each prize = \(\frac{The value of Exchange}{The number of prizes}\)
= \(\frac{1}{5}\) ÷ 3
Now,
We know that,
\(\frac{a}{b}\) ÷ a = \(\frac{a}{b}\) × \(\frac{1}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{5}\) ÷ 3
= \(\frac{1}{5}\) × \(\frac{1}{3}\)
= \(\frac{ 1 × 1}{5 × 3}\)
= \(\frac{1}{15}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conlude that the fraction of tickets you spend on each prize is: \(\frac{1}{15}\)
Question 10.
DIG DEEPER!
You have \(\frac{1}{8}\) gallon of melted crayon wax. You pour the wax equally into 8 different molds to make new crayons. What fraction of a cup of melted wax is in each mold? Think: 1 gallon is 16 cups.

Answer: The fraction of a cup of melted wax in each mold is: \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Explanation:
It is given that you have \(\frac{1}{8}\) gallon of melted crayon wax.
It is also given that you pour the wax equally into 8 different molds to make new crayons.
So,
The fraction of melted crayon wax in each mold in gallons = \(\frac{The total amount of melted crayon wax }{The number of molds}\)
= \(\frac{1}{8}\) ÷ 8
Now,
We know that,
\(\frac{a}{b}\) ÷ a = \(\frac{a}{b}\) × \(\frac{1}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{8}\) ÷ 8
= \(\frac{1}{8}\) × \(\frac{1}{8}\)
= \(\frac{ 1 × 1}{8 × 8}\)
= \(\frac{1}{64}\) gallons
But, it is given that
1 gallon = 16 cups
So,
The total number of cups that the melted crayon wax contained = \(\frac{1}{64}\) × \(\frac{16}{1}\)
= \(\frac{1 × 16 }{64 × 1}\)
= \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that there are \(\frac{1}{4}\) cups of melted crayon wax in each mold.
Review & Refresh
Question 11.
0.9 ÷ 0.1 = ___
Answer: 0.9 ÷ 0.1 = 9
Explanation:
The given decimal numbers are: 0.9 and 0.1
The representation of the decimal numbers in the fraction form is: \(\frac{9}{10}\) and \(\frac{1}{10}\)
Now,
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{9}{10}\) ÷ \(\frac{1}{10}\) = \(\frac{9}{10}\) × \(\frac{10}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 9 × 10}{10 × 1}\)
= 9
Hence, 0.9 ÷ 0.1 = 9
Question 12.
38.6 ÷ 100 = ___
Answer: 38.6 ÷ 100 = 0.386
Explanation:
The given numbers are: 38.6 and 100
The representation of the numbers in the fraction form is: \(\frac{386}{10}\) and \(\frac{100}{1}\)
Now,
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{386}{10}\) ÷ \(\frac{100}{1}\) = \(\frac{386}{10}\) × \(\frac{1}{100}\)
= \(\frac{ 386 × 1}{100 × 10}\)
= \(\frac{386}{1000}\)
= 0.386
Hence, 38.6 ÷ 100 = 0.386
Question 13.
2.57 ÷ 0.01 = ___
Answer: 2.57 ÷ 0.01 = 257
Explanation:
The given decimal numbers are: 2.57 and 0.01
The representation of the decimal numbers in the fraction form is: \(\frac{257}{100}\) and \(\frac{1}{100}\)
Now,
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{257}{100}\) ÷ \(\frac{1}{100}\) = \(\frac{257}{100}\) × \(\frac{100}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 257 × 100}{100 × 1}\)
= 257
Hence, 2.57 ÷ 0.01 = 257
Lesson 10.5 Problem Solving: Fraction Division
Explore and Grow
You want to make a \(\frac{1}{3}\) batch of the recipe. How you can use division to find the amount of each ingredient you need?
Answer:
It is given that you want to make a \(\frac{1}{3}\) batch of the recipe.
So,
From \(\frac{1}{3}\),
1 represents a batch of the recipe
3 represents the total number of ingredients in a batch
So,
The amount of each ingredient you need = \(\frac{The amount of the batch of the recipe }{The total number of ingredients}\)
= \(\frac{1}{3}\) ÷ 3
Now,
We know that,
\(\frac{a}{b}\) ÷ a = \(\frac{a}{b}\) × \(\frac{1}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{3}\) ÷ 3
= \(\frac{1}{3}\) × \(\frac{1}{3}\)
= \(\frac{ 1 × 1}{3 × 3}\)
= \(\frac{1}{9}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the amount of each ingredient you need is: \(\frac{1}{9}\)
Reasoning
Without calculating, explain how you can tell whether you need more than or less than 1 tablespoon of olive oil?
Answer: You need less than 1 tablespoon of olive oil
Explanation:
From the above problem,
The amount of each ingredient is: \(\frac{1}{9}\)
Since the amount of each ingredient is less than 1, you need less than 1 tablespoon of olive oil
Think and Grow: Problem Solving: Fraction Division
Example
You have 4 cups of yellow paint and 3 cups of blue paint. How many batches of green paint can you make?

Understand the Problem
What do you know?
- You have 4 cups of yellow paint and 3 cups of blue paint.
- One batch of green paint is made of \(\frac{1}{2}\) cup of yellow and \(\frac{1}{3}\) cup of blue.
What do you need to find?
- You need to find how many batches of green paint you can make.
Make a Plan
How will you solve?
- Find how many batches are possible from yellow, and how many from blue.
- Choose the lesser number of batches.
Solve
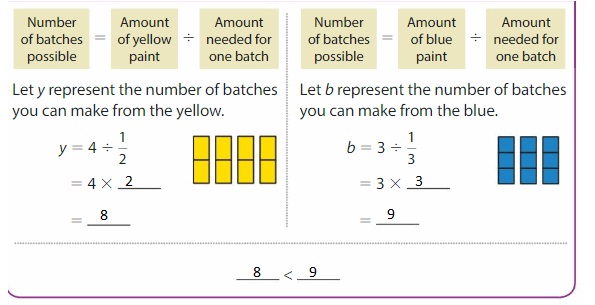
So, you can make 8 batches of green paint.
Show and Grow
Question 1.
In the example, explain why you choose the fewer number of batches.
Answer: In the above example, the yellow paint has the less number of batches as the amount of each batch of yellow paint-filled is more than the batch of green paint
Hence,
We choose the fewer number of batches of yellow paint
Apply and Grow: Practice
Understand the problem. What do you know? What do you need to find? Explain.
Question 2.
A landowner donates 3 acres of land to a city. The mayor of the city uses 1 acre of the land for a playground and the rest of the land for community garden plots. Each garden plot is \(\frac{1}{3}\) acre. How many plots are there?
Understand the problem. Then make a plan. How will you solve it? Explain?
Answer: The number of plots in the community is: 6
Explanation:
It is given that a landowner donates 3 acres of land to a city and the mayor of the city uses 1 acre of the land for a playground and the rest of the land for community garden plots.
So,
The portion of the land used for community garden plots is: 2 acres
It is also given that each garden plot is \(\frac{1}{3}\) acre.
So,
The number of plots = \(\frac{The portion of the land used for community garden plots}{The area of each garden plot}\)
= 2 ÷ \(\frac{1}{3}\)
= 2 × \(\frac{3}{1}\)
= \(\frac{2}{1}\) × \(\frac{3}{1}\)
= 6
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that there are 6 plots
Question 3.
A craftsman uses \(\frac{3}{4}\) gallon of paint to paint 4 identical dressers. He uses the same amount of paint on each dresser. How much paint does he use to paint 7 of the same dressers?

Answer: The paint used by the craftsman to paint 7 of the same dressers is: \(\frac{21}{16}\)
Explanation:
It is given that a craftsman uses \(\frac{3}{4}\) gallon of paint to paint 4 identical dressers.
So,
The paint used to paint each dresser = \(\frac{3}{4}\) ÷ 4
= \(\frac{3}{4}\) × \(\frac{1}{4}\)
= \(\frac{3}{16}\) gallon
So,
The amount of paint used to paint the 7 identical dressers = \(\frac{The paint used to paint each dresser}{1}\) × 7
= \(\frac{3}{16}\) × \(\frac{7}{1}\)
= \(\frac{3 × 7}{16 × 1}\)
= \(\frac{21}{16}\) gallon
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the paint used to paint 7 identical dressers is: \(\frac{21}{16}\) gallon
Question 4.
An airplane travels 125 miles in \(\frac{1}{4}\) hour. It travels the same number of miles each hour. How many miles does the plane travel in 5 hours?
Answer: The number of miles the plane travel in 5 hours is: 2,500 miles
Explanation:
It is given that an airplane travels 125 miles in \(\frac{1}{4}\) hour
So,
The number of miles traveled by plane in 1 hour = 125 ÷ \(\frac{1}{4}\)
= 125 × \(\frac{4}{1}\)
= 125 × 4
= 500 miles
So,
The number of miles traveled by plane in 5 hours = ( The number of miles traveled by plane in 1 hour ) × 5
= 500 × 5
= 2,500 miles
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the number of miles traveled by plane in 5 hours is: 2,500 miles
Question 5.
You make bows for gifts using \(\frac{2}{3}\) yard of ribbon for each bow. You have 4 feet of red ribbon and 5 feet of green ribbon. How many bows can you make?
Answer: The number of bows you can make is: 2 bows
Explanation:
It is given that you make bows for gifts using \(\frac{2}{3}\) yard of ribbon for each bow.
It is also given that you have 4 feet of red ribbon and 5 feet of green ribbon
So,
The total length of ribbon = 5 + 4 = 9 feet
we know that,
1 foot = \(\frac{1}{3}\) yards
So,
9 feet = 9 × \(\frac{1}{3}\) yards
= \(\frac{9}{1}\) yards × \(\frac{1}{3}\) yards
= 3 yards
So,
The number of bows you can make = \(\frac{2}{3}\) yards × 3
= 2 bows
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the number of bows we can make is: 2
Question 6.
A landscaper buys 1 gallon of plant fertilizer. He uses \(\frac{1}{5}\) of the fertilizer, and then divides the rest into 3 smaller bottles. How many gallons does he put into each bottle?
Answer: The number of gallons he put into each bottle is: \(\frac{4}{15}\)
Explanation:
It is given that a landscaper buys 1 gallon of plant fertilizer and he uses \(\frac{1}{5}\) of the fertilizer
So,
The remaining amount of the fertilizer = 1 – \(\frac{1}{5}\)
= \(\frac{4}{5}\) gallons
It is also given that he divided the remaining amount of fertilizer into 3 smaller bottles.
So,
The amount of fertilizer put into each bottle = \(\frac{The remaining amount of the fertilizer}{The total number of bottles}\)
= \(\frac{4}{5}\) ÷ 3
= \(\frac{4}{5}\) × \(\frac{1}{3}\)
= \(\frac{4 × 1}{5 × 3}\)
= \(\frac{4}{15}\) gallons
hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the amount of remaining fertilizer put into each bottle is: \(\frac{4}{15}\) gallons
Think and Grow: Modeling Real Life
Example
A sponsor donates $0.10 to a charity for every \(\frac{1}{4}\) kilometer of the triathlon an athlete completes. The athlete completes the entire triathlon. How much money does the sponsor donate?
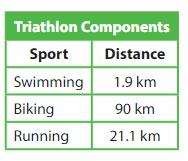
Think: What do you know? What do you need to find? How will you solve?
Write and solve an equation.
Add 1.9, 90, and 21.1 to find how many kilometers the athlete completes.
Divide the sum by \(\frac{1}{4}\) to find how many \(\frac{1}{4}\) kilometers the athlete completes.
Multiply the quotient by $0.10 to find how much money the sponsor donates.

Let m represent the total amount of money donated.

Show and Grow
Question 7.
You earn $5 for every \(\frac{1}{2}\) hour you do yard work. How much money do you earn in 1 week?
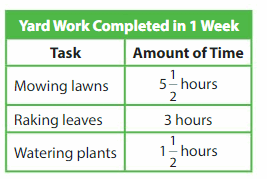
Answer: The amount you earn in 1 week is: $700
Explanation:
The given table is:

From the above table,
The total amount of time = 5\(\frac{1}{2}\) + 3 + 1\(\frac{1}{2}\)
= \(\frac{11}{2}\) + 3 + \(\frac{3}{2}\)
= \(\frac{11 + 3}{2}\) + 3
= 7 + 3
= 10 hours
It is given that you earn $5 for every \(\frac{1}{2}\) hour you do yard work
So,
The amount earned in 10 hours in a day = 10 ÷\(\frac{1}{2}\) × 5 ( Since we have the time in hours but the money earned is given in half an hour basis )
= 20 × 5
= $100
We know that 1 week = 7 days
So,
The amount earned in 1 week = 100 × 7 = $700
hence, from the above,
We can conclude that we can earn $700 in a week
Problem Solving: Fraction Division Homework & 10.5
Understand the problem. Then make a plan. How will you solve? Explain.
Question 1.
A train travels 75 miles in \(\frac{1}{2}\) hour. How many miles does the train travel in 8 hours?
Answer: The number of miles the train travel in hours is: 1,200 miles
Explanation:
It is given that a train travels 75 miles in \(\frac{1}{2}\) hour.
So,
The number of miles the train travel in 1 hour = 75 ÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\)
= 75 × 2
= 150 miles
So,
The number of miles the train travel in 8 hours = The number of miles traveled by train in 1 hour × 8
= 150 × 8
= 1,200 miles
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the train travels 1,200 miles in 8 hours.
Question 2.
You need \(\frac{2}{3}\) yard of fabric to create a headband. You have 12 feet of blue fabric and 4 feet of yellow fabric. How many headbands can you make with all of the fabric?
Answer: The number of headbands you can make with all of the fabric is: 8 headbands
Explanation:
It is given that you need \(\frac{2}{3}\) yard of fabric to create a headband.
It is also given that you have 12 feet of blue fabric and 4 feet of yellow fabric.
So,
The total length of the fabric = 12 + 4 = 16 feet
We know that
1 foot = \(\frac{1}{3}\) yards
So,
16 feet = \(\frac{16}{3}\) yards
So,
The number of headbands you can create with all the fabric = \(\frac{The total length of the fabric}{The length of each fabric}\)
= \(\frac{16}{3}\) ÷ \(\frac{2}{3}\)
= \(\frac{16}{3}\) × \(\frac{3}{2}\)
= \(\frac{16 × 3}{3 × 2}\)
= 8 headbands
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that we can create 8 headbands with all the fabric.
Question 3.
An art teacher has 8 gallons of paint. Her class uses \(\frac{3}{4}\) of the paint. The teacher divides the rest of the paint into 4 bottles. How much paint is in each bottle?
Answer: The amount of paint in each bottle is: \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation:
It is given that an art teacher has 8 gallons of paint and her class uses \(\frac{3}{4}\) of the paint.
So,
The remaining amount of paint = \(\frac{1}{4}\) × 8
= \(\frac{1}{4}\) × \(\frac{8}{1}\)
=\(\frac{1 × 8}{4 × 1}\)
= 2 gallons
It is also given that the remaining amount of the paint divided into 4 bottles by the teacher
So,
The amount of paint present in each bottle = 2 ÷ 4
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) gallons
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the amout of paint present in each bottle is: \(\frac{1}{2}\) gallons
Question 4.
You mix 3\(\frac{1}{4}\) cups of frozen strawberries and 4\(\frac{1}{2}\) cups of frozen blueberries in a bowl. A smoothie requires \(\frac{1}{2}\) cup of your berry mix. How many smoothies can you make?
Answer: The number of smoothies you can make is:
Explanation:
It is given that you mix 3\(\frac{1}{4}\) cups of frozen strawberries and 4\(\frac{1}{2}\) cups of frozen blueberries in a bowl.
So,
The amount of berry mix = 3\(\frac{1}{4}\) cups of frozen strawberries + 4\(\frac{1}{2}\) cups of frozen blueberries
= 3\(\frac{1}{4}\) + 4\(\frac{1}{2}\)
= \(\frac{13}{4}\) + \(\frac{9}{2}\)
In addition, equate the denominators
So,
Multiply \(\frac{9}{2}\) with \(\frac{2}{2}\)
So,
\(\frac{9}{2}\) = \(\frac{18}{4}\)
So,
The amount of berry mix = \(\frac{13}{4}\) + \(\frac{18}{4}\)
= \(\frac{31}{4}\)
Now,
It is also given that the smoothie requires \(\frac{1}{2}\) cup of your berry mix.
So,
The number of smoothies = \(\frac{31}{4}\) ÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\)
= \(\frac{31}{4}\) × \(\frac{2}{1}\)
= \(\frac{31 × 2}{4 × 1}\)
= \(\frac{31}{2}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the number of smoothies we can make are: \(\frac{31}{2}\)
Question 5.
Modeling Real Life
A sponsor donates $0.10 for every \(\frac{1}{4}\) dollar donated at the locations shown. How much money does the sponsor donate?
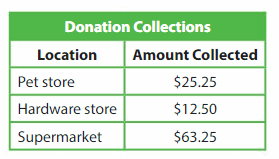
Answer: The amount of money the sponsor donates is: $40.4
Explanation:
The given table is:

From the above table,
The total amount of money collected = 25.25 + 12.50 + 63.25
= $101
It is given that a sponsor donates $0.10 for every \(\frac{1}{4}\) dollar
So,
the total amount of donated = The total amount of money collected ÷ \(\frac{1}{4}\) × 0.10
= 101 ÷ \(\frac{1}{4}\) × 0.10
= 101 × 4 × 0.10
= 04 × 0.10
= $40.4
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the amount of money donated by a sponsor is: $40.4
Question 6.
DIG DEEPER!
A nurse earns $16 for every \(\frac{1}{2}\) hour at work. How much money does she earn in 5 days?
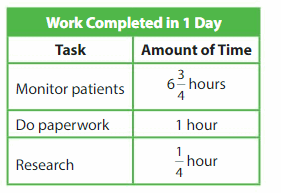
Answer: The money she earns in 5 days is: $1,280
Explanation:
The given table is:

From the above table,
The total amount of time = 6\(\frac{3}{4}\) + 1 + \(\frac{1}{4}\)
= \(\frac{27}{4}\) + 1 + \(\frac{1}{4}\)
= \(\frac{27 + 1}{4}\) + 1
= 7 + 1
= 8 hours
It is given that a nurse earns $16 for every \(\frac{1}{2}\) hour at work.
So,
The money she earned for 1 hour = 16 ÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\)
= 16 × 2 = $32
So,
The money earned for 8 hours = The money earned in 1 hour × 8
= 32 × 8 = $256
So,
The money earned in 5 days = The money earned in 1 day × 5
= 256 × 5 = $1,280
hence, from the above,
we can conclude that she can earn $1,280 in 5 days.
Review & Refresh
Find the quotient. Then check your answer.
Question 7.

Answer: 186 ÷ 12 = 1 R 4
Explanation:
Let 185.88 be rounded to 186
So,
By using the partial quotients method,
186 ÷ 12 = ( 120 + 36 + 24 ) ÷ 12
= ( 120 ÷ 12 ) + ( 36 ÷ 12 ) + ( 24 ÷ 12 )
= 10 + 3 + 2
= 17 R 4
Hence, 186 ÷ 12 = 17 R 4
Question 8.
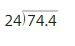
Answer: 74 ÷ 24 = 3 R 2
Explanation:
Let 74.4 be rounded to 74
So,
By using the partial quotients method,
74 ÷ 24 = 72 ÷ 24
= 3 R 2
Hence, 74 ÷ 24 = 3 R 2
Question 9.
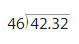
Answer: 42 ÷ 46 = 0.9
Explanation:
Let 42.32 be rounded to 42
So,
By using the partial quotients method,
42 ÷ 46 = 0.9
Hence,
42 ÷ 46 = 0.9
Divide Fractions Performance Task 10
Your city has a robotics competition. Each team makes a robot that travels through a maze. The time each robot spends in the maze is used to find the team’s score.
1. One-third of the students in your grade participate in the competition. The number of participating students is divided into 12 teams.
a. What fraction of the total number of students in your grade is on each team?
Answer: The fraction of the total number of students in your grade is: \(\frac{1}{36}\)
Explanation:
It is given that there are \(\frac{1}{3}\) of the students in your grade are participating in the competition.
It is also given that the participating students are divided into 12 teams.
So,
The fraction of the total number of students in each team = \(\frac{The number of participating students}{Th total number of teams}\)
= \(\frac{1}{3}\) ÷ 12
= \(\frac{1}{3}\) ÷ \(\frac{12}{1}\)
= \(\frac{1}{3}\) × \(\frac{1}{12}\)
= \(\frac{1 × 1}{12 × 3}\)
= \(\frac{1}{36}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the fraction of students that are in each team is: \(\frac{1}{36}\)
b. There are 3 students on each team. How many students are in your grade?
Answer: The number of students in your grade is: 36
Explanation:
It is given that the number of students is divided into 12 teams
It is also given that there are 3 students on each team
So,
The total number of students = The number of teams × The number of students in each team
= 12 × 3 = 36 students
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that there are 36 students in your grade
Question 2.
The maze for the competition is shown.
a. Write the length of the maze in feet.
Answer:
The given maze for the competition is:

From the above maze,
The total length of the maze is: 8 feet 6 inches
We know that,
1 foot = 12 inches
Hence,
1 inch = \(\frac{1}{12}\) feet
So,
6 inches = 6 × \(\frac{1}{12}\)
= \(\frac{1}{12}\) × \(\frac{6}{1}\)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) feet
So,
The total length of the maze in feet = 8 feet + \(\frac{1}{2}\) feet
= 8.5 feet or 8\(\frac{1}{2}\) feet
b. The length of the maze is divided into 6 equal sections. What is the length of each section of the maze?
Answer: The length of each section of the maze is: \(\frac{17}{12}\) feet
Explanation:
From the above Exercise,
The total length of the maze in feet is: 8.5 feet or 8\(\frac{1}{2}\) feet
It is given that the length of the maze is divided into 6 equal sections
So,
The length of each section of the maze = 8\(\frac{1}{2}\) ÷ 6
= 8\(\frac{1}{2}\) ÷ \(\frac{6}{1}\)
= 8\(\frac{1}{2}\) × \(\frac{1}{6}\)
= \(\frac{17}{2}\) × \(\frac{1}{6}\)
= \(\frac{17}{12}\) feet
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the length of each section in a maze is: \(\frac{17}{12}\) feet
Question 3.
Each team has 200 seconds to complete the maze. The rules require judges to use the expression (200 – x) ÷ \(\frac{1}{5}\), where x is the total number of seconds, to find a team’s total score.
a. Your robot completes the maze in 3 minutes 5 seconds. How many points does your team earn?
Answer: The number of points your team earn is: 75 points
Explanation:
It is given that each team has 200 seconds to complete the maze and the rules require judges to use the expression (200 – x) ÷ \(\frac{1}{5}\) where x is the total number of seconds
It is also given that your robot completes the maze in 3 minutes 5 seconds
We know that,
1 minute = 60 seconds
So,
The time taken by the robot to complete the maze in seconds = ( 3 × 60 ) + 5
= 185 seconds
So,
x= 185
So,
200 – x = 200 – 185 = 15
So,
The number of points the team earned = ( 200 – x ) ÷ \(\frac{1}{5}\)
= 15 ÷ \(\frac{1}{5}\)
= 15 × 5
= 75 points
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the number of points earned by the team is: 75 points
b. Do you think the team with the most points or the fewest points wins? Use an example to justify your answer.
Answer: The team with the most points wins the competition because
Reason:
Suppose team A takes 2 minutes and team B takes 3 minutes to complete the competition
So,
The time is taken by team A in seconds = 120 seconds
So,
x= 120
So,
200 – x = 200 – 120 = 80
Now,
The time is taken by team B in seconds = 180 seconds
So,
x= 180
So,
200 – x = 200 – 180 = 20
Now,
The number of points earned by team A = 80 ÷ \(\frac{1}{5}\)
= 400 points
The number of points earned by team B = 20 ÷ \(\frac{1}{5}\)
= 100 points
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the team with more points wins the competition
Divide Fractions Activity
Fraction Connection: Division
Directions:
- Players take turns rolling three dice.
- On your turn, evaluate the expression indicated by your roll and cover the answer.
- The first player to get four in a row, horizontally, vertically, or diagonally, wins!
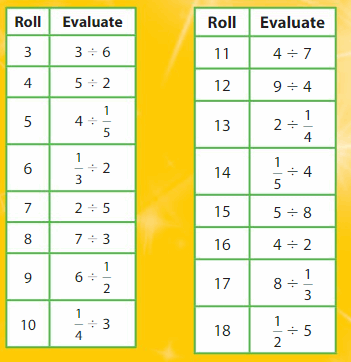
Divide Fractions Chapter Practice 10
10.1 Interpret Fractions as Division
Divide. Use a model to help.
Question 1.
1 ÷ 2 = ___
Answer: 1 ÷ 2 = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation:
We know that,
a ÷ b = \(\frac{a}{b}\)
Hence,
1 ÷ 2 = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 2.
3 ÷ 10 = __
Answer: 3 ÷ 10 = \(\frac{3}{10}\)
Explanation:
We know that,
a ÷ b = \(\frac{a}{b}\)
Hence,
3 ÷ 10 = \(\frac{3}{10}\)
Question 3.
4 ÷ 7 = __
Answer: 4 ÷ 7 = \(\frac{4}{7}\)
Explanation:
We know that,
a ÷ b = \(\frac{a}{b}\)
Hence,
4 ÷ 7 = \(\frac{4}{7}\)
Question 4.
11 ÷ 15 = ___
Answer: 11 ÷ 15 = \(\frac{11}{15}\)
Explanation:
We know that,
a ÷ b = \(\frac{a}{b}\)
Hence,
11 ÷ 15 = \(\frac{11}{15}\)
Question 5.
8 ÷ 9 = ___
Answer: 8 ÷ 9 = \(\frac{8}{9}\)
Explanation:
We know that,
a ÷ b = \(\frac{a}{b}\)
Hence,
8 ÷ 9 = \(\frac{8}{9}\)
Question 6.
13 ÷ 20 = ___
Answer: 13 ÷ 20 = \(\frac{13}{20}\)
Explanation:
We know that,
a ÷ b = \(\frac{a}{b}\)
Hence,
13 ÷ 20 = \(\frac{13}{20}\)
Question 7.
Modeling Real Life
Nine friends equally share 12 apples. What fraction of an apple does each friend get?
Answer: The fraction of an apple each friend get is: \(\frac{9}{12}\)
Explanation:
It is given that nine friends equally share 12 apples.
So,
The fraction of an apple each friend get = \(\frac{The number of friends}{The number of apples}\)
= \(\frac{9}{12}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the fraction of an apple each friend get is: \(\frac{9}{12}\)
10.2 Mixed Numbers as Quotients
Divide. Use a model to help
Question 8.
8 ÷ 3 = ___
Answer: 8 ÷ 3 = 2\(\frac{2}{3}\)
Explanation:
We know that,
a ÷ b = \(\frac{a}{b}\)
a\(\frac{b}{c}\) = \(\frac{ac + b}{c}\)
\(\frac{a}{b}\) = Remainder\(\frac{Quotient}{Divisor}\)
So,
8 ÷ 3 = \(\frac{8}{3}\)
By using the partial quotients method,
8 ÷ 3 = 6 ÷ 3
= 2 R 2
Hence,
8 ÷ 3 = 2\(\frac{2}{3}\)
Question 9.
6 ÷ 5 = ___
Answer: 6 ÷ 5 = 1\(\frac{1}{5}\)
Explanation:
We know that,
a ÷ b = \(\frac{a}{b}\)
a\(\frac{b}{c}\) = \(\frac{ac + b}{c}\)
\(\frac{a}{b}\) = Remainder\(\frac{Quotient}{Divisor}\)
So,
6 ÷ 5 = \(\frac{6}{5}\)
By using the partial quotients method,
6 ÷ 5 = 5 ÷ 5
= 1 R 1
Hence,
6 ÷ 5 = 1\(\frac{1}{5}\)
Question 10.
10 ÷ 4 = ___
Answer: 10 ÷ 4 = 2\(\frac{2}{4}\)
Explanation:
We know that,
a ÷ b = \(\frac{a}{b}\)
a\(\frac{b}{c}\) = \(\frac{ac + b}{c}\)
\(\frac{a}{b}\) = Remainder\(\frac{Quotient}{Divisor}\)
So,
10 ÷ 4 = \(\frac{10}{4}\)
By using the partial quotients method,
10 ÷ 4 = 8 ÷ 4
= 2 R 2
Hence,
10 ÷ 4 = 2\(\frac{2}{4}\)
Question 11.
20 ÷ 11 = __
Answer: 20 ÷ 11 = 1\(\frac{9}{11}\)
Explanation:
We know that,
a ÷ b = \(\frac{a}{b}\)
a\(\frac{b}{c}\) = \(\frac{ac + b}{c}\)
\(\frac{a}{b}\) = Remainder\(\frac{Quotient}{Divisor}\)
So,
20 ÷ 11 = \(\frac{20}{11}\)
By using the partial quotients method,
20 ÷ 11 = 11 ÷ 11
= 1 R 9
Hence,
20 ÷ 11 = 1\(\frac{9}{11}\)
Question 12.
25 ÷ 2 = ___
Answer: 25 ÷ 2 = 12\(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation:
We know that,
a ÷ b = \(\frac{a}{b}\)
a\(\frac{b}{c}\) = \(\frac{ac + b}{c}\)
\(\frac{a}{b}\) = Remainder\(\frac{Quotient}{Divisor}\)
So,
25 ÷ 2 = \(\frac{25}{2}\)
By using the partial quotients method,
25 ÷ 2 = 24 ÷ 2
= 12 R 1
Hence,
25 ÷ 2 = 12\(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 13.
64 ÷ 9 = ___
Answer: 64 ÷ 9 = 7\(\frac{1}{9}\)
Explanation:
We know that,
a ÷ b = \(\frac{a}{b}\)
a\(\frac{b}{c}\) = \(\frac{ac + b}{c}\)
\(\frac{a}{b}\) = Remainder\(\frac{Quotient}{Divisor}\)
So,
64 ÷ 9 = \(\frac{64}{9}\)
By using the partial quotients method,
64 ÷ 9 = 63 ÷ 9
= 7 R 1
Hence,
64 ÷ 9 = 7\(\frac{1}{9}\)
10.3 Divide Whole Numbers by Unit Fractions
Divide. Use a model to help.
Question 14.
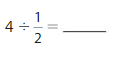
Answer: 4 ÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\) = 8
Explanation:
The given numbers are: 4 and \(\frac{1}{2}\)
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
4 ÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\) = 4 × \(\frac{2}{1}\)
= \(\frac{4}{1}\) × \(\frac{2}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 2 × 4}{1 × 1}\)
= 8
Hence,
4÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\) = 8
Question 15.
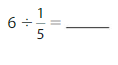
Answer: 6 ÷ \(\frac{1}{5}\) = 30
Explanation:
The given numbers are: 6 and \(\frac{1}{5}\)
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
6 ÷ \(\frac{1}{5}\) = 6 × \(\frac{5}{1}\)
= \(\frac{6}{1}\) × \(\frac{5}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 6 × 5}{1 × 1}\)
= 30
Hence,
6÷ \(\frac{1}{5}\) = 30
Question 16.
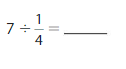
Answer: 7 ÷ \(\frac{1}{4}\) = 28
Explanation:
The given numbers are: 7 and \(\frac{1}{4}\)
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
7 ÷ \(\frac{1}{4}\) = 7 × \(\frac{4}{1}\)
= \(\frac{7}{1}\) × \(\frac{4}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 7 × 4}{1 × 1}\)
= 28
Hence,
7÷ \(\frac{1}{4}\) = 36
Question 17.
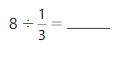
Answer: 8 ÷ \(\frac{1}{3}\) = 24
Explanation:
The given numbers are: 8 and \(\frac{1}{3}\)
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
8 ÷ \(\frac{1}{3}\) = 8 × \(\frac{3}{1}\)
= \(\frac{8}{1}\) × \(\frac{3}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 8 × 3}{1 × 1}\)
= 24
Hence,
8÷ \(\frac{1}{3}\) = 24
Question 18.
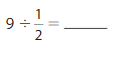
Answer: 9 ÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\) = 18
Explanation:
The given numbers are: 9 and \(\frac{1}{2}\)
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
9 ÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\) = 9 × \(\frac{2}{1}\)
= \(\frac{9}{1}\) × \(\frac{2}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 9 × 2}{1 × 1}\)
= 18
Hence,
9÷ \(\frac{1}{2}\) = 18
Question 19.
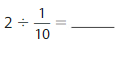
Answer: 2 ÷ \(\frac{1}{10}\) = 20
Explanation:
The given numbers are: 2 and \(\frac{1}{10}\)
We know that,
a ÷ \(\frac{a}{b}\) = a × \(\frac{b}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
2 ÷ \(\frac{1}{10}\) = 2 × \(\frac{10}{1}\)
= \(\frac{2}{1}\) × \(\frac{10}{1}\)
= \(\frac{ 2 × 10}{1 × 1}\)
= 20
Hence,
2÷ \(\frac{1}{10}\) = 20
10.4 Divide Unit Fractions by Whole Numbers
Divide. Use a model to help.
Question 20.
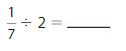
Answer: \(\frac{1}{7}\) ÷ 2 = \(\frac{1}{14}\)
Explanation:
The given numbers are: \(\frac{1}{7}\) and 2
We know that,
\(\frac{a}{b}\) ÷ a = \(\frac{a}{b}\) × \(\frac{1}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{7}\) ÷ 2
= \(\frac{1}{7}\) × \(\frac{1}{2}\)
= \(\frac{ 1 × 1}{7 × 2}\)
= \(\frac{1}{14}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{1}{7}\) ÷ 2 = \(\frac{1}{14}\)
Question 21.
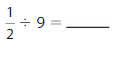
Answer: \(\frac{1}{2}\) ÷ 9 = \(\frac{1}{18}\)
Explanation:
The given numbers are: \(\frac{1}{2}\) and 9
We know that,
\(\frac{a}{b}\) ÷ a = \(\frac{a}{b}\) × \(\frac{1}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{2}\) ÷ 9
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × \(\frac{1}{9}\)
= \(\frac{ 1 × 1}{2 × 9}\)
= \(\frac{1}{18}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{1}{2}\) ÷ 9 = \(\frac{1}{18}\)
Question 22.
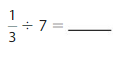
Answer: \(\frac{1}{3}\) ÷ 7 = \(\frac{1}{21}\)
Explanation:
The given numbers are: \(\frac{1}{3}\) and 7
We know that,
\(\frac{a}{b}\) ÷ a = \(\frac{a}{b}\) × \(\frac{1}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{3}\) ÷ 7
= \(\frac{1}{3}\) × \(\frac{1}{7}\)
= \(\frac{ 1 × 1}{7 × 3}\)
= \(\frac{1}{21}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{1}{3}\) ÷ 7 = \(\frac{1}{21}\)
Question 23.
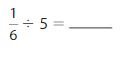
Answer: \(\frac{1}{6}\) ÷ 5 = \(\frac{1}{30}\)
Explanation:
The given numbers are: \(\frac{1}{6}\) and 5
We know that,
\(\frac{a}{b}\) ÷ a = \(\frac{a}{b}\) × \(\frac{1}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{6}\) ÷ 5
= \(\frac{1}{6}\) × \(\frac{1}{5}\)
= \(\frac{ 1 × 1}{6 × 5}\)
= \(\frac{1}{30}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{1}{6}\) ÷ 5 = \(\frac{1}{30}\)
Question 24.
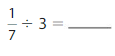
Answer: \(\frac{1}{7}\) ÷ 3 = \(\frac{1}{21}\)
Explanation:
The given numbers are: \(\frac{1}{7}\) and 3
We know that,
\(\frac{a}{b}\) ÷ a = \(\frac{a}{b}\) × \(\frac{1}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{7}\) ÷ 3
= \(\frac{1}{7}\) × \(\frac{1}{3}\)
= \(\frac{ 1 × 1}{7 × 3}\)
= \(\frac{1}{21}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{1}{7}\) ÷ 3 = \(\frac{1}{21}\)
Question 25.
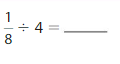
Answer: \(\frac{1}{8}\) ÷ 4 = \(\frac{1}{32}\)
Explanation:
The given numbers are: \(\frac{1}{8}\) and 4
We know that,
\(\frac{a}{b}\) ÷ a = \(\frac{a}{b}\) × \(\frac{1}{a}\)
a= \(\frac{a}{1}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{8}\) ÷ 4
= \(\frac{1}{8}\) × \(\frac{1}{4}\)
= \(\frac{ 1 × 1}{8 × 4}\)
= \(\frac{1}{32}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{1}{8}\) ÷ 4 = \(\frac{1}{32}\)
10.5 Problem Solving: Fraction Division
Question 26.
A mechanic buys 1 gallon of oil. She uses \(\frac{1}{6}\) of the oil, and then divides the rest into 4 smaller bottles. How much does she put into each bottle?

Answer: The amount of oil she put into each bottle is: \(\frac{5}{24}\)
Explanation:
It is given that a mechanic buys 1 gallon of oil and she uses \(\frac{1}{6}\) of the oil
So,
the remaining part of the oil = 1 – \(\frac{1}{6}\)
= \(\frac{5}{6}\)
It is also given that she divides the rest of the oil into 4 smaller bottles.
So,
The amount of oil in each bottle = \(\frac{The remaining part of the oil}{The number of bottles}\)
= \(\frac{5}{6}\) ÷ 4
= \(\frac{5}{6}\) × \(\frac{1}{4}\)
= \(\frac{5 × 1}{6 × 4}\)
= \(\frac{5}{24}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the amount of oil in each bottle is: \(\frac{5}{24}\)
Conclusion:
Make use of the quick links and try to solve the problems in a simple manner. Redefine your true self with the BIM Answer Key for Grade 5 curated by subject experts. Test your knowledge by solving the questions which are given at the end of the chapter.
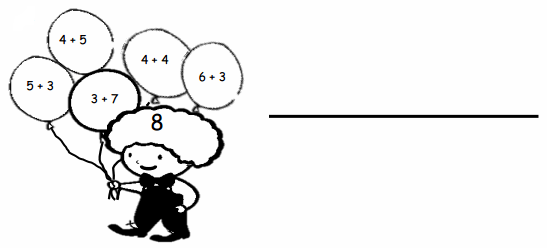
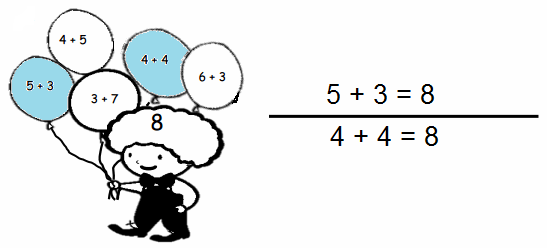


















![]()
![]()

![]()

![]()

![]()