Big Ideas Math Answers Grade 4 Chapter 7 Understand Fraction Equivalence and Comparison: It is mandatory for the students to learn the concepts in-depth if you want to become master in maths. Math is the scoring and easiest subject among all. Come fall in love with math by practicing the problems from our Big Ideas Math Answers Grade 4 Chapter 7 Understand Fraction Equivalence and Comparison. You can prove yourself in exams by practicing the problems from Bigideas Math Answer Key 4th Grade Chapter 7 Understand Fraction Equivalence and Comparison. So we suggest the students of Grade 4 to Download Big Ideas Math Solution Key Grade 4 Chapter 7 Understand Fraction Equivalence and Comparison pdf.
Big Ideas Math Book 4th Grade Answer Key Chapter 7 Understand Fraction Equivalence and Comparison
Pupils can easily observe the improvement and growth in math learning by practicing with the Big Ideas Math Answers Grade 4 Chapter 7 Understand Fraction Equivalence and Comparison. The best guide for math practice is Big Ideas Math Book 4th Grade Solution Key Chapter 7 Understand Fraction Equivalence and Comparison. Solve all the problems and learn the easy methods of math practice. Learn simple to solve the problems in Grade 4 Chapter 7 Understand Fraction Equivalence and Comparison. Access the links given below and start your preparation.
Lesson: 1 Model Equivalent Fractions
Lesson: 2 Generate Equivalent Fractions by Multiplying
- Lesson 7.2 Generate Equivalent Fractions by Multiplying
- Generate Equivalent Fractions by Multiplying Homework & Practice 7.2
Lesson: 3 Generate Equivalent Fractions by Dividing
- Lesson 7.3 Generate Equivalent Fractions by Dividing
- Generate Equivalent Fractions by Dividing Homework & Practice 7.3
Lesson: 4 Compare Fractions Using Benchmarks
- Lesson 7.4 Compare Fractions Using Benchmarks
- Compare Fractions Using Benchmarks Homework & Practice 7.4
Lesson: 5 Compare Fractions
Performance Task
- Understand Fraction Equivalence and Comparison Performance Task
- Understand Fraction Equivalence and Comparison Activity
- Understand Fraction Equivalence and Comparison Chapter Practice
- Understand Fraction Equivalence and Comparison of Cumulative Practice
- Understand Fraction Equivalence and Comparison STEAM Performance Task
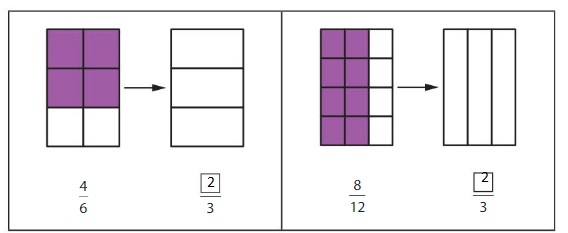
Lesson 7.1 Model Equivalent Fractions
Explore and Grow
Use the model to write fractions that are the same size as \(\frac{1}{2}\).
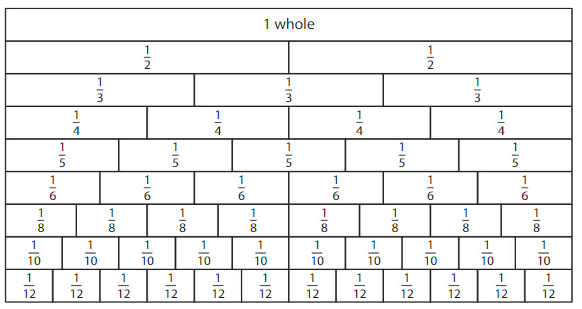
Answer: Using the model, the fractions that have the same size as \(\frac{1}{2}\) are:
\(\frac{2}{4}\), \(\frac{3}{6}\), \(\frac{4}{8}\), \(\frac{6}{12}\)
Explanation:
Given model is:

In the above table, the whole 1 is divided in to different fractions like \(\frac{1}{2}\),
\(\frac{1}{3}\), \(\frac{1}{4}\), \(\frac{1}{5}\), \(\frac{1}{6}\),
\(\frac{1}{8}\), \(\frac{1}{10}\), and \(\frac{1}{12}\)
So,
From this table, the fractions that give us the same size as of \(\frac{1}{2}\) are:
\(\frac{2}{4}\), \(\frac{3}{6}\), \(\frac{4}{8}\), \(\frac{6}{12}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the fractions that are having the same size as \(\frac{1}{2}\) are:
\(\frac{2}{4}\), \(\frac{3}{6}\), \(\frac{4}{8}\), \(\frac{6}{12}\)
Reasoning
Can you write a fraction with a denominator of 12 that is to the same size as \(\frac{2}{3}\) ? Explain.
Answer: The fraction with the denominator 12 that is to the same size as \(\frac{2}{3}\) is:
\(\frac{8}{12}\)
Explanation:
The given model is:

From the above table, the fractions having denominator 12 have only 1 row.
But, we want the same value of \(\frac{2}{3}\) by having the denominator 12
So, from the table,
When we add all \(\frac{1}{12}\), we will get the value \(\frac{8}{12}\)
So,
The value of \(\frac{2}{3}\) is equal to the \(\frac{8}{12}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the fraction with denominator 12 that is having the same size as \(\frac{2}{3}\) is:
\(\frac{8}{12}\)
Think and Grow: Model Equivalent Fractions
Two or more numbers that have the same value are. Two or equivalent more fractions that name the same part of a whole are equivalent. Equivalent fractions name the same point on a number line. fractions.
Example
Use models to find equivalent fractions for \(\frac{2}{3}\) .

One Way:
Draw models that show the same whole divided into different numbers of parts.
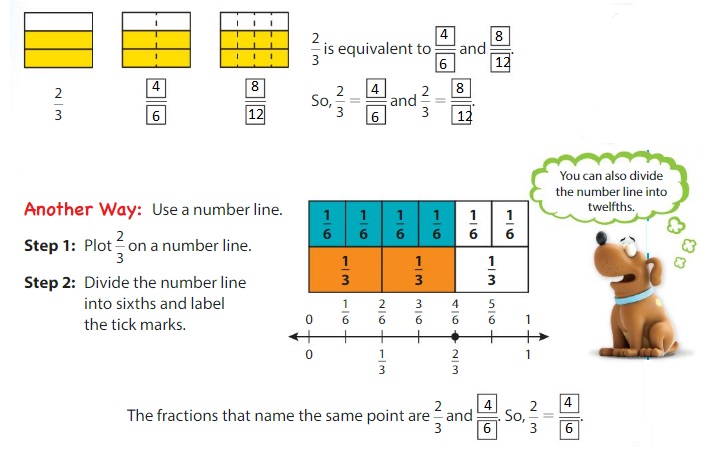
Show and Grow
Use the model to find an equivalent fraction for \(\frac{2}{5}\) .
Answer:

Answer: The equivalent fraction for \(\frac{2}{5}\) is: \(\frac{4}{10}\)
Explanation:
The given model is:

From the above model, we can say the fraction is: \(\frac{2}{5}\)
Now, the model for the equivalent fraction of \(\frac{2}{5}\) is:
From the above model, we can say that the fraction is: \(\frac{4}{10}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the equivalent of \(\frac{2}{5}\) is: \(\frac{4}{10}\)
Question 2.
Use the number line to find an1equivalent fraction for \(\frac{1}{6}\) .
Answer:
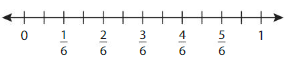
The equivalent fraction for \(\frac{1}{6}\) is: \(\frac{2}{12}\)
Explanation:
The given number line is:
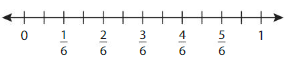
From the given line, we can say that every 2 lines represent \(\frac{1}{6}\) multiple.
So,
Each line of the given number line represents \(\frac{1}{12}\) multiple
So,
The number line with \(\frac{1}{12}\) will be like:
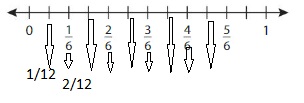
So, from the above number line,
We can say that the equivalent fraction of \(\frac{1}{6}\) is: \(\frac{1}{12}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the equivalent fraction of \(\frac{1}{6}\) is: \(\frac{1}{12}\)
Apply and Grow: Practice
Use the model to find an equivalent fraction.
Question 3.
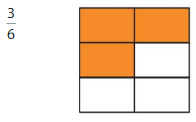
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{3}{6}\) is: \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation:
The given model is:

From the above model, we can say that the fraction is: \(\frac{3}{6}\)
So,
The model for the equivalent fraction is:

From the above, we can see that the model represents \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Note: \(\frac{3}{6}\) is equal to \(\frac{1}{2}\) because when we divide \(\frac{3}{6}\) with 3, then we can get the answer.
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that \(\frac{3}{6}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 4.
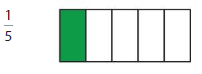
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{1}{5}\) is: \(\frac{2}{10}\)
Explanation:
The given model is:

From the above model, we can say that the fraction is: \(\frac{1}{5}\)
So,
The model for the equivalent fraction is:
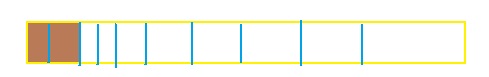
So,
The equivalent fraction from the above model is: \(\frac{2}{10}\)
So,
When \(\frac{2}{10}\) is divided by 2, we will get the equivalent fraction
Hence, from the above,
We can say that \(\frac{1}{5}\) = \(\frac{2}{10}\)
Question 5.
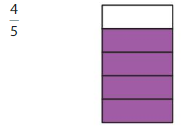
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{4}{5}\) is: \(\frac{8}{10}\)
Explanation:
The given model is:

From the above model, we can say the fraction is \(\frac{4}{5}\)
So,
The model for the equivalent fraction is:
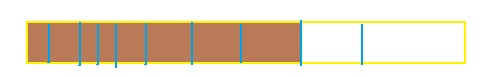
From the above model, we can say that the equivalent fraction is: \(\frac{8}{10}\)
So,
When \(\frac{8}{10}\) is divided by 2, we will get the equivalent fraction.
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that \(\frac{4}{5}\) = \(\frac{8}{10}\)
Question 6.
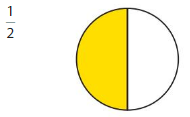
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{1}{2}\) is: \(\frac{5}{10}\)
Explanation:
The given model is:

From the above model, we can say that the fraction is: \(\frac{1}{2}\)
So,
The model for the equivalent fraction is:
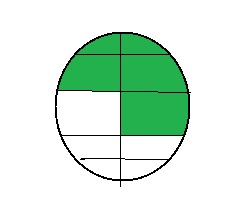
So, the model that represents the equivalent fraction is: \(\frac{5}{10}\)
So,
When \(\frac{5}{10}\) is divided by 5, we will get the equivalent fraction
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that \(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{5}{10}\)
Use a number line to find an equivalent fraction.
Question 7.
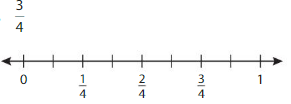
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{3}{4}\) is: \(\frac{6}{8}\)
Explanation:
The given number line is:
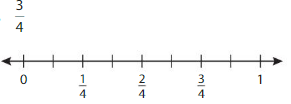
From the above-given number line,
Every 2 lines represent the value.i.e., \(\frac{1}{4}\)
So,
The value of each line represents \(\frac{1}{8}\)
So,
The model for the equivalent fraction is:
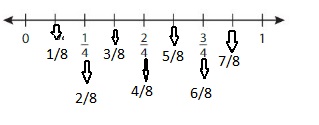
So,
From the equivalent number line,
We can say that \(\frac{3}{4}\) is equivalent to \(\frac{6}{8}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that \(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{6}{8}\)
Question 8.
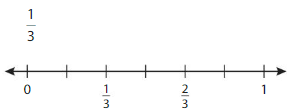
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{1}{3}\) is: \(\frac{3}{9}\)
Explanation:
The given number line is:
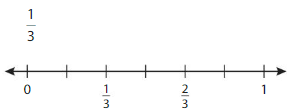
From the above number line,
The given fraction is: \(\frac{1}{3}\)
From the above number line,
Every 2 lines represent a value.
So,
if we divide the lines into 3 lines between the values, then we will get each line value with the denominator 9
So,
The number line for the equivalent fraction is:
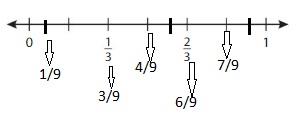
So, from the above number line,
We can say that the equivalent fraction of \(\frac{1}{3}\) is: \(\frac{3}{9}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that \(\frac{1}{3}\) = \(\frac{3}{9}\)
Question 9.
Open-Ended
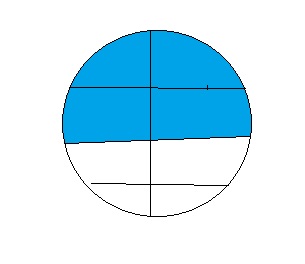
Write two equivalent fractions to describe the portion of the eggs that are white

Answer:
The two equivalent fractions to describe the portion of eggs that are white are:
\(\frac{6}{12}\) and \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation:
The given model is:

From the above model,
We can say that,
The number of colored eggs is: 6
The number of white eggs is: 6
So,
The total number of eggs are: 12
So,
The fraction form for the white eggs is = \(\frac{Number of white eggs}{Total number of eggs}\)
= \(\frac{6}{12}\)
Equivalent form for the white eggs:
Consider the colored eggs as 1 group and the white eggs as 1 group
So,
The number of White eggs is: 1
The number of colored eggs is: 1
So,
The total number of eggs are: 2
So,
The fraction that the eggs are white = \(\frac{Number of white eggs}{Total number of eggs}\)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can say that
The two equivalent fractions to describe the portion of eggs that are white are:
\(\frac{6}{12}\) and \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 10.
YOU BE THE TEACHER
Your friend says the models show equivalent fractions. Is your friend correct? Explain.
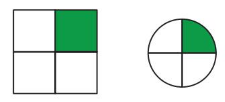
Answer: Yes, your friend is correct
Explanation:
Given models are:

Let the two models be named as 1st model and 2nd model.
So,
From the 1st model,
The total number of parts are: 4
The colored part is: 1
So,
The fraction form is: \(\frac{The colored part}{The total number of parts}\) = \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Now,
From the 2nd model,
The total number of parts are: 4
The colored part is: 1
So,
The fraction form is: \(\frac{The colored part}{The total number of parts}\) = \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the 2 fractions are equal and so, your friend is correct.
Think and Grow: Modeling Real Life
Example
You and your friend make braided paper bookmarks. Yours is \(\frac{2}{3}\) foot long. Your friend’s is \(\frac{7}{12}\) foot long. Are the bookmarks the same length?

Determine whether the fractions are equivalent. Plot the fractions on the same number line. Then compare.
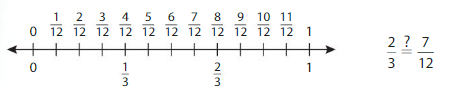
From the above number line,
we can observe that \(\frac{2}{3}\) is after the \(\frac{7}{12}\)
So,
\(\frac{2}{3}\) is greater than \(\frac{7}{12}\)
So,
The bookmarks do not have the same length.
Show and Grow
Question 11.
The lasagna pans are the same size. Are the amounts of lasagna left in the pans equal?
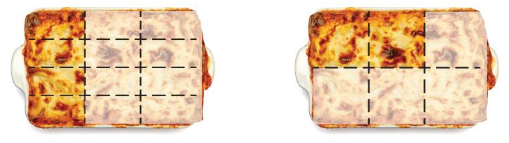
Answer: No, the amount of lasagna left in the pans are not equal
Explanation:
Given lasagna pans are:

Let the two lasagna pans be named as 1st model and 2nd model
From the first model,
The total number of parts are: 12
The number of parts that are occupied is: 4
The number of parts that are left is: 8
From the 2nd model,
The total number of parts are: 6
The number of parts that are occupied is: 2
The number of parts that are left is: 4
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the amount of lasagna left in the pans is not equal.
Question 12.
DIG DEEPER!
You run 3 laps around an outdoor track, where 4 laps are equal to 1 mile. Your friend runs 6 laps around the indoor track shown. Do you and your friend run the same distance? Explain.

Answer: Yes, you and your friend run the same distance.
Explanation:
Given that you run 3 laps around the outdoor track whereas for you, 4 laps is equal to 1 mile.
So,
The total distance covered by you = \(\frac{The number of laps that you run}{The number of laps that is equal to 1 mile}\)= \(\frac{3}{4}\)
It is also given that your friend runs 6 laps around the indoor track whereas, for your friend, 8 laps is equal to 1 mile.
So,
The total distance covered by your friend = \(\frac{The number of laps that your friend run}{The number of laps that is equal to 1 mile}\) = \(\frac{6}{8}\)
When \(\frac{3}{4}\) is multiplied and divide by 2 , we get \(\frac{6}{8}\)
So,
\(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{6}{8}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that you and your friend runs the same distance
Model Equivalent Fractions Homework & Practice 7.1
Use the model to find an equivalent fraction.
Question 1.

Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{3}{5}\) is: \(\frac{6}{10}\)
Explanation:
The given model is:

From the above model,
We can say that the fraction is: \(\frac{3}{5}\)
So,
The model for the Equivalent fraction is:
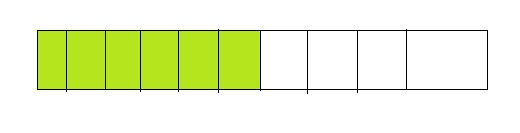
From the above model, we can say that the equivalent fraction is: \(\frac{6}{10}\)
So,
When we divide \(\frac{6}{10}\) by 2, we will get the equivalent value.
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that \(\frac{3}{5}\) = \(\frac{6}{10}\)
Question 2.
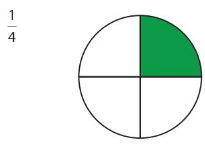
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{1}{4}\) is: \(\frac{2}{8}\)
Explanation:
The given model is:

From the above model, we can say that the fraction is: \(\frac{1}{4}\)
So,
The model for the equivalent fraction is:
From the above model,
So, we can say that the equivalent fraction is: \(\frac{2}{8}\)
So,
When \(\frac{1}{4}\) is multiplied and divided by 2, we can get the equivalent value.
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that \(\frac{1}{4}\) = \(\frac{2}{8}\)
Use a number line to find an equivalent fraction.
Question 3.
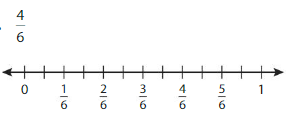
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{4}{6}\) is: \(\frac{8}{12}\)
Explanation:
The given Number line is:
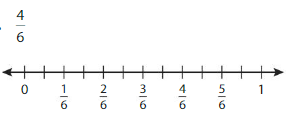
From the given number line,
we can see that every 2 lines represent a value.i.e., \(\frac{4}{6}\)
So, when there will be 2 lines between 2 values, then each line will become \(\frac{1}{12}\)
So,
The model for the equivalent fraction is:
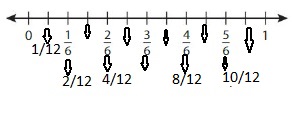
So, from the equivalent number line,
We can say that \(\frac{4}{6}\) is equal to \(\frac{8}{12}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that \(\frac{4}{6}\) = \(\frac{8}{12}\)
Question 4.
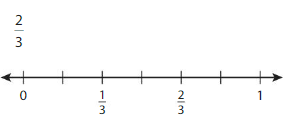
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{2}{3}\) is: \(\frac{4}{6}\)
Explanation:
The given number line is:
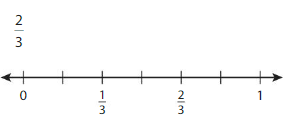
From the above number line,
we can say that 2 lines represent a value. i.e., \(\frac{2}{3}\)
So,
The value of each line when divided into 2 parts represent: \(\frac{1}{6}\)
So,
The equivalent number line is:
So, from the above equivalent number line,
We can see that \(\frac{2}{3}\) is equal to \(\frac{4}{6}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that \(\frac{2}{3}\) = \(\frac{4}{6}\)
Find the equivalent fraction.
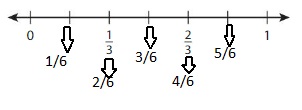
Question 5.
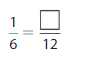
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{1}{6}\) is: \(\frac{2}{12}\)
Explanation:
When we multiply and divide \(\frac{1}{6}\) with 2, we will get the equivalent value of \(\frac{1}{6}\)
So,
![]()
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that \(\frac{1}{6}\) = \(\frac{2}{12}\)
Question 6.
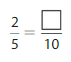
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{2}{5}\) is: \(\frac{4}{10}\)
Explanation:
When we multiply and divide \(\frac{2}{5}\) with 2, we will get the equivalent value of \(\frac{2}{5}\)
So,
![]()
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that \(\frac{2}{5}\) = \(\frac{4}{10}\)
Question 7.

Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{1}{4}\) is: \(\frac{2}{8}\)
Explanation:
When we multiply and divide \(\frac{1}{4}\) with 2, we will get the equivalent value of \(\frac{1}{4}\)
So,
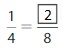
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that \(\frac{1}{4}\) = \(\frac{2}{8}\)
Question 8.
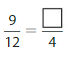
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{9}{12}\) is: \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Explanation:
When we divide the \(\frac{9}{12}\) by 3, we will get the equivalent value of \(\frac{9}{12}\)
So,
![]()
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that \(\frac{9}{12}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Question 9.
Which One Doesn’tBelong?
Which model does not belong with the other three? Explain
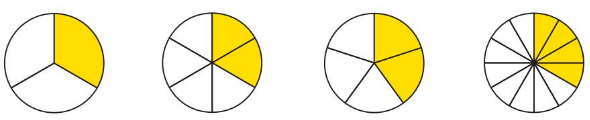
Answer:
Let the given figures be named as A), B), C) and D)
So,
from the fraction values, figure C) does not belong with the other three because the values of the denominators of A), B), D) are all the multiples of 3
Explanation:
There are 4 given figures.
Let it be named as A), B), C) and D)

From A),
The total number of parts are: 3
The colored part is: 1
So,
The fraction form is: \(\frac{The colored part}{The total number of parts}\) = \(\frac{1}{3}\)
From B),
The total number of parts are: 6
The colored part is: 3
So,
The fraction form is: \(\frac{The colored part}{The total number of parts}\) = \(\frac{3}{6}\)
From C),
The total number of parts are: 5
The colored part is: 2
So,
The fraction form is: \(\frac{The colored part}{The total number of parts}\) = \(\frac{2}{5}\)
From D),
The total number of parts are: 12
The colored part is: 4
So,
The fraction form is: \(\frac{The colored part}{The total number of parts}\) = \(\frac{4}{12}\)
Hence, from all the figures,
We can conclude that figure C) does not belong with the other three because the values of the denominators of A), B), D) are all the multiples of 3
Question 10.
Modeling Real Life
Your crayon is \(\frac{1}{6}\) foot long. Your friend’s crayon is \(\frac{3}{12}\) foot long. Are the crayons the same length?

Answer: No, the crayons are not of the same length because your crayon is shorter than the crayon of your friend.
Explanation:
Given that,
The length of your crayon is: \(\frac{1}{6}\) foot
The length of your friend’s crayon is: \(\frac{3}{12}\) foot
So,
When we compare \(\frac{1}{6}\) foot and \(\frac{3}{12}\) foot,
Now,
Multiply and divide \(\frac{1}{6}\) with 2, we will get \(\frac{2}{12}\) foot
So,
we can sayt that \(\frac{1}{6}\) foot is less than \(\frac{3}{12}\) foot
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the length of the crayons are not equal.
Review & Refresh
Find the product
Question 11.
5 × 437 = _______
Answer: 5 × 437 = 2,185
Explanation:
By using the partial products method,
5 × 437 = 5 × ( 400 + 30 + 7 )
= ( 5 × 400 ) + ( 5 × 30 ) + ( 5 × 7 )
= 2,000 + 150 + 35
= 2,185
Hence, 5 × 437 = 2,185
Question 12.
6,982 × 9 = _______
Answer: 6,982 × 9 = 62,838
Explanation:
By using the partial products method,
6,982 × 9 = ( 6,000 + 900 + 80 + 2 ) × 9
= ( 6,000 × 9 ) + ( 900 × 9 ) + ( 80 × 9 ) + ( 2 × 9 )
= 54,000 + 8,100 + 720 + 18
= 62,838
Hence, 6,982 × 9 = 62,838
Question 13.
8 × 708 = _______
Answer: 8 × 708 = 5,664
Explanation:
By using the partial products method,
8 × 708 = 8 × ( 700 + 8 )
= ( 8 × 700 ) + ( 8 × 8 )
= 5,600 + 64
= 5,664
Hence, 8 × 708 = 5,664
Lesson 7.2 Generate Equivalent Fractions by Multiplying
Explore and Grow
Shade the second model in each pair to show an equivalent fraction.Then write the fraction.
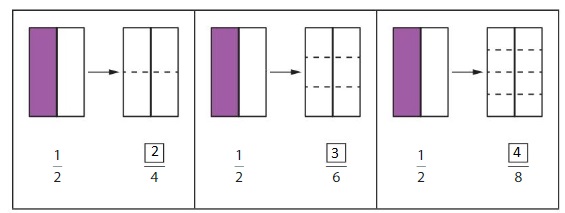
Describe the relationship between each pair of numerators and each pair of denominators.
Answer: From the three models, we can say that the equivalent fractions of the three models obtained by multiplying and dividing \(\frac{1}{2}\) with 2, 3 and 4
Hence,
In the first model,
\(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{2}{4}\)
In the second model,
\(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{3}{6}\)
In the third model,
\(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{4}{8}\)
Structure
How can you use multiplication to write equivalent fractions? Explain. Then use your method to find another fraction that is equivalent to \(\frac{1}{2}\).
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{1}{2}\) is: \(\frac{3}{6}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{3}{6}\)
Explanation:
We can multiply the given fraction by another fraction that have the same numerator and denominator to write equivalent fractions.
For example,
To write the equivalent fractions of \(\frac{1}{2}\), we can multiply so many fractions with the same numerator and denominator like \(\frac{2}{2}\), \(\frac{3}{3}\) etc.
Hence,
The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{1}{2}\) is: \(\frac{3}{6}\) or \(\frac{2}{4}\) or \(\frac{4}{8}\) or \(\frac{5}{10}\)
Think and Grow: Multiply to find Equivalent Fractions
You can find an equivalent fraction by multiplying the numerator and the denominator by the same number.
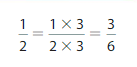
Example
Find an equivalent fraction for \(\frac{3}{5}\).
Show and Grow
Find an equivalent fraction.
Question 1.
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{5}{6}\) is: \(\frac{10}{12}\)
Explanation:
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So,
\(\frac{5}{6}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{2}{2}\)
Hence,
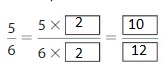
Question 2.
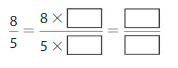
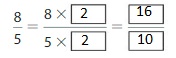
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{8}{5}\) is: \(\frac{16}{10}\)
Explanation:
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So,
\(\frac{8}{5}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{2}{2}\)
Hence,
Find the equivalent fraction.
Question 3.
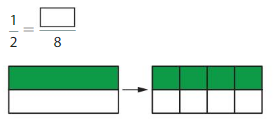
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{1}{2}\) is: \(\frac{4}{8}\)
Explanation:
The given model is:

The two models are the original model and its equivalent model.
So,
According to the models,
\(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{4}{8}\)
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So according to the Equivalet model,
\(\frac{1}{2}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{4}{4}\)
Hence,

Question 4.
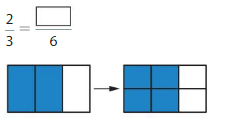
Answer: The equivalent fraction is: \(\frac{2}{3}\) is: \(\frac{4}{6}\)
Explanation:
The given model is:

The two models are the original model and the equivalent model.
So,
According to the models,
\(\frac{2}{3}\) = \(\frac{4}{6}\)
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So according to the Equivalent model,
\(\frac{1}{2}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{2}{2}\)
Hence,
![]()
Apply and Grow: Practice
Find the equivalent fraction.
Question 5.
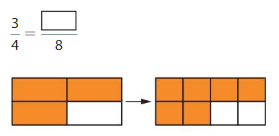
Answer: The equivalent model of \(\frac{3}{4}\) is: \(\frac{6}{8}\)
Explanation:
The given model is:

The two models are the original model and the equivalent model.
So,
According to the models,
\(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{6}{8}\)
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So according to the Equivalent model,
\(\frac{3}{4}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{2}{2}\)
Hence,
![]()
Question 6.
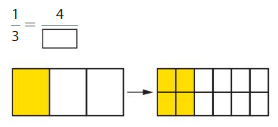
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{1}{3}\) is: \(\frac{4}{12}\)
Explanation:
The given model is:

The two models are the original model and the equivalent model.
So,
According to the models,
\(\frac{1}{3}\) = \(\frac{4}{12}\)
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So according to the Equivalent model,
\(\frac{1}{3}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{4}{4}\)
Hence,
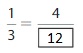
Question 7.

Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{9}{6}\) is: \(\frac{18}{12}\)
Explanation:
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So,
\(\frac{9}{6}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{2}{2}\)
Hence,
![]()
Question 8.

Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{7}{5}\) is: \(\frac{140}{100}\)
Explanation:
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So,
\(\frac{7}{5}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{20}{20}\)
Hence,
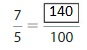
Find an equivalent fraction.
Question 9.
\(\frac{7}{6}\)
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{7}{6}\) is: \(\frac{14}{12}\)
Explanation:
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So,
\(\frac{7}{6}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{2}{2}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{7}{6}\) = \(\frac{14}{12}\)
Question 10.
\(\frac{10}{10}\)
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{10}{10}\) is: \(\frac{20}{20}\)
Explanation:
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So,
\(\frac{10}{10}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{2}{2}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{10}{10}\) = \(\frac{20}{20}\)
Question 11.
\(\frac{2}{4}\)
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{2}{4}\) is: \(\frac{4}{8}\)
Explanation:
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So,
\(\frac{2}{4}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{2}{2}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{2}{4}\) = \(\frac{4}{8}\)
Find two equivalent fractions.
Question 12.
\(\frac{5}{5}\)
Answer:
The two equivalent fractions of \(\frac{5}{5}\) are: \(\frac{10}{10}\) and \(\frac{15}{15}\)
Explanation:
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So,
\(\frac{5}{5}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{2}{2}\) and \(\frac{3}{3}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{5}{5}\) = \(\frac{10}{10}\) and \(\frac{15}{15}\)
Question 13.
\(\frac{4}{3}\)
Answer:
The two equivalent fractions of \(\frac{4}{3}\) are: \(\frac{8}{6}\) and \(\frac{12}{9}\)
Explanation:
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So,
\(\frac{4}{3}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{2}{2}\) and \(\frac{3}{3}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{4}{3}\) = \(\frac{8}{6}\) and \(\frac{12}{9}\)
Question 14.
\(\frac{1}{10}\)
Answer:
The two equivalent fractions of \(\frac{1}{10}\) are: \(\frac{2}{20}\) and \(\frac{3}{30}\)
Explanation:
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So,
\(\frac{1}{10}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{2}{2}\) and \(\frac{3}{3}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{1}{10}\) = \(\frac{2}{20}\) and \(\frac{3}{30}\)
Question 15.
Writing
Explain how \(\frac{1}{4}\) and \(\frac{2}{8}\) are equivalent using multiplication. Use models to support your answer.
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{1}{4}\) is: \(\frac{2}{8}\)
Explanation:
For the \(\frac{1}{4}\) and \(\frac{2}{8}\), the models are:
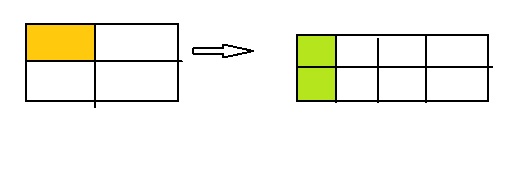
The two models are the original model and the equivalent model.
So,
According to the original model,
The total number of parts are: 4
The colored part is: 1
According to the Equivalent model,
The total number of parts are: 8
The colored part is: 2
Now,
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So,
When we multiply \(\frac{1}{4}\) with \(\frac{2}{2}\), we will get the \(\frac{2}{8}\) which is the equivalent value of \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Hence,
The equivalent value of \(\frac{1}{4}\) is: \(\frac{2}{8}\)
DIG DEEPER!
Write true or false for the statement. If false, explain why.
Question 16.
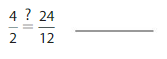
Answer: \(\frac{4}{2}\) = \(\frac{24}{12}\)
Explanation:
Given fractions are: \(\frac{4}{2}\) and \(\frac{24}{12}\)
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So,
When \(\frac{4}{2}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{6}{6}\), we will get \(\frac{24}{12}\) which is the equivalent value of \(\frac{4}{2}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{4}{2}\) = \(\frac{24}{12}\)
Question 17.
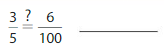
Answer: \(\frac{3}{5}\) is not equal to \(\frac{6}{100}\)
Explanation:
Given fractions are: \(\frac{3}{5}\) and \(\frac{6}{100}\)
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So,
When \(\frac{3}{5}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{2}{2}\), we will get \(\frac{6}{10}\) which is not the equivalent value of \(\frac{3}{5}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{3}{5}\) is not equal to \(\frac{6}{100}\)
Think and Grow: Modeling Real Life
Example
A recipe calls for \(\frac{3}{4}\) cup of oats. You only have a \(\frac{1}{8}\) cup measuring cup. What fraction of a cup of oats, in eighths,do you need? Use multiplication to write an equivalent fraction for \(\frac{3}{4}\) in eighths.


Show and Grow
Question 18.
You need \(\frac{1}{2}\) cup of water for a science experiment. You only have a \(\frac{1}{4}\) cup measuring cup. What fraction of a cup of water, in fourths, do you need?
Answer: You need \(\frac{2}{4}\), in fourths, of a cup of water
Explanation:
Given that you need \(\frac{1}{2}\) cup of water for a science experiment and you only have a \(\frac{1}{4}\) cup measuring cup.
So, in terms of \(\frac{1}{4}\), \(\frac{1}{2}\) can be written as:
\(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{1 × 2}{2 × 2}\)
= \(\frac{2}{4}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that we need \(\frac{2}{4}\) fraction of a cup of water, in fourths
Question 19.
A pedestrian needs to walk \(\frac{4}{5}\) mile to meet her goal. The path is marked at every tenth of a mile. What fraction of a mile, in tenths, should she walk?
Answer: She should walk \(\frac{8}{10}\), in tenths of a mile
Explanation:
Given that a pedestrian needs to walk \(\frac{4}{5}\) mile to meet her goal.
It is also given that the path is marked at every tenth of a mile.
So, in terms of \(\frac{1}{10}\), \(\frac{4}{5}\) can be written as:
\(\frac{4}{5}\) = \(\frac{4 × 2}{5 × 2}\)
= \(\frac{8}{10}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that she should walk \(\frac{8}{10}\), in tenths of a mile
Question 20.
DIG DEEPER!
You put together \(\frac{7}{10}\) of a puzzle. The puzzle has pieces. What fraction of the puzzle, in hundredths, is not put together? Explain.

Answer: The fraction of the puzzle not put together, in hundredths is: \(\frac{30}{100}\)
Explanation:
Given that you put together \(\frac{7}{10}\) of a puzzle.
So, from this, the part of the puzzle that is not put together is: \(\frac{3}{10}\)
We have to find the fraction of the puzzle that is not put together, in hundredths
So, in terms of \(\frac{1}{100}\), \(\frac{3}{10}\) can be written as:
\(\frac{3}{10}\) = \(\frac{3 × 10}{10 × 10}\)
= \(\frac{30}{100}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the fraction of the puzzle not put together, in hundredths is: \(\frac{30}{100}\)
Question 21.
You have \(\frac{3}{5}\) of a dollar in coins. What fraction of a dollar, in hundredths, do you have? Write one possible combination of coins that you have.

Answer: The fraction of a dollar in hundredths is: \(\frac{60}{100}\)
Explanation:
Given that you have \(\frac{3}{5}\) of a dollar in coins.
So, in terms of \(\frac{1}{100}\), \(\frac{3}{5}\) can be written as:
\(\frac{3}{5}\) = \(\frac{3 × 20}{5 × 20}\)
= \(\frac{60}{100}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the fraction of a dollar in hundredths is: \(\frac{60}{100}\)
Generate Equivalent Fractions by Multiplying Homework & Practice 7.2
Find an equivalent fraction.
Question 1.
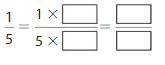
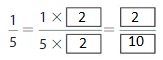
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{1}{5}\) is: \(\frac{2}{10}\)
Explanation:
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So,
\(\frac{1}{5}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{2}{2}\)
Hence,
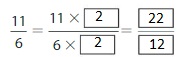
Question 2.
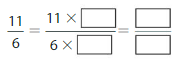
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{11}{6}\) is: \(\frac{22}{12}\)
Explanation:
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So,
\(\frac{11}{6}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{2}{2}\)
Hence,
Find an equivalent fraction.
Question 3.
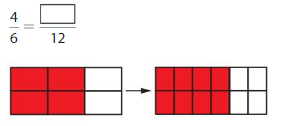
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{4}{6}\) is: \(\frac{8}{12}\)
Explanation:
The given model is:

The two models are the original model and its equivalent model.
So,
According to the models,
\(\frac{4}{6}\) = \(\frac{8}{12}\)
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So according to the Equivalent model,
\(\frac{4}{6}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{2}{2}\)
Hence,
![]()
Question 4.
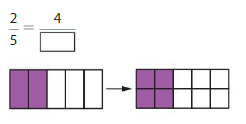
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{2}{5}\) is: \(\frac{4}{10}\)
Explanation:
The given model is:

The two models are the original model and its equivalent model.
So,
According to the models,
\(\frac{2}{5}\) = \(\frac{4}{10}\)
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So according to the Equivalent model,
\(\frac{2}{5}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{2}{2}\)
Hence,
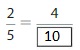
Question 5.

Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{3}{3}\) is: \(\frac{6}{6}\)
Explanation:
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So,
\(\frac{3}{3}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{2}{2}\)
Hence,
![]()
Question 6.

Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{7}{10}\) is: \(\frac{70}{100}\)
Explanation:
Explanation:
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So,
\(\frac{7}{10}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{10}{10}\)
Hence,
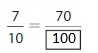
Find an equivalent fraction.
Question 7.
\(\frac{5}{3}\)
Answer: The equivalent value of \(\frac{5}{3}\) is: \(\frac{10}{6}\)
Explanation:
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So,
\(\frac{5}{3}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{2}{2}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{5}{3}\) = \(\frac{10}{6}\)
Question 8.
\(\frac{4}{4}\)
Answer: The equivalent value of \(\frac{4}{4}\) is: \(\frac{8}{8}\)
Explanation:
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So,
\(\frac{4}{4}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{2}{2}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{4}{4}\) = \(\frac{8}{8}\)
Question 9.
\(\frac{5}{10}\)
Answer: The equivalent value of \(\frac{5}{10}\) is: \(\frac{10}{20}\)
Explanation:
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So,
\(\frac{5}{10}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{2}{2}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{5}{10}\) = \(\frac{10}{20}\)
Find two equivalent fractions.
Question 10.
\(\frac{3}{2}\)
Answer:
The two equivalent fractions of \(\frac{3}{2}\) are: \(\frac{6}{4}\) and \(\frac{9}{6}\)
Explanation:
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So,
\(\frac{3}{2}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{2}{2}\) and \(\frac{3}{3}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{3}{2}\) = \(\frac{6}{4}\) and \(\frac{9}{6}\)
Question 11.
\(\frac{4}{10}\)
Answer:
The two equivalent fractions of \(\frac{4}{10}\) are: \(\frac{8}{20}\) and \(\frac{12}{30}\)
Explanation:
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So,
\(\frac{4}{10}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{2}{2}\) and \(\frac{3}{3}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{4}{10}\) = \(\frac{8}{20}\) and \(\frac{12}{30}\)
Question 12.
\(\frac{10}{5}\)
Answer:
The two equivalent fractions of \(\frac{10}{5}\) are: \(\frac{20}{10}\) and \(\frac{30}{15}\)
Explanation:
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So,
\(\frac{10}{5}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{2}{2}\) and \(\frac{3}{3}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{10}{5}\) = \(\frac{20}{10}\) and \(\frac{30}{15}\)
Question 13.
DIG DEEPER!
What is Descartes’s fraction?

Answer:
Question 14.
YOU BE THE TEACHER
Your friend says she can write a fraction equivalent to \(\frac{3}{4}\) that has a denominator of 10 and 4 and a whole number in the numerator. Is your friend correct? Explain.
Answer: Your friend is not correct
Explanation:
Given that your friend says she can write a fraction equivalent to \(\frac{3}{4}\) that has a denominator of 10 and 4 and a whole number in the numerator.
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So,
\(\frac{3}{4}\) will be multiplied with \(\frac{10}{25}\) to get the value of 10 in the denominator
\(\frac{3}{4}\) will be multiplied \(\frac{1}{1}\) to get the value of 4 in the denomintor.
So,
\(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{30}{100}\) But it is said this fraction has to ahve the denominator of 10 but we get the denominator of 100
Hence, from the above,
we can conclude that your friend is not correct
Question 15.
Modeling Real Life
A recipe calls for 1 teaspoon of cinnamon. You only have a \(\frac{1}{2}\) teaspoon measuring spoon. What fraction of a teaspoon of cinnamon, in halves, do you need?

Answer: You need \(\frac{1}{2}\) of a fraction of teaspoon, in halves
Explanation:
Given that a recipe calls for 1 teaspoon of cinnamon and you only have a \(\frac{1}{2}\) teaspoon measuring spoon.
So,
In terms of \(\frac{1}{2}\), we can write \(\frac{1}{2}\) as:
\(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{1× 1}{2 × 1}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that you need \(\frac{1}{2}\) of a fraction of teaspoon, in halves
Question 16.
A couple lives in Florida for \(\frac{1}{3}\) of the year. Each year has 12 months. What fraction of a year, in twelfths, does the couple live in Florida?
Answer: The couple lives in Florida for \(\frac{4}{12}\) of a year, in twelfths.
Explanation:
Given that a couple lives in Florida for \(\frac{1}{3}\) of the year.
It is also given that each year has 12 months
So,
In terms of \(\frac{1}{12}\), we can write \(\frac{1}{3}\) as:
\(\frac{1}{3}\) = \(\frac{1× 4}{3 × 4}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the couple lives in Florida for \(\frac{4}{12}\) of a year, in twelfths.
Review & Refresh
Divide. Then check your answer.
Question 17.
7√891
Answer: 891 ÷ 7 =127 R 2
Explanation:
By using the partial quotients method,
891 ÷ 7 = ( 840 + 49 ) ÷ 7
= ( 840 ÷ 7 ) + ( 49 ÷ 7 )
= 120 + 7
= 127 R 2
Hence, 891 ÷ 7 = 127 R 2
Question 18.
3√2,395
Answer: 2,395 ÷ 3 =798 R 1
Explanation:
By using the partial quotients method,
2,395 ÷ 3 = ( 2,100 + 180 + 39 + 72 + 3 ) ÷ 3
= ( 2,100 ÷ 3 ) + ( 180 ÷ 3 ) + ( 39 ÷ 3 ) + ( 72 ÷ 3 ) + ( 3 ÷ 3 )
=700 + 60 + 13 + 24 + 1
= 798 R 1
Hence, 2,395 ÷ 3 = 798 R 1
Question 19.
6√627
Answer: 627 ÷ 6 = 104 R 3
Explanation:
By using the partial quotients method,
627 ÷ 6 = ( 600 + 24 ) ÷ 6
= ( 600 ÷ 6 ) + ( 24 ÷ 6 )
= 100 + 4
= 104 R 3
Hence, 627 ÷ 6 = 104 R 3
Lesson 7.3 Generate Equivalent Fractions by Dividing
Explore and Grow
Shade the second model in each pair to show an equivalent fraction.Then write the fraction.
Describe the relationship between each pair of numerators and each pair of denominators.
Answer: The division of the fractions depends on the divisibility rules.
So,
When the numerator and denominator are even numbers, then they can only be divided by even numbers.
When the numerator and denominator are the multiples of 3, then they can only be divided by 3.
So, like these, we will divide the numerator and the denominator
Structure
How can you use division to write equivalent fractions? Explain and then use your method to find a fraction that is equivalent to \(\frac{6}{10}\).
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{6}{10}\) is: \(\frac{3}{5}\)
Explanation:
The division of the fractions depends on the divisibility rules of the numbers.
Now,
Divisibility rule of 2: If the one’s digit ends with 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, then that number is divisible by 2
So,
\(\frac{6}{10}\) has the numbers 6 and 10 which has the one’s digit of 6 and 0.
So,
We can divide the \(\frac{6}{10}\) by 2
So,
We will get ,
\(\frac{6}{10}=\frac{6 \div 2}{10 \div 2}=\frac{3}{5}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that from the above method, the equivalent of \(\frac{6}{10}\) is: \(\frac{3}{5}\)
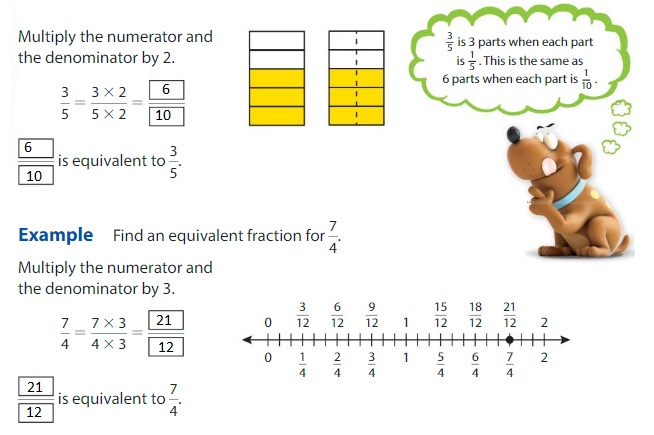
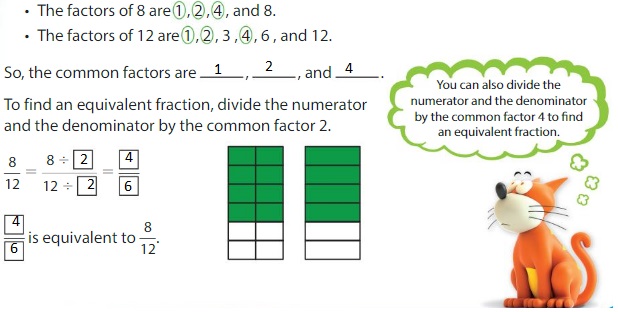
Think and Grow: Divide to Find Equivalent Fractions
A factor that is shared bytwo or more given numbers is a common factor. You can find an equivalent fraction by dividing the numerator and the denominator by a common factor.
\(\frac{2}{4}=\frac{2 \div 2}{4 \div 2}=\frac{1}{2}\)
Example
Find an equivalent fraction for \(\frac{8}{12}\) .
Find the common factors of 8 and 12.
Show and Grow
Find an equivalent fraction.
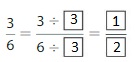
Question 1.
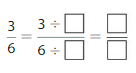
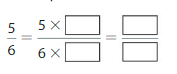
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{3}{6}\) is: \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is \(\frac{3}{6}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 3 and 6
3 and 6 are the multiples of 3.
So,
We have to divide the \(\frac{3}{6}\) with 3
So,
\(\frac{3}{6}=\frac{3 \div 3}{6 \div 3}=\frac{1}{2}\)
Hence,
Question 2.
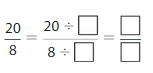
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{20}{8}\) is: \(\frac{10}{4}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is \(\frac{20}{8}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 20 and 8
20 and 8 are the multiples of 2.( SInce the one’s digit are 0 and 8)
So,
We have to divide the \(\frac{20}{8}\) with 2
So,
\(\frac{20}{8}=\frac{20 \div 2}{8 \div 2}=\frac{10}{4}\)
Hence,
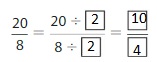
Find the equivalent fraction.
Question 3.
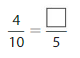
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{4}{10}\) is: \(\frac{2}{5}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is \(\frac{4}{10}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 4 and 10
4 and 10 are the multiples of 2.( SInce the one’s digit are 0 and 4)
So,
We have to divide the \(\frac{4}{10}\) with 2
So,
\(\frac{4}{10}=\frac{4 \div 2}{10 \div 2}=\frac{2}{5}\)
Hence,
![]()
Question 4.
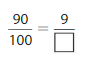
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{90}{100} is: [latex]\frac{9}{10}
Explanation:
The given fraction is [latex]\frac{90}{100}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 90 and 100
90 and 100 are the multiples of 10.
So,
We have to divide the \(\frac{90}{100}\) with 10
So,
\(\frac{90}{100}=\frac{90 \div 10}{100 \div 10}=\frac{9}{10}\)
Hence,
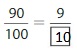
Question 5.
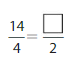
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{14}{4}\) is: \(\frac{7}{2}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is \(\frac{14}{4}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 14 and 4
14 and 4 are the multiples of 2. ( Since, the one’s digit is 4 )
So,
We have to divide the \(\frac{14}{4}\) with 2
So,
\(\frac{14}{4}=\frac{14 \div 2}{4 \div 2}=\frac{7}{2}\)
Hence,
![]()
Apply any Grow: Practice
Find the equivalent fraction.
Question 6.
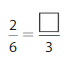
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{2}{6}\) is: \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is \(\frac{2}{6}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 2 and 6
2 and 6 are the multiples of 2. ( Since, the one’s digit is 2 and 6 )
So,
We have to divide the \(\frac{2}{6}\) with 2
So,
\(\frac{2}{6}=\frac{2 \div 2}{6 \div 2}=\frac{1}{3}\)
Hence,
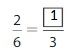
Question 7.
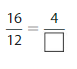
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{16}{12}\) is: \(\frac{4}{3}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is \(\frac{16}{12}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 16 and 12
16 and 12 are the multiples of 4.
So,
We have to divide the \(\frac{16}{12}\) with 4
So,
\(\frac{16}{12}=\frac{16 \div 4}{12 \div 4}=\frac{4}{3}\)
Hence,
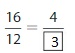
Question 8.
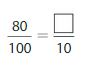
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{80}{100}\) is: \(\frac{8}{10}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is \(\frac{80}{100}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 80 and 100
80 and 100 are the multiples of 10.
So,
We have to divide the \(\frac{80}{100}\) with 10
So,
\(\frac{80}{100}=\frac{80 \div 10}{100 \div 10}=\frac{8}{10}\)
Hence,
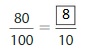
Question 9.
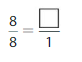
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{8}{8}\) is: \(\frac{1}{1}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is \(\frac{8}{8}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 8 and 8
8 and 8 are the multiples of 8.
So,
We have to divide the \(\frac{8}{8}\) with 8
So,
\(\frac{8}{8}=\frac{8 \div 8}{8 \div 8}=\frac{1}{1}\)
Hence,
Question 10.
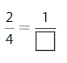
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{2}{4}\) is: \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is \(\frac{2}{4}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 2 and 4
2 and 4 are the multiples of 2.
So,
We have to divide the \(\frac{2}{4}\) with 2
So,
\(\frac{2}{4}=\frac{2 \div 2}{4 \div 2}=\frac{1}{2}\)
Hence,
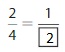
Question 11.
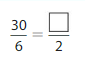
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{30}{6}\) is: \(\frac{10}{2}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is \(\frac{30}{6}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 30 and 6
30 and 6 are the multiples of 3. ( Since the sum of the digits of the numerator and the denominator are the multiples of 3 )
So,
We have to divide the \(\frac{30}{6}\) with 3
So,
\(\frac{30}{6}=\frac{30 \div 3}{6 \div 3}=\frac{10}{2}\)
Hence,
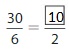
Find an equivalent fraction for the point on the number line.
Question 12.
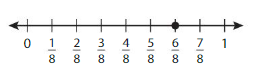
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{6}{8}\) is: \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Explanation:
The Given number line is:

In the given line, the point on the marked line is at \(\frac{6}{8}\)
So,
The numerator and denominator of \(\frac{6}{8}\) are: 6 and 8 which are the multiples of 2
So,
\(\frac{6}{8}\) is divided by 2
So,
\(\frac{6}{8}=\frac{6 \div 2}{8 \div 2}=\frac{3}{4}\)
Hence,
The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{6}{8}\) is: \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Question 13.
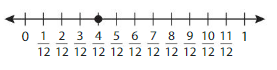
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{4}{12}\) is: \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Explanation:
The given number line is:
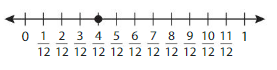
In the given line, the point on the marked line is at \(\frac{4}{12}\)
So,
The numerator and denominator of \(\frac{4}{12}\) are: 4 and 12 which are the multiples of 2
So,
\(\frac{4}{12}\) is divided by 2
So,
\(\frac{4}{12}=\frac{4 \div 2}{12 \div 2}=\frac{2}{6}\)
Hence,
The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{4}{12}\) is: \(\frac{2}{6}\)
Find an equivalent fraction.
Question 14.
\(\frac{3}{12}\)
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{3}{12}\) is: \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is \(\frac{3}{12}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 3 and 12
3 and 12 are the multiples of 3. ( Since the sum of the digits of the numerator and the denominator are the multiples of 3 )
So,
We have to divide the \(\frac{3}{12}\) with 3
So,
\(\frac{3}{12}=\frac{3 \div 3}{12 \div 3}=\frac{1}{4}\)
Hence,
The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{3}{12}\) is: \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Question 15.
\(\frac{18}{6}\)
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{18}{6}\) is: \(\frac{6}{2}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is \(\frac{18}{6}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 18 and 6
18 and 6 are the multiples of 3. ( Since the sum of the digits of the numerator and the denominator are the multiples of 3 )
So,
We have to divide the \(\frac{18}{6}\) with 3
So,
\(\frac{18}{6}=\frac{18 \div 3}{6 \div 3}=\frac{6}{2}\)
Hence,
The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{18}{6}\) is: \(\frac{3}{1}\)
Find two equivalent fractions.
Question 16.
\(\frac{20}{10}\)
Answer: The two equivalent fractions of \(\frac{20}{10}\) is: \(\frac{2}{1}\) and \(\frac{10}{5}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is \(\frac{20}{10}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 20 and 10
20 and 10 are the multiples of 10 and 2
So,
We have to divide the \(\frac{20}{10}\) with 10 and 2
So,
\(\frac{20}{10}=\frac{20 \div 10}{10 \div 10}=\frac{2}{1}\)
\(\frac{20}{10}=\frac{20 \div 2}{10 \div 2}=\frac{10}{5}\)
Hence,
The two equivalent fractions of \(\frac{20}{10}\) is: \(\frac{2}{1}\) and \(\frac{10}{5}\)
Question 17.
\(\frac{75}{100}\)
Answer: The two equivalent fractions of \(\frac{75}{100}\) is: \(\frac{15}{20}\) and \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is \(\frac{75}{100}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 75 and 100
75 and 100 are the multiples of 5 and 25 ( Since the one’s digit is 5 and 0 ).
So,
We have to divide the \(\frac{75}{100}\) with 5 and 25
So,
\(\frac{75}{100}=\frac{75 \div 5}{100 \div 5}=\frac{15}{20}\)
\(\frac{75}{100}=\frac{75 \div 25}{100 \div 25}=\frac{3}{4}\)
Hence,
The two equivalent fractions of \(\frac{75}{100}\) is: \(\frac{15}{20}\) and \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Question 18.
Reasoning
Your friend begins to divide the numerator and denominator of \(\frac{12}{6}\) by 4 and then gets stuck. Explain why your friend gets stuck.
Answer: The numerator and denominator of \(\frac{12}{6}\) is 12 and 6
when we find out the sum of the digits of the numerator and denominator, we find out that they are the multiples of 3.
So, we have to divide the \(\frac{12}{6}\) by 3 instead of 4
So, your friend get struck
Explanation:
The given fraction is: \(\frac{12}{6}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and the denominator are: 12 and 6
When we find the sum of the digits of the numerator and the denominator, we can find out that the sum of the digits is the multiples of 3.
So,
We have to divide \(\frac{12}{6}\) by 3 instead of 4
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that your friend is struck
Question 19.
DIG DEEPER!
Can you write an equivalent fraction with a lesser numerator and denominator when the numerator and denominator of a fraction are both odd numbers? Explain.
Answer:
Let the fraction with both the numerator and denominator odd numbers is: \(\frac{15}{9}\)
So,
The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{15}{9}\) is: \(\frac{5}{3}\)
Explanation:
Given that you have to write an equivalent fraction with a lesser numerator and denominator when the numerator and denominator of a fraction are both odd numbers.
Now,
Let the fraction with numerator and denominator odd numbers are: \(\frac{15}{9}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 15 and 9
15 and 9 are the multiples of 3 ( Since the sum of the digits is a multiple of 3 ).
So,
We have to divide the \(\frac{15}{9}\) with 3
So,
\(\frac{15}{9}=\frac{15 \div 3}{9 \div 3}=\frac{5}{3}\)
Hence,
The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{15}{9}\) is: \(\frac{5}{3}\)
Think and Grow: Modeling Real Life
Example
The Lechtal High Trail is a 100-kilometer hiking trail in Austria. A hiker has completed 70 kilometers of the trail. What fraction of the trail, in tenths, has the hiker completed?

Use the distances to write the fraction of the trail the hiker has completed.

Show and Grow
Question 20.
A puzzle cube has 54 stickers. Nine of the stickers are orange. A cube has 6 faces. What fraction of the stickers, in sixths, are orange?

Answer: The fraction of the stickers, in sixths, that are orange is: \(\frac{1}{6}\)
Explanation:
Given that a puzzle has 54 stickers and each cube has 6 faces.
It is also given that 9 of the stickers are orange.
So,
The fraction of the stickers that are in orange = The number of stickers that are in orange ÷ The total number of stickers
= 9 ÷ 54
=\(\frac{1}{6}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the fraction of the stickers, in sixths, that are orange are: \(\frac{1}{6}\)
Question 21.
There are 28 students in a class. Seven of the students pack their lunch. What fraction of the students, in fourths, pack their lunch?
Answer: The fraction of the students, in fourths that pack their lunch, is: \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Explanation:
It is given that there are 28 students in a class and 7 of the students pack their lunch.
So,
The fraction of students, in fourths, that pack their lunch = The number of students that pack their lunch ÷ The total number of students
= 7 ÷ 28
= \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the fraction of students, in fourths that pack their lunch, are: \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Question 22.
DIG DEEPER!
There are 45 apps on a tablet. Nine of the apps are games. What fraction of the apps, in fifths, are not games? Explain.
Answer: The fraction of the apps, in fifths that are not games, is: \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Explanation:
Given that there are 45 apps on a tablet and nine of the apps are games.
So,
The fraction, in fifths that are games = The number of apps that are games ÷ The total number of games
= 9 ÷ 45
= \(\frac{1}{5}\)
Now,
The fraction of the apps, in fifths that are not games = 1- ( \(\frac{1}{5}\) )
= ( 5 – 1 ) ÷ 5
= \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the fraction of apps, in fifths that are not games, is: \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Generate Equivalent Fractions by Dividing Homework & Practice 7.3
Find an equivalent fraction.
Question 1.
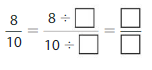
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{8}{10}\) is: \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is \(\frac{8}{10}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 8 and 10
8 and 10 are the multiples of 2. ( Since, the one’s digit is 8 and 0 )
So,
We have to divide the \(\frac{8}{10}\) with 2
So,
\(\frac{8}{10}=\frac{8 \div 2}{10 \div 2}=\frac{4}{5}\)
Hence,
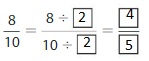
Question 2.
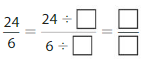
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{24}{6}\) is: \(\frac{8}{2}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is \(\frac{24}{6}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 24 and 6
24 and 6 are the multiples of 3. ( Since, the sum of the digits is the multiples of 3 )
So,
We have to divide the \(\frac{24}{6}\) with 3
So,
\(\frac{24}{6}=\frac{24 \div 3}{6 \div 3}=\frac{8}{2}\)
Hence,

Find the equivalent fraction.
Question 3.
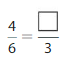
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{4}{6}\) is: \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is \(\frac{4}{6}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 4 and 6
4 and 6 are the multiples of 2. ( Since, the one’s digits are 4 and 6 )
So,
We have to divide the \(\frac{4}{6}\) with 2
So,
\(\frac{4}{6}=\frac{4 \div 2}{6 \div 2}=\frac{2}{3}\)
Hence,
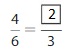
Question 4.
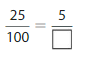
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{25}{100}\) is: \(\frac{5}{20}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is \(\frac{25}{100}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 25 and 100
25 and 100 are the multiples of 5. ( Since, the one’s digits are 5 and 0 )
So,
We have to divide the \(\frac{25}{100}\) with 5
So,
\(\frac{25}{100}=\frac{25 \div 5}{100 \div 5}=\frac{5}{20}\)
Hence,
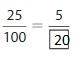
Find an equivalent fraction for the point on the number line.
Question 5.
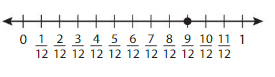
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{9}{12}\) is: \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Explanation:
The Given number line is:

In the given line, the point on the marked line is at \(\frac{9}{12}\)
So,
The numerator and denominator of \(\frac{9}{12}\) are: 9 and 12 which are the multiples of 3
So,
\(\frac{9}{12}\) is divided by 3
So,
\(\frac{9}{12}=\frac{9 \div 3}{12 \div 3}=\frac{3}{4}\)
Hence,
The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{9}{12}\) is: \(\frac{3}{4}\)
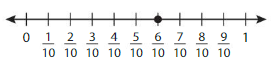
Question 6.
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{6}{10}\) is: \(\frac{3}{5}\)
Explanation:
The Given number line is:

In the given line, the point on the marked line is at \(\frac{6}{10}\)
So,
The numerator and denominator of \(\frac{6}{10}\) are: 6 and 10 which are the multiples of 2
So,
\(\frac{6}{10}\) is divided by 2
So,
\(\frac{6}{10}=\frac{6 \div 2}{10 \div 2}=\frac{3}{5}\)
Hence,
The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{6}{10}\) is: \(\frac{3}{5}\)
Find an equivalent fraction.
Question 7.
\(\frac{3}{6}\)
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{3}{6}\) is: \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is \(\frac{3}{6}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 3 and 6
3 and 6 are the multiples of 3. ( Since the the numerator and the denominator are the multiples of 3 )
So,
We have to divide the \(\frac{3}{6}\) with 3
So,
\(\frac{3}{6}=\frac{3 \div 3}{6 \div 3}=\frac{1}{2}\)
Hence,
The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{3}{6}\) is: \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 8.
\(\frac{8}{4}\)
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{8}{4}\) is: \(\frac{4}{2}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is \(\frac{8}{4}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 8 and 4
8 and 4 are the multiples of 2. ( Since the one’s digit is 8 and 4 )
So,
We have to divide the \(\frac{8}{4}\) with 2
So,
\(\frac{8}{4}=\frac{8 \div 2}{4 \div 2}=\frac{4}{2}\)
Hence,
The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{8}{4}\) is: \(\frac{4}{2}\)
Question 9.
\(\frac{15}{5}\)
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{15}{5}\) is: \(\frac{3}{1}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is \(\frac{15}{5}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 15 and 5
15 and 5 are the multiples of 5. ( Since the last digits are 5 )
So,
We have to divide the \(\frac{15}{5}\) with 5
So,
\(\frac{15}{5}=\frac{15 \div 5}{5 \div 5}=\frac{3}{1}\)
Hence,
The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{15}{5}\) is: \(\frac{3}{1}\)
Find two equivalent fractions.
Question 10.
\(\frac{4}{100}\)
Answer: The two equivalent fractions of \(\frac{4}{100}\) is: \(\frac{1}{25}\) and \(\frac{2}{50}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is \(\frac{4}{100}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 4 and 100
4 and 100 are the multiples of 2 and 4
So,
We have to divide the \(\frac{4}{100}\) with 4 and 2
So,
\(\frac{4}{100}=\frac{4 \div 2}{100 \div 2}=\frac{2}{50}\)
\(\frac{4}{100}=\frac{4 \div 4}{100 \div 4}=\frac{1}{25}\)
Hence,
The two equivalent fractions of \(\frac{4}{100}\) is: \(\frac{2}{50}\) and \(\frac{1}{25}\)
Question 11.
\(\frac{6}{6}\)
Answer: The two equivalent fractions of \(\frac{6}{6}\) is: \(\frac{1}{1}\) and \(\frac{2}{2}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is \(\frac{6}{6}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 6 and 6
6 and 6 are the multiples of 3 and 6
So,
We have to divide the \(\frac{6}{6}\) with 6 and 2
So,
\(\frac{6}{6}=\frac{6 \div 2}{6 \div 2}=\frac{3}{3}\)
\(\frac{6}{6}=\frac{6 \div 6}{6 \div 6}=\frac{1}{1}\)
Hence,
The two equivalent fractions of \(\frac{6}{6}\) is: \(\frac{1}{1}\) and \(\frac{3}{3}\)
Question 12.
\(\frac{24}{8}\)
Answer: The two equivalent fractions of \(\frac{24}{8}\) is: \(\frac{6}{2}\) and \(\frac{12}{4}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is \(\frac{24}{8}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 24 and 8
24 and 8 are the multiples of 4 and 2
So,
We have to divide the \(\frac{24}{8}\) with 4 and 2
So,
\(\frac{24}{8}=\frac{24 \div 4}{8 \div 4}=\frac{6}{2}\)
\(\frac{24}{8}=\frac{24 \div 2}{2 \div 2}=\frac{12}{4}\)
Hence,
The two equivalent fractions of \(\frac{24}{8}\) is: \(\frac{6}{2}\) and \(\frac{12}{4}\)
Question 13.
Writing
Explain how to find an equivalent fraction using division.
Answer:
Let the fraction be \(\frac{a}{b}\)
Let the equivalent fraction of \(\frac{a}{b}\) is: \(\frac{x}{y}\)
Let the number that divides \(\frac{a}{b}\) be p.
So,
Now, by using division,
\(\frac{a}{b}=\frac{a \div p}{b \div p}=\frac{x}{y}\)
Hence, like the above,
We can find th eequivalent fraction by using division.
Question 14.
Patterns
Describe and complete the pattern.
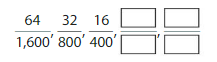
Answer: The remaining pattern is: \(\frac{8}{200}\) and \(\frac{4}{100}\)
Explanation:
The given pattern is:
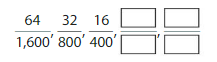
From the above pattern, we can say that the given pattern is divided by 2.
Now,
\(\frac{64}{1,600}=\frac{64 \div 2}{1,600 \div 2}=\frac{32}{800}\)
So, like the above,
The remaining two patterns will be:
\(\frac{16}{400}=\frac{16 \div 2}{400 \div 2}=\frac{8}{200}\)
\(\frac{8}{200}=\frac{8 \div 2}{200 \div 2}=\frac{4}{100}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude the pattern will be:
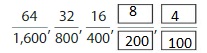
Question 15.
Modeling Real Life
A book shows100 hieroglyphic symbols. You have learned the meanings of 30 of them. What fraction of the symbols’ meanings, in tenths, have you learned?
Answer: The fraction of the symbols’ meaning, in tenths you have learned, is: \(\frac{3}{10}\)
Explanation:
Given that a book shows 100 hieroglyphic symbols
It is also given that you have learned the meanings of 30 of them.
So,
The fraction of the symbols’ meaning, in tenths, you have read = The number of meanings of the symbols’ you have learned ÷ The total number of symbols
= 30 ÷ 100
= \(\frac{3}{10}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the fraction of the symbols’ meaning, in tenths, you have learned is: \(\frac{3}{10}\)
Question 16.
DIG DEEPER!
There are 54 players in a beach volleyball club. Nine of the players cannot attend a game night. The coach needs to make even teams with the players that are there. What fraction of the players, in sixths, are at the game night?

Answer: The fraction of the players, in sixths, are at the game night is: \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Explanation:
Given that there are 54 players in a beach volleyball club.
It is also given that nine of the players can not attend a game night and also the coach needs to make even teams with the players that are there.
So,
The fraction of the players, in sixths, that are not in the game night = \(\frac{The number of players that are not in the game night}{The total number of players}\)
= \(\frac{9}{54}\)
So,
we have to divide \(\frac{9}{54}\) with 9 ( Since 9 and 54 are the multiples of 9 )
So,
\(\frac{9}{54}=\frac{9 \div 9}{54 \div 9}=\frac{1}{6}\)
So,
The fraction of players, in sixths, that attended a game night = 1 – \(\frac{1}{6}\)
= \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the fraction of the players, in sixths, that attended a game night is: \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Review & Refresh
Find the product. Check whether your answer is reasonable.
Question 17.
71 × 63 = _______
Answer: 71 × 63 = 4,473
Explanation:
Let 71 be rounded to 70
Let 63 be rounded to 65
So,
By using the place-value method,
70 × 65 = 7 tens × 65
= 455 tens
= 4,550
Hence, from the above 2 values 4,473 and 4,550,
We can conclude that the answer is not reasonable.
Question 18.
24 × 98 = _______
Answer: 24 × 98 = 2,352
Explanation:
Let 24 be rounded to 25
Let 98 be rounded to 100
So,
By using the place-value method,
25 × 100 = 10 tens × 25
= 250 tens
= 2,500
Hence, from the above 2 values 2,352 and 2,500,
We can conclude that the answer is not reasonable
Question 19.
85 × 27 = _______
Answer: 85 × 27 = 2,295
Explanation:
Let 27 be rounded to 25
So,
By using the partial products method,
85 × 25 = ( 80 + 5 ) × ( 20 + 5 )
= ( 80 × 20 ) + ( 80 × 5 ) + ( 5 × 20 ) + ( 5 × 5 )
= 1,600 + 400 + 100 + 25
= 2,125
Hence, from the above 2 values 2,295 and 2,125,
We can conclude that the answer is not reasonable
Lesson 7.4 Compare Fractions Using Benchmarks
Explore and Grow

Answer: 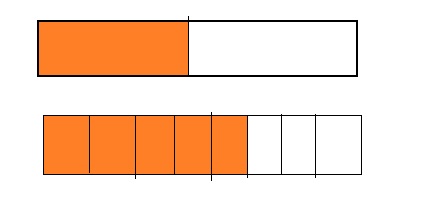
By using the above models,
5 is greater than half of the value of 8 i.e., 4
So,
We can conclude that \(\frac{5}{8}\) is greater than \(\frac{2}{5}\)
Structure
How does the numerator of a fraction compare tothe11denominator when the fraction is less than \(\frac{1}{2}\)? greater than \(\frac{1}{2}\) ? equal to \(\frac{1}{2}\)? Explain.
Answer:
Think and Grow: Compare Fractions Using Benchmarks
A benchmark is a commonly used number that you can use to compare other numbers. You can use the benchmarks \(\frac{1}{2}\) and 1 to help you compare fractions.

Example
Use fraction strips to compare \(\frac{7}{10}\) and \(\frac{3}{8}\).
Show and Grow
Compare. Use a model to help
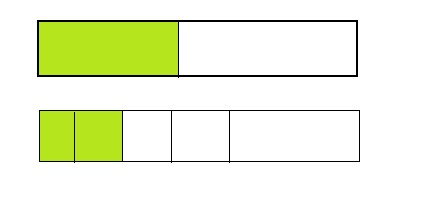
Question 1.
Answer: \(\frac{5}{12}\) is less than \(\frac{3}{5}\)
Explanation:
From the above model,
5 is less than half of the value of 12 i.e., 6
So,
We can conclude that \(\frac{5}{12}\) is less than \(\frac{3}{5}\)
Question 2.
Answer: \(\frac{3}{4}\) is equal to \(\frac{6}{8}\) which is the equivalent fraction of \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Explanation:
From the above model,
When we simplify \(\frac{6}{8}\) i.e., divide it by 2, we will get \(\frac{3}{4}\)
So,
We can conclude that \(\frac{3}{4}\) is equal to \(\frac{6}{8}\)
Question 3.
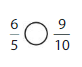
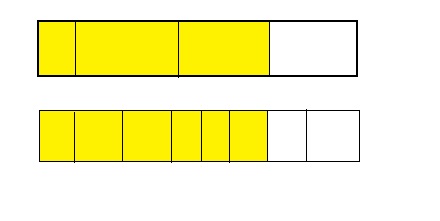
Answer: \(\frac{6}{5}\) is greater than \(\frac{9}{10}\)
Explanation:
From the above model,
6 is greater than half of the value of 5.
So,
We can conclude that \(\frac{6}{5}\) is greater than \(\frac{9}{10}\)
Apply and Grow: Practice
Compare. Use a model to help
Question 4.
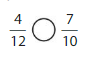
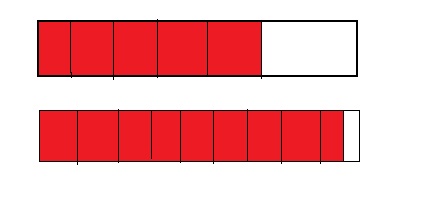
Answer: \(\frac{4}{12}\) is less than \(\frac{7}{10}\)
Explanation:
Given fractions are: \(\frac{4}{12}\) and \(\frac{7}{10}\)
Now,
From \(\frac{4}{12}\),
we can see that 4 is less than half of the value of 12 ie., 6
Hence,
We can conclude that \(\frac{4}{12}\) is less than \(\frac{7}{10}\)
Question 5.
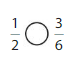
Answer: \(\frac{1}{2}\) is equal to \(\frac{3}{6}\) which is the equivalent fraction of \(\frac{3}{6}\)
Explanation:
Given fractions are: \(\frac{1}{2}\) and \(\frac{3}{6}\)
Now,
When we simplify \(\frac{3}{6}\), by divideing with 3, we will get \(\frac{1}{2}\)
So,
We can conclude that \(\frac{1}{2}\) isequal to \(\frac{3}{6}\) which is the equivalent fraction of
\(\frac{3}{6}\)
Question 6.
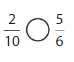
Answer: \(\frac{2}{10}\) is less than \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Explanation:
Given fractions are: \(\frac{2}{10}\) and \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Now,
From \(\frac{2}{10}\),
We can see that 2 is less than half of the value of 10 i.e., 5
So,
We can conclude that \(\frac{2}{10}\) is less than \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Question 7.
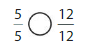
Answer: \(\frac{5}{5}\) is equal to \(\frac{12}{12}\)
Explanation:
Given fractions are: \(\frac{5}{5}\) and \(\frac{12}{12}\)
Now,
From \(\frac{5}{5}\),
We can see that the numerator and denominator are equal, so we will get the same result in both the numerator and the denominator
So,
We can conclude that \(\frac{5}{5}\) is equal to \(\frac{12}{12}\)
Question 8.
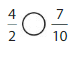
Answer: \(\frac{4}{2}\) is greater than \(\frac{7}{10}\)
Explanation:
Given fractions are: \(\frac{4}{2}\) and \(\frac{7}{10}\)
Now,
From \(\frac{4}{2}\),
We can see that 4 is greater than half of the value of 2.
So,
We can conclude that \(\frac{4}{2}\) is greater than \(\frac{7}{10}\)
Question 9.
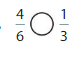
Answer: \(\frac{4}{6}\) is greater than \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Explanation:
Given fractions are: \(\frac{4}{6}\) and \(\frac{1}{3}\)
When we simplify \(\frac{4}{6}\), we will get \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Now,
From \(\frac{2}{3}\),
We can see that 2 is greater than half of the value of 3.
So,
We can conclude that \(\frac{4}{6}\) is greater than \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Question 10.
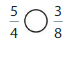
Answer: \(\frac{5}{4}\) is greater than \(\frac{3}{8}\)
Explanation:
Given fractions are: \(\frac{5}{4}\) and \(\frac{3}{8}\)
Now,
From \(\frac{5}{4}\),
We can say that 5 is greater than half of the value of 4 i.e., 2
So,
We can conclude that \(\frac{5}{4}\) is greater than \(\frac{3}{8}\)
Question 11.
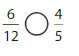
Answer: \(\frac{6}{12}\) is less than \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Explanation:
Given fractions are: \(\frac{6}{12}\) and \(\frac{4}{5}\)
When we simplify \(\frac{6}{12}\), we will get \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Now,
From \(\frac{4}{5}\),
We can say that 4 is greater than half of the value of 5
So,
We can conclude that \(\frac{6}{12}\) is less than \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Question 12.

Answer: \(\frac{3}{2}\) is greater than \(\frac{80}{100}\)
Explanation:
The given fractions are: \(\frac{3}{2}\) and \(\frac{80}{100}\)
When we simplify \(\frac{80}{100}\) by dividing with 20, we will get \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Now,
From \(\frac{3}{2}\),
We can say that 3 is greater than half of the value of 2 i.e., 1
So,
We can conclude that \(\frac{3}{2}\) is greater than \(\frac{80}{100}\)
Question 13.
A black bear hibernates for \(\frac{7}{12}\) of 1 year. A bat hibernates for \(\frac{1}{4}\) of 1 year. Which animal hibernates longer? How do you know?
Answer: The black bear hibernates for a longer time than the bat
Explanation:
It is given that a black bear hibernates for \(\frac{7}{12}\) of 1 year and a bat hibernates for \(\frac{1}{4}\) of 1 year.
So,
The time that a black bear hibernates is: \(\frac{7}{12}\) of 1 year
The time that a bat hibernates is: \(\frac{1}{4}\) of 1 year
So,
To make the total time 1 year, we have to multiply \(\frac{1}{4}\) with \(\frac{3}{3}\)
So,
\(\frac{1}{4}\) = \(\frac{3}{12}\)
Hence,
When we compare \(\frac{7}{12}\) and \(\frac{3}{12}\),
We can conclude that a black bear hibernates for a long time.
Question 14.
Writing
Explain how you can tell whether a fraction is greater than, less than, or equal to1, just by looking at the numerator and the denominator
Answer: We will compare the numerator with half of the value of the denominator. In this way, we will determine the relationship between the fractions.
Now,
Let the 2 fractions be \(\frac{a}{b}\) and \(\frac{x}{y}\)
So,
Compare the first fraction’s a and b
When a > ( b / 2 ), \(\frac{a}{b}\) > \(\frac{x}{y}\)
When a < ( b / 2 ), \(\frac{a}{b}\) < \(\frac{x}{y}\)
When a = ( b / 2 ), \(\frac{a}{b}\) = \(\frac{x}{y}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that we can compare the two fractions just by looking at the numerator and the denominator
Question 15.
DIG DEEPER.!
You and your friend pack lunch. You eat \(\frac{2}{6}\) of your lunch. Your friend eats \(\frac{3}{4}\) of his lunch. Can you tell who ate more? Explain.
Answer: Your friend ate more lunch than you
Explanation:
Given that you and your friend pack lunch.
It is also given that you eat \(\frac{2}{6}\) of your lunch and your friend eats \(\frac{3}{4}\) of his lunch.
So,
The amount of lunch you ate = \(\frac{2}{6}\)
By simplifying \(\frac{2}{6}\) i.e., dividing by 2, we will get \(\frac{1}{3}\)
So,
The amount of lunch you ate = \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Now,
The amount of lunch your friend ate = \(\frac{3}{4}\)
So, when we compare \(\frac{1}{3}\) and \(\frac{3}{4}\),
Now,
From \(\frac{1}{3}\),
1 is less than half of the value of the 3
From \(\frac{3}{4}\),
3 is greater than half of the value of 4
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that your friend ate more than you
Think and Grow: Modeling Real Life
Example
You have \(\frac{3}{5}\) of a bottle of blue paint and \(\frac{7}{8}\) of a bottle of yellow paint. Do you have enough of each paint color to make the recipe? Explain.

Compare each fraction of a paint bottle to the benchmark \(\frac{1}{2}\).
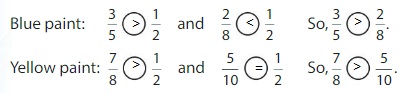
So,
You have enough of each paint color to make the recipe.
Show and Grow
Question 16.
You have \(\frac{3}{8}\) tablespoon of baking soda, \(\frac{2}{3}\) tablespoon of contact lens solution, and \(\frac{5}{3}\) cups of glue. Do you have enough of each ingredient to make the recipe? Explain.

Answer: You have enough ingredients of contact lens solution and glue.
Explanation:
It is given that you have \(\frac{3}{8}\) tablespoon of baking soda, \(\frac{2}{3}\) tablespoon of contact lens solution, and \(\frac{5}{3}\) cups of glue.
But it is given that

So, when we compare the two values,
For the tablespoon of baking soda,
\(\frac{3}{8}\) is less than \(\frac{3}{4}\)
For the tablespoon of contact lens solution,
\(\frac{2}{3}\) is less than \(\frac{3}{2}\)
For the tablespoon of glue,
\(\frac{5}{3}\) is greater than \(\frac{6}{8}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that you have enough ingredients to make the recipe.
Question 17.
DIG DEEPER!
You and your friend are making posters for a science fair. The posters are the same size. Your poster has 8 equal parts and you are halfway done. Your friend’s poster has 12 equal parts. Your friend has completed \(\frac{9}{12}\) of her poster. Who has a greater amount of posters left to complete?
Answer: You have a greater amount of posters left to complete
Explanation:
Given that you and your friend are making posters for a science fair and the posters are the same size.
Given that,
Your poster has 8 equal parts and you are halfway done.
So,
The representation of your work is: \(\frac{4}{8}\)
The simple form of \(\frac{4}{8}\) is: \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Now,
It is also given that your friend’s poster has 12 equal parts and you have completed \(\frac{9}{12}\) of her poster.
So,
The representation of your friend’s work is: \(\frac{9}{12}\)
The simplified form of \(\frac{9}{12}\) is: \(\frac{3}{4}\)
So,
The amount of work left by you is: \(\frac{1}{2}\)
The amount of work left by your friend is: \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that you have a greater amount of posters left to complete.
Compare Fractions Using Benchmarks Homework & Practice 7.4
Compare. Use a model to help.
Question 1.
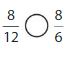
Answer: \(\frac{8}{12}\) is less than \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Explanation:
The given fractions are: \(\frac{8}{12}\) and \(\frac{8}{6}\)
Now,
The simple form of \(\frac{8}{12}\) is: \(\frac{2}{3}\)
The simple form of \(\frac{8}{6}\) is: \(\frac{4}{3}\)
So,
When we compare \(\frac{2}{3}\) and \(\frac{4}{3}\),
We can say that \(\frac{2}{3}\) is less than \(\frac{4}{3}\)
Question 2.
Answer: \(\frac{9}{10}\) is greater than \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Explanation:
The given fractions are: \(\frac{9}{10}\) and \(\frac{1}{3}\)
For \(\frac{9}{10}\) and \(\frac{1}{3}\)
When we compare 9 with half of the value of 10 i.e., 5, and when we compare 1 with half of the value of 3,
We will conclude that \(\frac{9}{10}\) is greater than \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Question 3.
Answer: \(\frac{5}{2}\) is greater than \(\frac{7}{8}\)
Explanation:
The given fractions are: \(\frac{5}{2}\) and \(\frac{7}{8}\)
For \(\frac{5}{2}\) and \(\frac{7}{8}\)
When we compare 5 with half of the value of 2 i.e., 1, and when we compare 7 with half of the value of 8,
We will conclude that \(\frac{5}{2}\) is greater than \(\frac{7}{8}\)
Question 4.
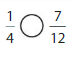
Answer: \(\frac{1}{4}\) is less than \(\frac{7}{12}\)
Explanation:
The given fractions are: \(\frac{1}{4}\) and \(\frac{7}{12}\)
For \(\frac{1}{4}\) and \(\frac{7}{12}\)
When we compare 1 with half of the value of 4 i.e., 2, and when we compare 7 with half of the value of 6,
We will conclude that \(\frac{1}{4}\) is less than \(\frac{7}{1}\)
Question 5.
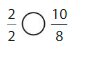
Answer: \(\frac{2}{2}\) is less than \(\frac{10}{8}\)
Explanation:
The given fractions are: \(\frac{2}{2}\) and \(\frac{10}{8}\)
For \(\frac{2}{2}\) and \(\frac{10}{8}\)
When we compare 2 with the value of 2, and when we compare 10 with half of the value of 8,
We will conclude that \(\frac{2}{2}\) is less than \(\frac{10}{8}\)
Question 6.
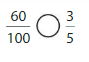
Answer: \(\frac{60}{100}\) is equal to \(\frac{3}{5}\)
Explanation:
The given two fractions are: \(\frac{60}{100}\) and \(\frac{3}{5}\)
When we simplify (i.e., divide by 20) \(\frac{60}{100}\), we will get \(\frac{3}{5}\)
So,
When we compare the two fractions,
We will conclude that \(\frac{60}{100}\) is equal to \(\frac{3}{5}\)
Question 7.
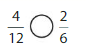
Answer: \(\frac{4}{12}\) is equal to \(\frac{2}{6}\)
Explanation:
The two given fractions are: \(\frac{4}{12}\) and \(\frac{2}{6}\)
When \(\frac{4}{12}\) is divided by 4, we will get \(\frac{1}{3}\)
When \(\frac{2}{6}\) is divided by 2, we will get \(\frac{1}{3}\)
So, when we compare the two fractions,
We will conclude that the two fractions are equal.
Question 8.
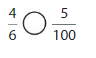
Answer: \(\frac{4}{6}\) is greater than \(\frac{5}{100}\)
Explanation:
The given two fractions are: \(\frac{4}{6}\) and \(\frac{5}{100}\)
When \(\frac{4}{6}\) is divided by 2, we will get \(\frac{2}{3}\)
When \(\frac{5}{100}\) is divided by 5, we will get \(\frac{1}{20}\)
So,
When we compare 2 with half of the value of 3,
We will conclude that \(\frac{4}{6}\) is greater than \(\frac{5}{100}\)
Question 9.
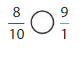
Answer: \(\frac{8}{10}\) is less than \(\frac{9}{1}\)
Explanation:
The given two fractions are: \(\frac{8}{10}\) and \(\frac{9}{1}\)
When we cross multiply the two fractions, i.e., 8 × 1 and 9 × 10,
We will get the values of 8 and 90,
So, from the above,
We will conclude that \(\frac{8}{10}\) is less than \(\frac{9}{1}\)
Question 10.
In a litter of kittens, \(\frac{3}{4}\) are white, and \(\frac{2}{8}\) are gray. Are there more white or more gray kittens?

Answer: There are more white kittens than grey kittens
Explanation:
Given that,
The number of white kittens are: \(\frac{3}{4}\)
The number of gray kittens are: \(\frac{2}{8}\)
Simplify \(\frac{2}{8}\) by dividing it with 2
So,
\(\frac{2}{8}\) = \(\frac{1}{4}\)
So,
The number of white kittens are: \(\frac{1}{4}\)
The number of gray kittens are: \(\frac{3}{4}\)
So,
When we compare the number of white and gray kittens,
We will conclude that white kittens are more than gray kittens
Open-Ended
Complete the statement.
Question 11.
Answer: The missing fraction is: \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is: \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Let the missing fraction be: \(\frac{1}{3}\)
So,
When we compare the 2 fractions by cross multiplying the two fractions,
We will conclude that
Question 12.
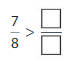
Answer: The missing fraction is:\(\frac{5}{8}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is: \(\frac{7}{8}\)
Let the missing fraction be: \(\frac{5}{8}\)
So,
When we compare the two fractions by cross multiplying the two fractions,
We will conclude that
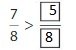
Question 13.
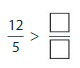
Answer: The missing fraction is: \(\frac{2}{5}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is: \(\frac{12}{5}\)
Let the missing fraction be: \(\frac{2}{5}\)
So,
When we compare the two fractions by cross multiplication,
We will conclude that
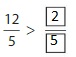
Question 14.
Number Sense
Which statements are true

Answer:
Let the given statements be named as A), B), ) and D)
So,
From these four statements, A), B) statements are true
Explanation:
Let the four statements be named as: A), B), C) and D)
Now, the given statements are:

Cross multiply each statement
So,
From A), we will get 48 >15
From B), we will get 100 >48
From C), we will get 12 < 9
From D), we will get 8 < 8
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that A) and B) statements are true
Question 15.
Modeling Real Life
You have \(\frac{1}{3}\) cup of oranges and \(\frac{5}{4}\) cups of strawberries. Do you have enough of each ingredient to make the smoothie? Explain.

Answer: We have only enough strawberries ingredient
Explanation:
The given recipe is:

It is also given that you have \(\frac{1}{3}\) cup of oranges and \(\frac{5}{4}\) cups of strawberries.
But, from the recipe,
It is given that \(\frac{3}{2}\) cup of oranges and \(\frac{7}{8}\) cups of strawberries.
So,
When we compare \(\frac{1}{3}\) and \(\frac{3}{2}\) cup of oranges, we can say that we have less amount of oranges to make the recipe.
When we compare \(\frac{5}{4}\) and \(\frac{7}{8}\) cups of strawberries, we can say that we have enough amount of strawberries to make the recipe.
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that we have only enough strawberry ingredients to make the recipe.
Question 16.
DIG DEEPER!
Newton and Descartes are picking apples at a farm. Newton’s bag of 4apples weighs \(\frac{4}{5}\) pound. Descartes’s bag weighs \(\frac{3}{2}\) pounds. How much money will Newton and Descartes each pay for their bag of apples?

Answer: The amount of money will Newton and Descartes each pay for their bag of apples is: $301
Explanation:
It is given that Newton and Descartes are picking apples at a farm.
It is also given that Newton’s bag of 4 apples weighs \(\frac{4}{5}\) pound.

So,
\(\frac{4}{5}\) is in between \(\frac{1}{2}\) pound and 1 pound
So,
As per the figure, the pice of Newton’s bag is: $75
So,
The amount paid by Newton = 4 × 75 = $300
It is also given that Descartes’s bag weighs \(\frac{3}{2}\) pounds.
So,
\(\frac{3}{2}\) is greater than 1 pound
So,
The amount paid by Descartes is: $1
Hence, from the above,
The amount paid by Newton and Descartes = 300 + 1 = $301
Review & Refresh
Find the factor pairs for the number.
Question 17.
12
Answer: The factor pairs of 12 are: 1 and 12, 2 and 6, 3 and 4
Explanation:
Factors are the numbers that divide the original number completely.
Hence,
The factor pairs of 12 are: 1 × 12, 2 × 6, 3 × 4
Question 18.
50
Answer: The factor pairs of 50 are: 1 and 50, 2 and 25, 5 and 10
Explanation:
Factors are the numbers that divide the original number completely.
Hence,
The factor pairs of 50 are: 1 × 50, 2 × 25, 5 × 10
Question 19.
17
Answer: The factor pairs of 17 are: 1 and 17, 17 and 1
Explanation:
Factors are the numbers that divide the original number completely.
hence,
The factor pairs of 17 are: 1 × 17, 17 × 1
Lesson 7.5 Compare Fractions
Explore and Grow
Shade each pair of models to compare \(\frac{1}{3}\) and \(\frac{5}{12}\). Explain how each pair of models helps you compare the fractions differently.
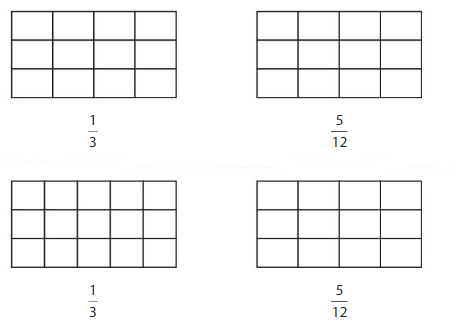
Answer:
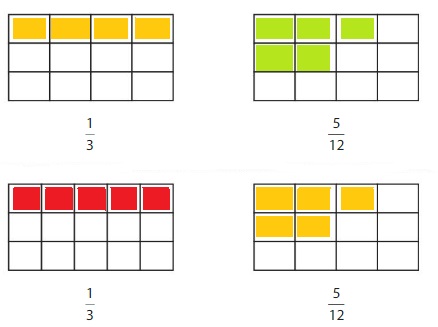
From the first pattern,
The first fraction is:
\(\frac{1}{3}\) = \(\frac{4}{12}\)
The second fraction is: \(\frac{5}{12}\)
By comparing the two fractions’ numerators,
We can conclude that \(\frac{4}{12}\) is less than \(\frac{5}{12}\)
From the second pattern,
The first fraction is:
\(\frac{1}{3}\) = \(\frac{5}{15}\)
The second fraction is: \(\frac{5}{12}\)
By comparing the two fractions’ denominators,
We can conclude that \(\frac{5}{15}\) is greater than \(\frac{5}{12}\)
Reasoning
How can you use equivalent fractions to compare fractions with different numerators and different denominators?
Answer:
We can use the equivalent fractions to compare the different numerators and different denominators by making either both the fractions’ numerators or both the fractions’ denominators.
Think and Grow: Compare Fractions
Example
Compare \(\frac{3}{5}\) and \(\frac{9}{10}\).
One Way:
Use a like denominator. Find an equivalent fraction for \(\frac{3}{5}\) that has a denominator of 10.
Multiply the numerator and the denominator of \(\frac{3}{5}\) by 2

Another Way:
Use a like numerator. Find an equivalent fraction for \(\frac{3}{5}\) that has a numerator of 10.
Multiply the numerator and the denominator of \(\frac{3}{5}\) by 3
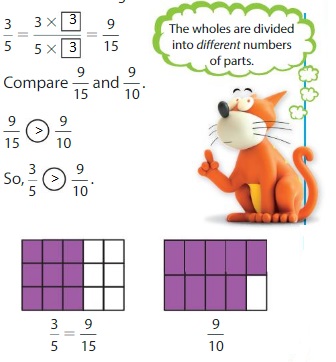
Show and Grow
Compare. Use a model to help.
Question 1.
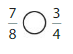
Answer: \(\frac{7}{8}\) is greater than \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Explanation:
The given fractions are: \(\frac{7}{8}\) and \(\frac{3}{4}\)
So,
Let make the denominator of the two fractions equal so that we can compare the numerators
To make the denominators equal, multiply the second fraction with 2
So,
\(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{6}{8}\)
So, when we compare the 2 fractions,
We can conclude that \(\frac{7}{8}\) is greater than \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Question 2.
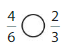
Answer: \(\frac{4}{6}\) is equal to \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Explanation:
The given fractions are: \(\frac{4}{6}\) and \(\frac{2}{3}\)
So,
Let make the denominator of the two fractions equal so that we can compare the numerators
To make the denominators equal, multiply the second fraction with 2
So,
\(\frac{2}{3}\) = \(\frac{4}{6}\)
So, when we compare the 2 fractions,
We can conclude that \(\frac{4}{6}\) is equal to \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Question 3.
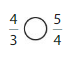
Answer: \(\frac{4}{3}\) is greater than \(\frac{5}{4}\)
Explanation:
The given fractions are: \(\frac{4}{3}\) and \(\frac{5}{4}\)
So,
Let make the denominator of the two fractions equal so that we can compare the numerators
To make the denominators equal, multiply the first fraction with 4 and the second fraction with 3
So,
\(\frac{4}{3}\) = \(\frac{16}{12}\)
\(\frac{5}{4}\) = \(\frac{15}{12}\)
So, when we compare the 2 fractions,
We can conclude that \(\frac{4}{3}\) is greater than \(\frac{5}{4}\)
Apply and Grow: Practice
Compare. Use a model to help
Question 4.
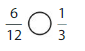
Answer: \(\frac{56}{12}\) is greater than \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Explanation:
The given fractions are: \(\frac{6}{12}\) and \(\frac{1}{3}\)
So,
Let make the denominator of the two fractions equal so that we can compare the numerators
To make the denominators equal, multiply the second fraction with 4
So,
\(\frac{1}{3}\) = \(\frac{4}{12}\)
So, when we compare the 2 fractions,
We can conclude that \(\frac{6}{12}\) is greater than \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Question 5.
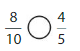
Answer: \(\frac{8}{10}\) is equal to \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Explanation:
The given fractions are: \(\frac{8}{10}\) and \(\frac{4}{5}\)
So,
Let make the denominator of the two fractions equal so that we can compare the numerstors
To make the denominators equal, multiply the second fraction with 2
So,
\(\frac{4}{5}\) = \(\frac{8}{10}\)
So, when we compare the 2 fractions,
We can conclude that \(\frac{8}{10}\) is equal to \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Question 6.
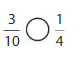
Answer: \(\frac{3}{10}\) is greater than \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Explanation:
The given two fractions are: \(\frac{3}{10}\) and \(\frac{1}{4}\)
So,
Let make the denominators equal so that we can compare the numerators
So,
To make the denominators equal, multiply the first fraction with 4 and the second fraction with 10
So,
\(\frac{3}{10}\) = \(\frac{12}{40}\)
\(\frac{1}{4}\) = \(\frac{10}{40}\)
So, when we compare the 2 fractions,
We can conclude that \(\frac{3}{10}\) is greater than \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Question 7.
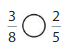
Answer: \(\frac{3}{8}\) is less than \(\frac{2}{5}\)
Explanation:
The given two fractions are: \(\frac{3}{8}\) and \(\frac{2}{5}\)
So,
Let make the denominators equal so that we can compare the numerators
So,
To make the denominators equal, multiply the first fraction with 5 and the second fraction with 8
So,
\(\frac{3}{8}\) = \(\frac{15}{40}\)
\(\frac{2}{5}\) = \(\frac{16}{40}\)
So, when we compare the 2 fractions,
We can conclude that \(\frac{3}{8}\) is less than \(\frac{2}{5}\)
Question 8.
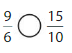
Answer: \(\frac{9}{6}\) is equal to \(\frac{15}{10}\)
Explanation:
The given two fractions are: \(\frac{9}{6}\) and \(\frac{15}{10}\)
So,
Let make the denominators equal so that we can compare the numerators
So,
To make the denominators equal, multiply the first fraction with 10 and the second fraction with 6
So,
\(\frac{9}{6}\) = \(\frac{90}{60}\)
\(\frac{15}{10}\) = \(\frac{90}{60}\)
So, when we compare the 2 fractions,
We can conclude that \(\frac{9}{6}\) is equal to \(\frac{15}{10}\)
Question 9.
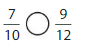
Answer: \(\frac{7}{10}\) is less than \(\frac{9}{12}\)
Explanation:
The given two fractions are: \(\frac{7}{10}\) and \(\frac{9}{12}\)
So,
Let make the denominators equal so that we can compare the numerators
So,
To make the denominators equal, multiply the first fraction with 12 and the second fraction with 10
So,
\(\frac{7}{10}\) = \(\frac{84}{120}\)
\(\frac{9}{12}\) = \(\frac{90}{120}\)
So, when we compare the 2 fractions,
We can conclude that \(\frac{7}{10}\) is less than \(\frac{9}{12}\)
Question 10.
Writing
Explain why writing fractions with like denominators or like numerators is helpful when comparing them.
Answer: If we write the fractions with the like numerators and like denominators, then the comparison will be easy when we do the cross multiplication of the fractions.
Explanation:
\(\frac{1}{2}\) is less than \(\frac{3}{4}\)
So, to make the like denominators, multiply the first fraction with 2
So, \(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{2}{4}\)
Since the denominators are equal, compare the numerstors and we will get the conclusion \(\frac{1}{2}\) is less than \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Question 11.
DIG DEEPER!
Use the fractions and symbols to make two true statements.
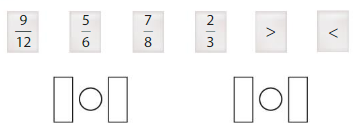
Answer:
The two statements are:
\(\frac{9}{12}\) < \(\frac{5}{6}\)
\(\frac{7}{8}\) > \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Explanation:
Given pattern is:

Given fractions from the above are:
\(\frac{9}{12}\), \(\frac{5}{6}\), \(\frac{7}{8}\) and \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Now, first take the 2 fractions for comparison.
The 2 fractions are: \(\frac{9}{12}\), \(\frac{5}{6}\)
So, to make the denominators of these 2 fractions equal, multiply the second fraction with 2
So,
\(\frac{5}{6}\) = \(\frac{10}{12}\)
Hence,
The first statement is:
\(\frac{9}{12}\) < \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Now, take the remaining 2 fractions.
The remaining 2 fractions are: \(\frac{7}{8}\) and \(\frac{2}{3}\)
So, to make the denominators of these 2 fractions equal, multiply the first fraction with 3 and the second fraction with 8
So,
\(\frac{7}{8}\) = \(\frac{21}{24}\)
\(\frac{2}{3}\) \(\frac{16}{24}\)
Hence,
The second statement is:
\(\frac{7}{8}\) > \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Think and Grow: Modeling Real Life
Example
You try to use a \(\frac{13}{16}\)-inch socket to tighten a bolt, but it is too big. Should you try a \(\frac{3}{4}\) -inch socket or a \(\frac{7}{8}\)-inch socket next?

Write each fraction using a like denominator.
Because 4 and 8 are both factors of 16, use 16 as the denominator.

Show and Grow
Question 12.
You drill a hole using a \(\frac{5}{16}\) -inch drill bit. The hole is too small. Which drill bit should you use to enlarge the hole?

Answer: You should use \(\frac{3}{8}\)– inch drill bit to enlarge the hole.
Explanation:
It is given that you drill a hole using a \(\frac{5}{16}\) and by using this, the hole is too small.
To enlarge a drill bit, it is also given 2 types of drill bits. They are:
A) \(\frac{3}{8}\) B) \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Now, to find the type of drill bit which is used to enlarge the hole, compare \(\frac{5}{16}\) with the given 2 drill bits
Now,
A) \(\frac{3}{8}\) and \(\frac{5}{16}\)
So, to make the denominators equal, \(\frac{3}{8}\) with 2.
So,
\(\frac{3}{8}\)= \(\frac{6}{16}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{6}{16}\) > \(\frac{5}{16}\)
Now,
B) \(\frac{5}{16}\) and \(\frac{1}{4}\)
So, to make the denominators equal, multiply \(\frac{1}{4}\) with 4
So,
\(\frac{1}{4}\) = \(\frac{4}{16}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{5}{16}\) < \(\frac{4}{16}\)
Hence, from the above two,
We can conclude that we can use \(\frac{3}{8}\) – inch bit drill to enlarge a hole which is made by \(\frac{5}{16}\) – inch bit drill
Question 13.
DIG DEEPER!
Order the animals from lightest to heaviest.
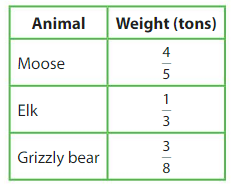
Answer: The order of animals from the lightest to heaviest is: Elk < Grizzly Bear < Mouse
Explanation:
The given table is:

So,
The weights of the animals from the above table are:
Mouse: \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Elk: \(\frac{1}{3}\)
Grizzly bear: \(\frac{3}{8}\)
To find the weights of all the 3 animals, we have to make the denominators of the three equal.
So, to make the denominators equal, multiply the three fractions by 120.
So, we will get
The weight of Mouse is:
\(\frac{4}{5}\) = \(\frac{96}{120}\)
The weight of Elk is:
\(\frac{1}{3}\) = \(\frac{40}{120}\)
The weight of Grizzly bear is:
\(\frac{3}{8}\) = \(\frac{45}{120}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can say that the order of the weights of the animals from the lightest to heaviest is: Elk < Grizzly Bear < Mouse
Compare Fractions Homework & Practice 7.5
Compare. Use model to help.
Question 1.
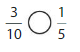
Answer: \(\frac{3}{10}\) is greater than \(\frac{1}{5}\)
Explanation:
The given two fractions are: \(\frac{3}{10}\) and \(\frac{1}{5}\)
So,
Let make the denominators equal so that we can compare the numerators
So,
To make the denominators equal, multiply the second fraction with 2
So,
\(\frac{1}{5}\) = \(\frac{2}{10}\)
So, when we compare the 2 fractions,
We can conclude that \(\frac{3}{10}\) is greater than \(\frac{1}{5}\)
Question 2.
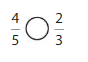
Answer: \(\frac{4}{5}\) is greater than \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Explanation:
The given two fractions are: \(\frac{4}{5}\) and \(\frac{2}{3}\)
So,
Let make the denominators equal so that we can compare the numerators
So,
To make the denominators equal, multiply the first fraction with 3 and the second fraction with 5
So,
\(\frac{4}{5}\) = \(\frac{12}{15}\)
\(\frac{2}{3}\) = \(\frac{10}{15}\)
So, when we compare the 2 fractions,
We can conclude that \(\frac{4}{5}\) is greater than \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Question 3.
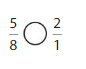
Answer: \(\frac{5}{8}\) is less than \(\frac{2}{1}\)
Explanation:
The given two fractions are: \(\frac{5}{8}\) and \(\frac{2}{1}\)
So,
Let make the denominators equal so that we can compare the numerators
So,
To make the denominators equal, multiply the second fraction with 8
So,
\(\frac{2}{1}\) = \(\frac{16}{8}\)
So, when we compare the 2 fractions,
We can conclude that \(\frac{5}{8}\) is less than \(\frac{2}{1}\)
Compare. Use a model to help.
Question 4.
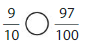
Answer: \(\frac{9}{10}\) is less than \(\frac{97}{100}\)
Explanation:
The given two fractions are: \(\frac{9}{10}\) and \(\frac{97}{100}\)
So,
Let make the denominators equal so that we can compare the numerators
So,
To make the denominators equal, multiply the first fraction with 10
So,
\(\frac{9}{10}\) = \(\frac{90}{100}\)
So, when we compare the 2 fractions,
We can conclude that \(\frac{9}{10}\) is less than \(\frac{97}{100}\)
Question 5.
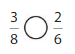
Answer: \(\frac{3}{8}\) is greater than \(\frac{2}{6}\)
Explanation:
The given two fractions are: \(\frac{3}{8}\) and \(\frac{2}{6}\)
So,
Let make the denominators equal so that we can compare the numerators
So,
To make the denominators equal, multiply the first fraction with 3 and the second fraction with 4
So,
\(\frac{3}{8}\) = \(\frac{9}{24}\)
\(\frac{2}{6}\) = \(\frac{8}{24}\)
So, when we compare the 2 fractions,
We can conclude that \(\frac{3}{8}\) is greater than \(\frac{2}{6}\)
Question 6.
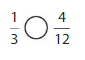
Answer: \(\frac{1}{3}\) is equal to \(\frac{4}{12}\)
Explanation:
The given two fractions are: \(\frac{1}{3}\) and \(\frac{4}{12}\)
So,
Let make the denominators equal so that we can compare the numerators
So,
To make the denominators equal, multiply the first fraction with 4
So,
\(\frac{1}{3}\) = \(\frac{4}{12}\)
So, when we compare the 2 fractions,
We can conclude that \(\frac{1}{3}\) is equal to \(\frac{4}{12}\)
Question 7.
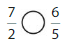
Answer: \(\frac{7}{2}\) is greater than \(\frac{6}{5}\)
Explanation:
The given two fractions are: \(\frac{7}{2}\) and \(\frac{6}{5}\)
So,
Let make the denominators equal so that we can compare the numerators
So,
To make the denominators equal, multiply the first fraction with 5 and the second fraction with 2
So,
\(\frac{7}{2}\) = \(\frac{35}{10}\)
\(\frac{6}{5}\) = \(\frac{12}{10}\)
So, when we compare the 2 fractions,
We can conclude that \(\frac{7}{2}\) is less than \(\frac{6}{5}\)
Question 8.
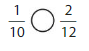
Answer: \(\frac{1}{10}\) is less than \(\frac{2}{12}\)
Explanation:
The given two fractions are: \(\frac{1}{10}\) and \(\frac{2}{12}\)
So,
Let make the denominators equal so that we can compare the numerators
So,
To make the denominators equal, multiply the first fraction with 12 and the second fraction with 10
So,
\(\frac{1}{10}\) = \(\frac{12}{120}\)
\(\frac{2}{12}\) = \(\frac{20}{120}\)
So, when we compare the 2 fractions,
We can conclude that \(\frac{1}{10}\) is less than \(\frac{2}{12}\)
Question 9.
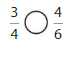
Answer: \(\frac{3}{4}\) is greater than \(\frac{4}{6}\)
Explanation:
The given two fractions are: \(\frac{3}{4}\) and \(\frac{4}{6}\)
So,
Let make the denominators equal so that we can compare the numerators
So,
To make the denominators equal, multiply the first fraction with 3 and the second fraction with 2
So,
\(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{9}{12}\)
\(\frac{4}{6}\) = \(\frac{8}{12}\)
So, when we compare the 2 fractions,
We can conclude that \(\frac{3}{4}\) is greater than \(\frac{4}{6}\)
Question 10.
Structure
Compare \(\frac{3}{8}\) and \(\frac{1}{4}\) two different ways.
Answer: \(\frac{3}{8}\) is greater than \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Explanation:
The given two fractions are: \(\frac{3}{8}\) and \(\frac{1}{4}\)
First way of Comparison:
Let make the denominators equal so that we can compare the numerators
So,
To make the denominators equal, multiply the second fraction with 2
So,
\(\frac{1}{4}\) = \(\frac{2}{8}\)
So, when we compare the 2 fractions,
We can conclude that \(\frac{3}{8}\) is greater than \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Second Way of Comparison:
The given two fractions are: \(\frac{3}{8}\) and \(\frac{1}{4}\)
So,
Let make the numerators equal so that we can compare the denominators
So,
To make the numerators equal, multiply the second fraction with 3
So,
\(\frac{1}{4}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\)
So, when we compare the 2 fractions,
We can conclude that \(\frac{3}{8}\) is greater than \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Question 11.
Modeling Real Life
A sailor is making a ship in a bottle. The last thing he needs to do is seal the bottle with a cork stopper. He tries a \(\frac{3}{4}\) -inch cork stopper, but it is too small. Should he try a \(\frac{1}{2}\)-inch cork stopper or a \(\frac{4}{5}\)-inch cork stopper next? Explain.

Answer: He had to use \(\frac{4}{5}\) -inch cork stopper
Explanation:
It is given that a sailor is making a ship in a bottle and he needs to seal the bottle after making the ship.
It is also given that he tried a \(\frac{3}{4}\) -inch cork stopper which is small
So, to make the big cork stopper so that it can close the bottle, there are 2 choices given.
The two choices are:
A) \(\frac{1}{2}\) B) \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Now,
Compare \(\frac{1}{2}\) with \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Now,
Let make the denominators equal so that we can compare the numerators
So,
To make the denominators equal, multiply the second fraction with 2
So,
\(\frac{1}{2}\) = \(\frac{2}{4}\)
So, when we compare the 2 fractions,
We can conclude that \(\frac{1}{2}\) is less than \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Now,
Compare \(\frac{4}{5}\) with \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Now,
Let make the denominators equal so that we can compare the numerators
So,
To make the denominators equal, multiply the first fraction with 4 and the second fraction with 5
So,
\(\frac{4}{5}\) = \(\frac{16}{20}\)
\(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{15}{20}\)
So, when we compare the 2 fractions,
We can conclude that \(\frac{4}{5}\) is greater than \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Hence, from the above 2 comparisons,
We can conclude that we can use \(\frac{4}{5}\) – inch cork stopper.
Question 12.
DIG DEEPER!
Order the lengths of hair donated from greatest to least.
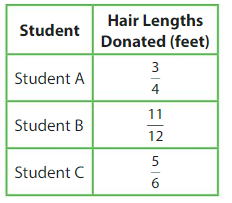
Answer: The order of lengths of hair donated from the greatest to the least is: C > B > A
Explanation:
The given table is:

From the above table,
The length of the hair donated by student A is: \(\frac{3}{4}\)
The length of the hair donated by student B is: \(\frac{11}{12}\)
The length of the hair donated by student C is: \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Now,
Let make the denominators equal so that we can compare the numerators
So,
To make the denominators equal, multiply the first fraction with 3, the second fraction with 1 and the third fraction with 2
So,
\(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{9}{12}\)
\(\frac{5}{6}\) = \(\frac{10}{12}\)
\(\frac{11}{12}\) = \(\frac{11}{12}\)
So, when we compare the 3 fractions,
We can conclude that the order of the lengths of hair donated from highest to least is: C > B > A
Review & Refresh
Question 13.
Extend the pattern of shapes by repeating the rule “triangle, pentagon, octagon.”What is the 48th shape in the pattern?

Answer: The 48th shape in the given pattern is: Octagon
Explanation:
The given pattern is:

From the above pattern,
The given rule is: Triangle, pentagon, octagon
So,
The total number of figures in the given pattern = 3
So,
The 48th figure in the given pattern = 48 ÷ 3
Now,
By using the partial quotients method,
48 ÷ 3 = ( 30 + 18 ) ÷ 3
= ( 30 ÷ 3 ) + ( 18 ÷ 3 )
= 10 + 6
= 16 R 0
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the 48th figure in the given pattern is: Octagon
Understand Fraction Equivalence and Comparison Performance Task
Question 1.
a. Your art teacher wants you to complete the design below. Half of the squares are colored black. Complete the table. Then use the table to finish the design.
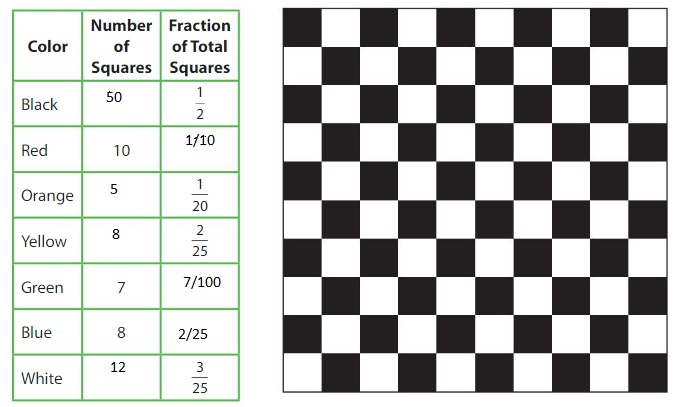
b.Which two colors cover the same portion of the design? Explain.
Answer: Green and Blue colors cover the same portion of the design
Explanation:
The teacher has given a board that has a total of 100 squares and according to the table, we have to complete the design of the squares.
The table is:
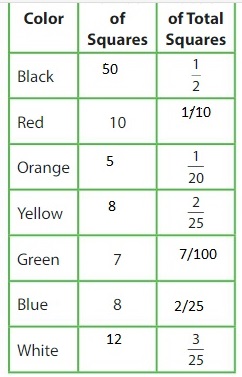
Hence, from the above table,
We can conclude that Blue and Yellow colors cover the same portion of the design.
Question 2.
Your teacher displays 30 designs in a rectangular array on the wall. Show two different ways your teacher can arrange the designs.
Answer: The different ways that your teacher can arrange the designs are: 1 × 30, 2 × 15, 3 × 5, 5 × 3, 15 × 2, 30 × 1
Explanation:
It is given that your teacher displays 30 designs in a rectangular array on the wall.
So, we can arrange the 30 designs in different ways by using the factor pairs of 30
Now,
The factor pairs of 30 are: 1 × 30, 2 × 15, 3 × 5, 5 × 3, 15 × 2, 30 × 1
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the different ways to arrange the 30 designs in a rectangular array is: 1 × 30, 2 × 15, 3 × 5, 5 × 3, 15 × 2, 30 × 1
Understand Fraction Equivalence and Comparison Activity
Fraction Boss
Directions:
1. Divide the Fraction Boss Cards equally between both players.
2. Each player flips a Fraction Boss Card.
3. Players compare their fractions. The player with the greater fraction takes both cards.
4. If the fractions are equal, each player flips another card. Players compare their fractions. The player with the greater fraction takes all four cards.
5. The player with the most cards at the end of the round wins!

Understand Fraction Equivalence and Comparison Chapter Practice
7.1 Model Equivalent Fractions
Question 1.
Use the model to find an equivalent fraction for \(\frac{3}{4}\).

Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{3}{4}\) is: \(\frac{6}{8}\)
Explanation:
The given model is:

From the above model,
We can say that the fraction is: \(\frac{3}{4}\)
So,
The model for the Equivalent fraction is:

From the above model, we can say that the equivalent fraction is: \(\frac{6}{8}\)
So,
When we divide \(\frac{6}{8}\) by 2, we will get the equivalent value.
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that \(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{6}{8}\)
Question 2.
Use the number line to find an equivalent fraction for \(\frac{2}{5}\).
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{2}{5}\) is: \(\frac{4}{10}\)
Explanation:
The given number line is:
From the above number line,
we can say that 2 lines represent a value. i.e., \(\frac{2}{5}\)
So,
The value of each line when divided into 2 parts represent: \(\frac{1}{10}\)
So,
The equivalent number line is:
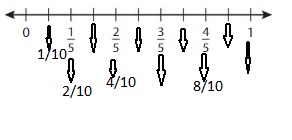
So, from the above equivalent number line,
We can see that \(\frac{2}{5}\) is equal to \(\frac{4}{10}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that \(\frac{2}{5}\) = \(\frac{4}{10}\)
Question 3.
Open-Ended
Write two equivalent fractions to describe the portion of the apples that are red.

Answer:
The two equivalent fractions to describe the portion of apples that are red is:
\(\frac{4}{8}\) and \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation:
The given model is:

From the above model,
We can say that,
The number of colored apples is: 4
The number of red apples is: 4
So,
The total number of apples are: 8
So,
The fraction form for the red apples is = \(\frac{Number of red apples}{Total number of apples}\)
= \(\frac{4}{8}\)
Equivalent form for the red apples:
Consider the colored apples as 1 group and the red apples as 1 group
So,
The number of red apples is: 1
The number of colored apples is: 1
So,
The total number of apples are: 2
So,
The fraction that the apples are red = \(\frac{Number of red apples}{Total number of apples}\)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can say that
The two equivalent fractions to describe the portion of apples that are red are:
\(\frac{4}{8}\) and \(\frac{1}{2}\)
7.2 Generate Equivalent Fractions by Multiplying
Find the equivalent fraction.
Question 4.

Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{3}{4}\) is: \(\frac{9}{12}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is \(\frac{3}{4}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 3 and 4
It is given that the denominator value is 12.
So, to make the value 12 from 4, we have to multiply the fraction with 3
So,
\(\frac{3}{4} is multiplied with [latex]\frac{3}{3}.
Hence,

Question 5.
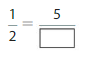
Answer: The equivalent fraction of [latex]\frac{1}{2}\) is: \(\frac{5}{10}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is \(\frac{1}{2}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 1 and 2
It is given that the numerator value is 5.
So, to make the value 5 from 1, we have to multiply the fraction with 5
So,
\(\frac{1}{2} is multiplied with [latex]\frac{5}{5}.
Hence,
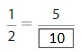
Question 6.
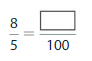
Answer: The equivalent fraction of [latex]\frac{8}{5}\) is: \(\frac{160}{100}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is \(\frac{8}{5}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 8 and 5
It is given that the denominator value is 100.
So, to make the value 100 from 5, we have to multiply the fraction with 20
So,
\(\frac{8}{5} is multiplied with [latex]\frac{20}{20}.
Hence,
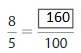
Find an equivalent fraction.
Question 7.
[latex]\frac{1}{6}\)
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{1}{6}\) is: \(\frac{2}{12}\)
Explanation:
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So,
\(\frac{1}{6}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{2}{2}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{1}{6}\) = \(\frac{2}{12}\)
Question 8.
\(\frac{5}{5}\)
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{5}{5}\) is: \(\frac{10}{10}\)
Explanation:
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So,
\(\frac{5}{5}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{2}{2}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{5}{5}\) = \(\frac{10}{10}\)
Question 9.
\(\frac{1}{4}\)
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{1}{4}\) is: \(\frac{2}{8}\)
Explanation:
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So,
\(\frac{1}{4}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{2}{2}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{1}{4}\) = \(\frac{2}{8}\)
Find two equivalent fractions.
Question 10.
\(\frac{3}{2}\)
Answer:
The two equivalent fractions of \(\frac{3}{2}\) is: \(\frac{6}{4}\) and \(\frac{9}{6}\)
Explanation:
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So,
\(\frac{3}{2}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{2}{2}\) and \(\frac{3}{3}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{3}{2}\) = \(\frac{6}{4}\) and \(\frac{9}{6}\)
Question 11.
\(\frac{1}{3}\)
Answer:
The two equivalent fractions of \(\frac{1}{3}\) is: \(\frac{2}{6}\) and \(\frac{3}{9}\)
Explanation:
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So,
\(\frac{1}{3}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{2}{2}\) and \(\frac{3}{3}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{1}{3}\) = \(\frac{2}{6}\) and \(\frac{3}{9}\)
Question 12.
\(\frac{4}{5}\)
Answer:
The two equivalent fractions of \(\frac{4}{5}\) is: \(\frac{8}{10}\) and \(\frac{12}{15}\)
Explanation:
When we multiply the fraction with the fraction having the same number as the numerator as the denominator, we will get the equivalent fraction.
So,
\(\frac{4}{5}\) is multiplied with \(\frac{2}{2}\) and \(\frac{3}{3}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{4}{5}\) = \(\frac{8}{10}\) and \(\frac{12}{15}\)
7.3 Generate Equivalent Fractions by Dividing
Find the equivalent fraction.
Question 13.

Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{3}{12}\) is: \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is: \(\frac{3}{12}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 3 and 12
3 and 12 are the multiples of 3.
So,
\(\frac{3}{12}=\frac{3 \div 3}{12 \div 3}=\frac{1}{4}\)
Hence,
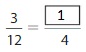
Question 14.
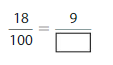
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{18}{100}\) is: \(\frac{9}{50}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is: \(\frac{18}{100}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 18 and 100
18 and 100 are the multiples of 2.
So,
\(\frac{18}{100}=\frac{18 \div 2}{100 \div 2}=\frac{9}{50}\)
Hence,
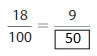
Question 15.
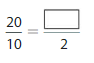
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{20}{10}\) is: \(\frac{4}{2}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is: \(\frac{20}{10}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 20 and 10
20 and 10 are the multiples of 5. ( 20 and 10 are also multiples of 2 and 10 but in the denominator, 2i s given which can only be obtained by divideing 10 with 5 )
So,
\(\frac{20}{10}=\frac{20 \div 5}{10 \div 5}=\frac{4}{2}\)
Hence,
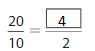
Find an equivalent fraction.
Question 16.
\(\frac{4}{6}\)
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{4}{6}\) is: \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is: \(\frac{4}{6}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 4 and 6
4 and 6 are the multiples of 2. ( 4 and 6 are multiples of 2 )
So,
\(\frac{4}{6}=\frac{4 \div 2}{6 \div 2}=\frac{2}{3}\)
Hence,
The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{4}{6}\) is: \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Question 17.
\(\frac{16}{4}\)
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{16}{4}\) is: \(\frac{8}{2}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is: \(\frac{16}{4}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 16 and 4
16 and 4 are the multiples of 2.
So,
\(\frac{16}{4}=\frac{16 \div 2}{4 \div 2}=\frac{8}{2}\)
Hence,
The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{16}{4}\) is: \(\frac{8}{2}\)
Question 18.
\(\frac{20}{8}\)
Answer: The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{20}{8}\) is: \(\frac{10}{4}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is: \(\frac{20}{8}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 20 and 8
20 and 8 are the multiples of 2.
So,
\(\frac{20}{8}=\frac{20 \div 2}{8 \div 2}=\frac{10}{4}\)
Hence,
The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{20}{8}\) is: \(\frac{10}{4}\)
Find two equivalent fractions.
Question 19.
\(\frac{80}{100}\)
Answer: The two equivalent fractions of \(\frac{80}{100}\) is: \(\frac{4}{5}\) and \(\frac{20}{25}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is: \(\frac{80}{100}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 80 and 100
80 and 100 are the multiples of 20 and 4
So,
We have to divide \(\frac{80}{100}\) with 20and 4
So,
\(\frac{80}{100}=\frac{80 \div 20}{100 \div 20}=\frac{4}{5}\)
\(\frac{80}{100}=\frac{80 \div 4}{100 \div 4}=\frac{20}{25}\)
Hence,
The two equivalent fractions of \(\frac{80}{100}\) is: \(\frac{4}{5}\) and \(\frac{20}{25}\)
Question 20.
\(\frac{6}{12}\)
Answer: The two equivalent fractions of \(\frac{6}{12}\) is: \(\frac{2}{4}\) and \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is: \(\frac{6}{12}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 6 and 12
6 and 12 are the multiples of 3 and 6
So,
We have to divide \(\frac{6}{12}\) with 3 and 6
So,
\(\frac{6}{12}=\frac{6 \div 3}{12 \div 3}=\frac{2}{4}\)
\(\frac{6}{12}=\frac{6 \div 6}{12 \div 6}=\frac{1}{2}\)
Hence,
The two equivalent fractions of \(\frac{6}{12}\) is: \(\frac{2}{4}\) and \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 21.
\(\frac{40}{4}\)
Answer: The two equivalent fractions of \(\frac{40}{4}\) is: \(\frac{20}{2}\) and \(\frac{10}{1}\)
Explanation:
The given fraction is: \(\frac{40}{4}\)
From the above fraction, the numerator and denominator are: 40 and 4
40 and 4 are the multiples of 2 and 4
So,
We have to divide \(\frac{40}{4}\) with 2 and 4
So,
\(\frac{40}{4}=\frac{40 \div 2}{4 \div 2}=\frac{20}{2}\)
\(\frac{40}{4}=\frac{40 \div 4}{4 \div 4}=\frac{10}{1}\)
Hence,
The two equivalent fractions of \(\frac{40}{4}\) is: \(\frac{20}{2}\) and \(\frac{10}{1}\)
Question 22.
Modeling Real Life
You have 90$. What fraction of a dollar, in tenths, do you have?
Answer: The fraction of a dollar, in tenths, is: \(\frac{1}{10}\)
Explanation:
It is given that you have 90$
So,
The fraction of a dollar, in tenths that pack their lunch = The number of dollars ÷ The total number of dollars
= 90 ÷ 100
= \(\frac{9}{10}\)
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the number of dollars, in tenths, is: \(\frac{9}{10}\)
7.4 Compare Fractions Using Benchmarks
Compare. Use a model to help.
Question 23.
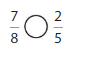
Answer: \(\frac{7}{8}\) is greater than \(\frac{2}{5}\)
Explanation:
The given fractions are: \(\frac{7}{8}\) and \(\frac{2}{5}\)
For the two fractions, the models are:
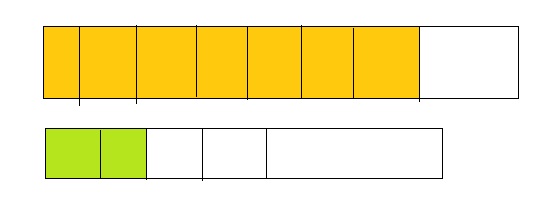
So,
Let make the denominators equal so that we can compare the numerators
So,
To make the denominators equal, multiply the first fraction with 5 and the second fraction with 8
So,
\(\frac{7}{8}\) = \(\frac{35}{40}\)
\(\frac{2}{5}\) = \(\frac{16}{40}\)
So, when we compare the 2 fractions,
We can conclude that \(\frac{7}{8}\) is greater than \(\frac{2}{5}\)
Question 24.
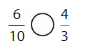
Answer: \(\frac{6}{10}\) is less than \(\frac{4}{3}\)
Explanation:
The given fractions are: \(\frac{6}{10}\) and \(\frac{4}{3}\)
For the two fractions, the models are:
So,
Let make the denominators equal so that we can compare the numerators
So,
To make the denominators equal, multiply the first fraction with 3 and the second fraction with 10
So,
\(\frac{6}{10}\) = \(\frac{18}{30}\)
\(\frac{4}{3}\) = \(\frac{40}{30}\)
So, when we compare the 2 fractions,
We can conclude that \(\frac{6}{10}\) is less than \(\frac{4}{3}\)
Question 25.
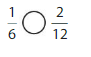
Answer: \(\frac{1}{6}\) is equal to \(\frac{2}{12}\)
Explanation:
The given fractions are: \(\frac{1}{6}\) and \(\frac{2}{12}\)
For the two fractions, the models are:
So,
Let make the denominators equal so that we can compare the numerators
So,
To make the denominators equal, multiply the first fraction with 2
So,
\(\frac{1}{6}\) = \(\frac{2}{12}\)
So, when we compare the 2 fractions,
We can conclude that \(\frac{1}{6}\) is equal to \(\frac{2}{12}\)
7.5 Compare Fractions
Compare. Use a model to help.
Question 26.
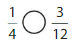
Answer: \(\frac{1}{4}\) is equal to \(\frac{3}{12}\)
Explanation:
The given two fractions are: \(\frac{1}{4}\) and \(\frac{3}{12}\)
So,
Let make the denominators equal so that we can compare the numerators
So,
To make the denominators equal, multiply the first fraction with 3
So,
\(\frac{1}{4}\) = \(\frac{3}{12}\)
So, when we compare the 2 fractions,
We can conclude that \(\frac{1}{4}\) is equal to \(\frac{3}{12}\)
Question 27.
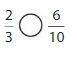
Answer: \(\frac{2}{3}\) is greater than \(\frac{6}{10}\)
Explanation:
The given two fractions are: \(\frac{2}{3}\) and \(\frac{6}{10}\)
So,
Let make the denominators equal so that we can compare the numerators
So,
To make the denominators equal, multiply the first fraction with 10 and the second fraction with 3
So,
\(\frac{2}{3}\) = \(\frac{20}{30}\)
\(\frac{6}{10}\) = \(\frac{18}{30}\)
So, when we compare the 2 fractions,
We can conclude that \(\frac{2}{3}\) is greater than \(\frac{6}{10}\)
Question 28.
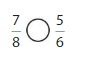
Answer: \(\frac{7}{8}\) is greater than \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Explanation:
The given two fractions are: \(\frac{7}{8}\) and \(\frac{5}{6}\)
So,
Let make the denominators equal so that we can compare the numerators
So,
To make the denominators equal, multiply the first fraction with 6 and the second fraction with 8
So,
\(\frac{7}{8}\) = \(\frac{42}{48}\)
\(\frac{5}{6}\) = \(\frac{40}{48}\)
So, when we compare the 2 fractions,
We can conclude that \(\frac{7}{8}\) is greater than \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Understand Fraction Equivalence and Comparison of Cumulative Practice
Question 1.
Which number is a common factor of 12, 16, and 40?
A. 5
B. 8
C. 3
D. 4
Answer: D) 4
Explanation:
Given numbers are: 12, 16 and 40
The factors are the numbers that divide the original number completely.
So,
The factors of 12 are: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12
The factors of 16 are: 1, 2, 4, 8, 16
The factors of 40 are: 1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 10, 20, 40
So,
The common factors of 12, 16, and 20 are: 1, 2, 4
Question 2.
Which statements describe the difference between 77,986 and 21,403?

Answer: The given numbers are: 77,986 and 21,403
So,
The difference between 77,986 and 21,403 is: 56,583
The below statements describe the difference between 77,986 and 21,403
Question 3.
Which product is between 5,050 and 5,100?
A. 652 × 8
B. 566 × 9
C. 1,023 × 5
D. 1,257 × 4
Answer: B) 566 × 9
Explanation:
Let the given product Expressions be named as A), B), C) and D)
So,
The given products are:
A) 652 × 8 B) 566 × 9 C) 1,023 × 5 D) 1,257 × 4
Now,
By using the partial products method,
A. 652 × 8 = 5,216
B. 566 × 9 = 5,094
C. 1,023 × 5 = 5,115
D. 1,257 × 4 = 5,028
So,
From the above values,
The product that is between 5,050 and 5,100 is: 566 × 9
Question 4.
Use the advertisement to answer the question.

What is the greatest number of miles that the car could have been driven?
A. 84,699
B. 84,750
C. 84,749
D. 84,650
Answer: The greatest number of miles that the car should have been driven is: 84,699 miles
Explanation:
Given that the car should have been driven approximate 84,700 miles ( rounded to the nearest 100 )
The given options are: A) 84,699 B) 84,750 C) 84,749 D) 84,650
The greatest number that is close to 84,700 is: 84, 699
Hence, from the above,
We can conclude that the greatest number of miles that the car should have been driven is: 84,699 miles
Question 5.
Which multiplication expressions could be represented by the area model?
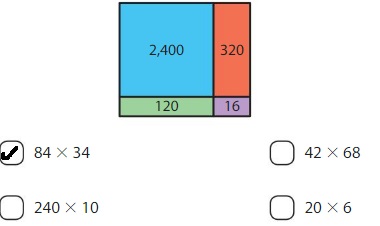
Answer: The multiplication Expression represented by the area model is: 84 × 34
Explanation:
The given area model is:
So, from the area model,
The factor pairs of 2,400 are: 80 × 30, 60 × 40
The factor pairs of 120 are: 4 × 30, 6 × 20
From the above two factors, we can say that
The area model can be formed from 80, 4 and 30
Hence,
The product for the given area model is: 84 × 34
Question 6.
Your neighbor buys yogurt in packages of 4. If your neighbor only buys complete packages, how many yogurts could he have bought?

A. 2
B. 20
C. 34
D. 18
Answer: The complete packages of yogurts that he could have brought is: 20
Explanation:
It is given that your neighbor bought yogurt in packages of 4
So, for complete packages, the number of packages that he takes should not have any extra yogurt i.e., remainder yogurt when packing completely in the packs of 4.
So,
From the above options,
We have only 20 yogurts that can be packed completely in packs of 4.
Question 7.
Which fraction makes the statement true?
Answer: \(\frac{1}{4}\) makes the statement true.
Explanation:
Given fraction is: \(\frac{6}{8}\)
So,
We have to compare \(\frac{6}{8}\) with the given options to satisfy the relation the option < \(\frac{6}{8}\)
Now,
A) The two fractions are: \(\frac{1}{4}\) and \(\frac{6}{8}\)
So, to make the denominators equal, multiply the first fraction with 2
So,
\(\frac{1}{4}\) = \(\frac{2}{8}\)
Hence,
\(\frac{1}{4}\) < \(\frac{6}{8}\)
Question 8.
Which division equation is represented by the counters?
Answer: D) 26 ÷ 6 = 4 R 2
Explanation:
Given counters are:
From the above model,
The total number of counters are: 6
The number of parts that each counter has: 4
The number of parts that has leftover is: 2
So,
The total number of parts in 6 counters = 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 = 24
The total number of parts = The number of parts in 6 counters + The number of parts leftover = 24 + 2 = 26
Hence, from the above, the division Expression can be represented as:
26 ÷ 6 = 4 R 2
Question 9.
Which statements are true?

Answer: The below statements are true:

Prime numbers:
The numbers that have exactly 2 factors 1 and itself are ” Prime numbers”
Composite numbers:
The numbers that have more than 2 factors are “Composite numbers”
Question 10.
What is the quotient of 3,258 and 3?

Answer: The quotient of 3,258 and 3 is: 1,086
Explanation:
By using the partial quotients method,
3,258 ÷ 3 = ( 3,000 + 240 + 18 ) ÷ 3
= ( 3,000 ÷ 3 ) + ( 240 ÷ 3 ) + ( 18 ÷ 3 )
= 1,000 + 80 + 6
= 1,086
Hence, from the above,
The quotient of 3,258 and 3 is: 1,086
Question 11.
Which model shows an equivalent fraction for the fraction shown by the model below?
Answer: The equivalent fraction for the given model in shown in Option C)
Explanation:
From the given model,
The fraction is:\(\frac{3}{6}\)
From\(\frac{3}{6}\),
The number of colored parts is: 3
The total number of parts are: 6
So,
As 3 and 6 are the multiples of 3, divide \(\frac{3}{6}\) with 3
So, we get
\(\frac{3}{6}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
So,
The equivalent fraction of \(\frac{3}{6}\) is \(\frac{1}{2}\) which is shown in the model of Option C)
Question 12.
What is the product of 68 and 45?
A. 8,420
B. 3,060
C. 612
D. 27,360
Answer: 68 × 45 = 3,060
Explanation:
By using the partial products method,
68 × 45 = ( 60 + 8 ) × ( 40 + 5 )
= ( 60 × 40 ) + ( 8 × 5 ) + ( 60 × 5 ) + ( 8 × 40 )
= 2,400 + 40 + 300 + 320
= 3,060
Hence,
68 × 45 = 3,060 which is Option B)
Question 13.
Which pattern uses the same rule as the pattern below?
2, 10, 18, 26, 34, 42
A. 15, 23, 31, 39, 47, 55
B. 5, 25, 125, 625, 3, 125, 15, 625,
C. 70, 62, 54, 46, 38, 30
D. 25, 34, 43, 52, 61, 70
Answer: Option A) follows the same pattern as the given pattern
Explanation:
Given pattern is: 2, 10, 18, 26, 34, 42
From the above pattern,
The rule is: Add 8
So,
By checking the options,
We can conclude that option A) satisfies the same rule as in the given pattern
Question 14.
Which statements are true?
Answer: The statements that are true are:
Explanation:
Compare the given fractions by making either both the denominators or the numerators equal.
Question 15.
Part A At a summer camp, 67 students are in a line to rent kayaks. Each kayak can hold 4 people. How many kayaks will be full?
Think
Solve
Explain

Part B How many kayaks will be used?
Part C How many students will be in the last kayak? Explain.
Answer:
Part A: 16 kayaks will be full
Part B: 17 kayaks will be used
Part C: 3 students will be in the last kayak
Explanation:
Given that there are 67 students standing in a line to rent a kayak and each kayak holds 4 people.
So,
The number of kayaks is: 67 ÷ 4
Now,
67 ÷ 4 = ( 60 + 4 ) ÷ 4
= ( 60 ÷ 4 ) + ( 4 ÷ 4 )
= 15 + 1
= 16 R 3
Hence, from the above
The number of kayaks that are full is: 16
The number of kayaks that will be used is: 17
The number of students that will be in the last kayak is: 3
Question 16.
How many zeros will the product of 80 and 50 have?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Answer: The product of 80 and 50 will have 3 zeroes
Explanation:
By using the place-value method,
80 × 50 = 8 tens × 50
= 400 tens
= 4,000
Hence,
The number of zeroes in 80 × 50 is: 3
Question 17.
There are 57 electronic books checked out of a library. There are 8 times as many printed books checked out as electronic books. How many total books are checked out of the library?
A. 513
B. 4,113
C. 122
D. 456
Answer: A) The total number of books that are checked out of the library: 513
Explanation:
It is given that there are 57 electronic books checked out of a library.
It is also given that there are 8 times as many printed books checked out as electronic books
So,
The total number of printed books = 57 × 8 = 456
Hence,
The total number of books = The number of electronic books + The number of printed books
= 57 + 456
= 513 books
Question 18.
Which number is equal to 100,000 + 5,000 + 80 + 4?
A. 1,584
B. 105084
C. 15,084
D. 105,840
Answer: B) 1,05,084
Explanation:
The given Expanded form is: 100,000 + 0 + 5,000 + 0 + 80 + 4
Hence,
The standard form is: 105,084
Understand Fraction Equivalence and Comparison STEAM Performance Task
Question 1.
Sea level is the average level of the oceans on Earth. The global sea level is rising about \(\frac{1}{8}\) inch each year.
a. If this pattern continues, how much will the sea level rise in 80 years?
b. You read from another source that the sea level is1rising about \(\frac{1}{2}\) inch every 4 years. Did your source use the same fact as above? Explain.

c. In 10 years, will the sea level rise more or less than an inch? Explain.

d. How many years will it take the sea level to rise about 1 foot?
e. Use the Internet or some other resource to learn about rising sea levels. Write one interesting fact that you learn.
Answer:
a) The amount of sea-level rise in 80 years is: 10 inches
b) Yes, your source does not use the same fact as above
c) In 10 years, the sea level will be an inch.
d) The amount of years that the sea-level will rise to about 1 foot is: 96 years
e) The sea-level will be more in the coastal areas
Explanation:
It is given that the global sea-level is rising about \(\frac{1}{8}\) inch every year
So,
The amount of sea-level that will rise in 80 years = 80 × \(\frac{1}{8}\) = 10 inches
It is also given that another Internet source given that the sea-level is rising about \(\frac{1}{4}\) inches every 4 years
So,
The amount of sea-level that will rise every year = \(\frac{1}{4}\) × \(\frac{1}{4}\) = \(\frac{1}{16}\)
So,
Your source does not use the same source as above
We know that,
1 inch = 12 foot
But from above,
We can see that the amount of sea-level that will rise in 80 years in only 10 inch
So,
The amount os sea-level will be less than an inch in 10 year
The number of years that will take for the sea-level that will rise about 1 foot = 96 years
Question 2.
The gravitational pull of the moon affects the high and low tides of the oceans on Earth. Cities along the coasts use tide tables each day. Use the tide table to answer the questions.
a. When swimming, why is it important to understand tide tables?
Answer: When swimming, the tide tables is important because we can’t swim when there will be high tides. Otherwise, there is a chance, that we will be suffocated by water and die
b. What are the common factors of the water heights?
Answer: The common factors of water heights are: 1, 2, 4
c. Make a picture graph of the water heights.
d. What pattern do you notice about the water heights? Explain.
Answer: All water heights are the multiples of 4
Conclusion:
Free PDF of Big Ideas Math Answers Grade 4 Chapter 7 Understand Fraction Equivalence and Comparison is available here. Learn the easy tricks and tips to solve Grade 4 questions. Practice Books and questions are provided along with the explanations. Refer to Big Ideas Math Answers Grade 4 Chapter 7 Understand Fraction Equivalence and Comparison and score marks in the exams.