Hello Students!!! Do you wanna become a pro in maths? If yes, then learn the tricks to solve math problems with simple methods. Here we are providing Big Ideas Math Book Geometry Answer Key Chapter 11 Circumference, Area, and Volume with step-by-step explanations. So, students who are unable to solve Chapter 11 Circumference, Area, and Volume can make use of our Big Ideas Math Geometry Answers. Get free access to BIM Big Ideas Math Geometry Answers Chapter 11 Circumference, Area, and Volume from here.
Big Ideas Math Book Geometry Answer Key Chapter 11 Circumference, Area, and Volume
The topics covered in Big Ideas Math Book Geometry Ch 11 Answer Key are Circumference and Arc length, area of circles and sectors, areas of polygons, three-dimensional figures, volume of prisms and cylinders, pyramids, cones, spheres etc. So, check out the list with your textbook and start practicing the problems with the help of our Big Ideas Math Book Geometry Answer Key Chapter 11 Circumference, Area, and Volume. Hit the links you wish to practice and enhance your knowledge.
- Circumference, Area, and Volume Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
- Circumference, Area, and Volume Monitoring Progress
- 11.1 Circumference and Arc Length
- Lesson 11.1 Circumference and Arc Length
- Exercise 11.1 Circumference and Arc Length
- 11.2 Areas of Circles and Sectors
- Lesson 11.2 Areas of Circles and Sectors
- Exercise 11.2 Areas of Circles and Sectors
- 11.3 Areas of Polygons
- Lesson 11.3 Areas of Polygons
- Exercise 11.3 Areas of Polygons
- 11.4 Three-Dimensional Figures
- Lesson 11.4 Three-Dimensional Figures
- Exercise 11.4 Three-Dimensional Figures
- 11.1 – 11.4 Quiz
- 11.5 Volumes of Prisms and Cylinders
- Lesson 11.5 Volumes of Prisms and Cylinders
- Exercise 11.5 Volumes of Prisms and Cylinders
- 11.6 Volumes of Pyramids
- Lesson 11.6 Volumes of Pyramids
- Exercise 11.6 Volumes of Pyramids
- 11.7 Surface Areas and Volumes of Cones
- Lesson 11.7 Surface Areas and Volumes of Cones
- Exercise 11.7 Surface Areas and Volumes of Cones
- 11.8 Surface Areas and Volumes of Spheres
- Lesson 11.8 Surface Areas and Volumes of Spheres
- Exercise 11.8 Surface Areas and Volumes of Spheres
- Circumference, Area, and Volume Review
- Circumference, Area, and Volume Test
- Circumference, Area, and Volume Cumulative Assessment
Circumference, Area, and Volume Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
Find the surface area of the prism.
Question 1.
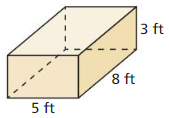
Answer:
The surface area of the prism = 158 sq ft.
Explanation:
Given that,
l = 5 ft, w = 8 ft, and h = 3 ft
where l = length, w = width, and h = height
The surface area of the rectangular prism = 2(lw + lh + wh)
SA = 2(5 x 8) + (5 x 3) + (8 x 3)
SA = 2(40 + 15 + 24)
SA = 2 x 79
SA = 158 sq ft.
Question 2.
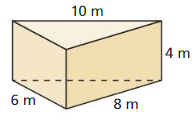
Answer:
The surface area of the triangular prism = 68 sq m.
Explanation:
Given that,
l = 10 m, p = 4 m, and h = 10.
The surface area of the triangular prism = 2B + (p x h)
b = base, p = perimeter, and h = height
SA = 2(6 + 8) + (4 x10)
SA = (2 x14) + 40
SA = 28 + 40
SA = 68 sq m
Question 3.
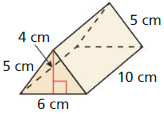
Answer:
The surface area of the triangular prism = 42 sq m.
Explanation:
Given that,
w = 10 cm, p = 4 cm, and h = 5 cm, l = 6 cm.
The surface area of the triangular prism = 2B + (p x h)
b = base, p = perimeter, and h = height
SA = 2(6 + 5) + (4 x 5)
SA = (2 x 11) + 20
SA = 22 + 20
SA = 42 sq cm
Find the missing dimension.
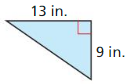
Question 4.
A rectangle has a perimeter 0f 28 inches and a width of 5 inches. What is the length of the rectangle?
Answer:
The length of the rectangle = 9 in.
Explanation:
Given that,
A rectangle has a perimeter of 28 inches and a width of 5 inches.
length of the rectangle = p/2 – w
where perimeter = 28 in, and w = 5 in
l = 28/2 – 5
l = 14 – 5
l = 9
So, the length of the rectangle = 9 in.
Question 5.
A triangle has an area of 12 square centimeters and a height of 12 centimeters. What is the base of the triangle?
Answer:
The base of the triangle = 2 cm.
Explanation:
Given that,
A triangle has an area of 12 sq cm and a height of 12 cm.
The base of the triangle = 2(A)/h.
b = 2(12)/12
b = 24/12
b = 2cm
So, the base of the triangle = 2 cm.
Question 6.
A rectangle has an area of 84 square feet and a width of 7 feet. What is the length of the rectangle?
Answer:
The length of the rectangle = 12 ft.
Explanation:
Given that,
A rectangle has an area of 84 sq ft and a width of 7 feet.
Area of the rectangle = l x b
where as length = l; breadth = b
84 = l x 7
l = 84/7
l = 12
So, the length of the rectangle = 12 ft.
Question 7.
ABSTRACT REASONING
Write an equation for the surface area of a Prism with a length, width, and height of x inches. What solid figure does the prism represent?
Answer:
The surface area of a prism = 2(lw + wh + lh).
Explanation:
Given that,
length = l, width = w, and height = x inches.
The surface area of the prism = 2(lw + wh + lh).
So, the prism represent the rectangular prism.
Circumference, Area, and Volume Monitoring Progress
Draw a net of the three-dimensional figure. Label the dimensions.
Question 1.
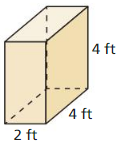
Answer:
The surface area of the prism = 64 sq cm.
Explanation:
Given that,
l = 2 ft, w = 4 ft, and h = 4 ft.
where l = length, w = width, and h = height.
The surface area of the rectangular prism = 2(lw + lh + wh).
SA = 2(2 x 4 + 4 x 4 + 4 x 2)
SA = 2(8 + 16 + 8)
SA = 2 x 32
SA = 64 sq cm.
Question 2.
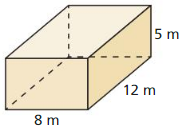
Answer:
The surface area of the prism = 392 sq m.
Explanation:
Given that,
l =8 m, w = 12 m, and h = 5 m
where l = length, w = width, and h = height
The surface area of the rectangular prism = 2(lw + lh + wh)
SA = 2(8×12 + 12×5 + 5×8)
SA = 2(96 + 60 + 40)
SA = 2 x 196
SA = 392 sq m
Question 3.
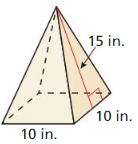
Answer:
The surface area of the triangular prism = 170 sq in.
Explanation:
Given that,
B = 10 in, p = 15 in, and h = 15 in, l = 10 in
the surface area of the triangular prism = 2B + ph
b = base, p = perimeter, and h = height
SA = 2(10) + 15(10)
SA = 2(10) + 150
SA = 20 + 150
SA = 170 in
11.1 Circumference and Arc Length
Exploration 1
Finding the Length of a Circular Arc
Work with a partner: Find the length of each red circular arc.
a. entire circle
Answer:
The Formula for the Arc Length is 2r(θ/360)
r = 4
θ = 260 degrees
Arc length = 2(4)(360/360)
= 8(1)
= 8
b. one-fourth of a circle
Answer:
The Formula for the Arc Length is 2r(θ/360)
r = 4
θ = 90 degrees.
Arc length = 2(4)(90/360)
= 8(90/360)
= 2
c. one-third of a circle
Answer:
The Formula for the Arc Length is 2r(θ/360)
r = 5
θ = 100 degrees.
Arc length = 2(5)(100/360)
= 10(100/360)
= 2.7
d. five-eights of a circle
Answer:
The Formula for the Arc Length is 2r(θ /360)
r = 3
θ = 225 degrees.
Arc length = 2(3)(225/360)
= 6(225/360)
= 3.75
Exploration 2
Using Arc Length
Work with a partner: The rider is attempting to stop with the front tire of the motorcycle in the painted rectangular box for a skills test. The front tire makes exactly one-half additional revolution before stopping. The diameter of the tire is 25 inches. Is the front tire still in contact with the painted box? Explain.

Answer:
Given,
The diameter of the tire is 25 inches
C = πd
C = 25π or 78.54 inch
Half of revolution = 1/2 (78.54) = 39.27 inch
Communicate Your Answer
Question 3.
How can you find the length of a circular arc?
Answer:
Any distance along the curved line that makes up the arc is known as the arc length.
The length of an arc is longer than any straight line distance between its endpoints.
So, the length of a circular arc = 2π(r)
where as,
π = 22/7; r = radius.
LOOKING FOR REGULARITY IN REPEATED REASONING
To be proficient in math, you need to notice if calculations are repeated and look both for general methods and for shortcuts.
Question 4.
A motorcycle tire has a diameter of 24 inches. Approximately how many inches does the motorcycle travel when its front tire makes three-fourths of a revolution?
Answer:
D = 24 in.
One revelation = 360 degrees.
Three-fourths of one revelation = 270 degrees.
The motorcycles travel = 2r(θ/360)
Radius r = d/2 = 24/2 = 12
θ = 270 degrees.
= 2(12)(270/360)
= 24(270/360)
= 18
Lesson 11.1 Circumference and Arc Length
Monitoring Progress
Question 1.
Find the circumference of a circle with a diameter of 5 inches.
Answer:
C = 15.7 in
Explanation:
Given,
diameter = 5 in
Circumference C = πd
π = 3.14 or 22/7
C = 3.14 x 5
C = 15.7 in.
Question 2.
Find the diameter of a circle with a circumference of 17 feet.
Answer:
Diameter = 5.41 ft.
Explanation:
Given,
circumference = 17 ft.
Diameter = C/π
π = 3.14 or 22/7
d = 17/π
d = 17 \(\frac{22}{7}\)
d = 5.41 ft.
Find the indicated measure.
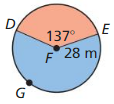
Question 3.
arc length of \(\widehat{P Q}\)
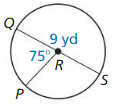
Answer:
Arc length of \(\widehat{P Q}\) is 5.887
Explanation:
Based on the information given in the figure,
\(\widehat{P Q}\) = \(\frac { 75 }{ 360 } \) . π(9)
where as π is 3.14
\(\widehat{P Q}\) = 0.208 x 28.26
\(\widehat{P Q}\) = 5.887
Question 4.
circumference of ⊙N
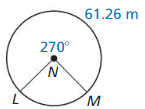
Answer:
Circumference = 81.68
Explanation:
Based on the information given in the figure,
arc length of LM/C = LM/360
61.26/C = 270/360
C = 81.68
Question 5.
radius of ⊙G
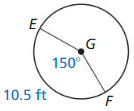
Answer:
radius = 10.09 ft
Explanation:
Based on the information given in the above figure,
arc length of EF = \(\frac { 60 }{ 360 } \) • 2πr
where as π is 3.14
10.5 = \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 } \) • 2πr
10.5 = \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 } \) • 6.28r
10.5 = 1.046r
r = 10.5/1.046
r = 10.09 ft.
Question 6.
A car tire has a diameter of 28 inches. How many revolutions does the tire make while traveling 500 feet?
Answer:
69 revolutions.
Explanation:
Given that,
A car tire has a diameter of 28 inches and travelled for 500 feet.
Circumference C = 2πr or πd
C = 28π
Distance travelled = number of revolutions x C
500 x 12 = number of revolutions x 28π
where as π is 3.14
number of revolutions = (500 x 12) ÷ (28 x 3.14)
= 6000 ÷ 88
= 68.18
Question 7.
In Example 4. the radius of the arc for a runner on the blue path is 44.02 meters, as shown in the diagram. About how far does this runner travel to go once around the track? Round to the nearest tenth of a meter.
Answer:
The arc radius for a runner on the blue path is 44.02 meters.
The diameter of the track is 2r = 2(44.02) = 88.04
The circumference of the track is πd = π(88.04) = 276.44
The runner travels around the track 276.44 cm.
Question 8.
Convert 15° to radians.
Answer:
15° = \(\frac { π }{ 12 } \) radians.
Explanation:
To convert the value of the angle in degree to its equivalent radians,
we need to multiply the given value with π/180.
\(\frac { π radians }{ 180° } \) = \(\frac { 15π }{ 180 } \) radians
= \(\frac { π }{ 12 } \) radians.
Question 9.
Convert \(\frac{4 \pi}{3}\) radians to degrees.
Answer:
240 degrees.
Explanation:
Given,
\(\frac{4 \pi}{3}\) radians.
= \(\frac{4 \pi}{3}\) radians x \(\frac { 180° }{ π radians } \)
= 60 x 4
= 240 degrees.
Exercise 11.1 Circumference and Arc Length
Vocabulary and Core Concept Check
Question 1.
COMPLETE THE SENTENCE
The circumference of a circle with diameter d is C = _______ .
Answer:
![]()
Question 2.
WRITING
Describe the difference between an arc measure and an arc length.
Answer:
An arc measure is measured in degrees.
An Arc measure is equal to the central angle that forms the intercepted arc.
An Arc length is a fraction of the circumference of the circle.
An Arc length is the distance along an arc measured in linear units.
Monitoring Progress and Modeling with Mathematics
In Exercises 3 – 10, find the indicated measure.
Question 3.
circumference of a circle with a radius of 6 inches
Answer:
circumference = 37.70 in.
Explanation:
Given,
radius = 6 in.
we know that π = 22/7 or 3.14

Question 4.
diameter of a circle with a circumference of 63 feet
Answer:
diameter = 20.05 ft
Explanation:
Given,
circumference = 63 feet,
we know that π = 22/7 or 3.141
C = πd
d = π/c
d = 63 ÷ 3.141
d = 20.05 ft
Question 5.
radius of a circle with a circumference of 28π
Answer:
radius = 14 units.
Explanation,
Given,

Question 6.
exact circumference of a circle with a diameter of 5 inches
Answer:
circumference = 15.707
Explanation:
Given,
diameter = 5 in
we know that π = 22/7 or 3.141
C = πd
C = 5 x 3.141 = 15.707
Question 7.
arc length of \(\widehat{A B}\)
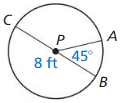
Answer:
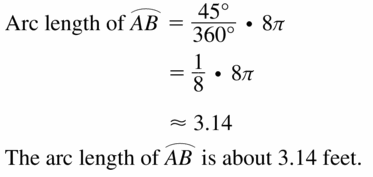
Question 8.
m\(\widehat{D E}\)
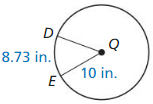
Answer:
DE = 50.01°
Explanation:
With reference to the information given in the above figure,
\(\frac { arc length of DE }{ 2πr } \) = \(\frac { DE }{ 360 } \)
\(\frac { 8.73 }{ 2π(10) } \) = \(\frac { DE }{ 360 } \)
where as π = 22/7 or 3.141
By cross multiplying on both sides, we get
DE = 50.01°
Question 9.
circumference of ⊙C
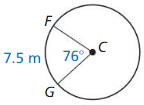
Answer:

Question 10.
radius of ⊙R
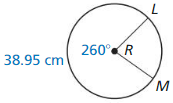
Answer:
r = 8.583 cm
Explanation:
With reference to the information given in the above figure,
\(\frac { arc length of LM }{ 2πr } \) = \(\frac { LM }{ 360 } \)
\(\frac { 38.95 }{ 2πr } \) = \(\frac { 260 }{ 360 } \)
where as π = 22/7 or 3.141
By cross multiplying on both sides, we get
r = 8.583 cm
Question 11.
ERROR ANALYSIS
Describe and correct the error in finding the circumference of ⊙C.
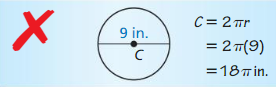
Answer:

Question 12.
ERROR ANALYSIS
Describe and correct the error in finding the length of \(\widehat{G H}\).
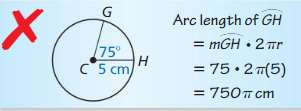
Answer:
The length of \(\widehat{G H}\) = 13.08 cm
Explanation:
with reference to the above data given,
\(\frac { arc length of GH }{ 2πr } \) = \(\frac { m GH }{ 360 } \)
\(\widehat{G H}\). = \(\frac { 5 }{ 24 } \) . 2π(10)
= 13.08 cm
Question 13.
PROBLEM SOLVING
A measuring wheel is used to calculate the length of a path. The diameter of the wheel is 8 inches. The wheel makes 87 complete revolutions along the length of the path. To the nearest foot, how long is the path?

Answer:

Question 14.
PROBLEM SOLVING
You ride your bicycle 40 meters. How many complete revolutions does the front wheel make?

Answer:
19.58 revolutions.
Estimate: 20 revolutions.
Explanation:
with reference to the data given in the figure,
Circumference of the front wheel = 2πr
radius = 32.5 cm
= 2π(32.5)
= 65π cm
Distance covered = 40 m
convert meters to centimeters.
40 x 100 = 4000 cm
Number of revolutions = \(\frac { 4000 }{ 65π } \)
we know that π= 22/7 or 3.141
So, number of revolutions = 19.58
In Exercises 15-18 find the perimeter of the shaded region.
Question 15.
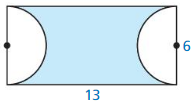
Answer:

Question 16.
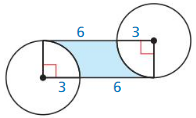
Answer:
12 π
Explanation:
We know that,
Perimeter of a circle = 2π
Given,
Two horizontal edges are 2 . 3 = 6
Circumference of circle = 2π
c = 2π(3)
c = 6π
So, the perimeter of the shaded region = 6 + 6π or 12π
Question 17.
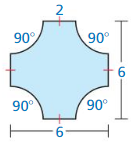
Answer:
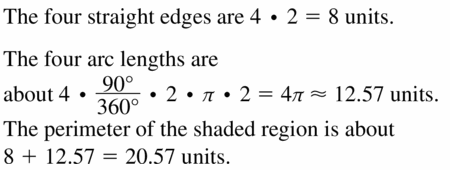
Question 18.
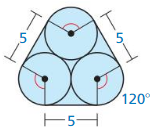
Answer:
Length of the shape excluding three arcs = 5 + 5 + 5 = 15
Radius of the arc = 2.5
Arc length = 120/360 × 2π(2.5)
= 1/3 × 5 × 3.14
= 5 × 3.14/3
= 5.23
perimeter of the shaded region = length of shape excluding three arcs + three times arc length
= 15 + 3(5.23)
= 15 + 15.69
= 30.69
In Exercises 19 – 22, convert the angle measure.
Question 19.
Convert 70° to radians.
Answer:
\(\frac { 7π }{ 18 } \) radians.
Explanation:
Angle in Radians × 180°/π = Angle in Degrees
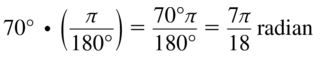
Question 20.
Convert 300° to radians.
Answer:
\(\frac { 5π }{ 3 } \) radians.
Explanation:
Angle in Radians × 180°/π = Angle in Degrees.
Given, 300 degrees.
300 • (\(\frac { π }{ 180 } \))
\(\frac { 10π }{ 6 } \) radians
= \(\frac { 5π }{ 3 } \) radians.
Question 21.
Convert \(\frac{11 \pi}{12}\) radians to degrees.
Answer:
165 degrees.
Explanation:
Given,
\(\frac{11 \pi}{12}\) radians
We know that,
Radian measure × (180°/π).
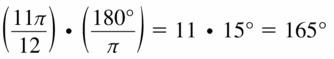
Question 22.
Convert \(\frac{\pi}{8}\) radian to degrees.
Answer:
22.5 degrees.
Explanation:
Given,
\(\frac{11 \pi}{8}\) radians
We know that,
Radian measure × (180°/π).
\(\frac { π }{ 8 } \) • \(\frac { 180 }{ π } \))
180/8 = 22.5°
Question 23.
PROBLEM SOLVING
The London Eye is a Ferris wheel in London, England, that travels at a speed of 0.26 meter per second. How many minutes does it take the London Eye to complete one full revolution?
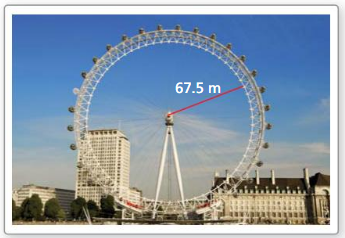
Answer:
Question 24.
PROBLEM SOLVING
You are planning to plant a circular garden adjacent to one of the corners of a building, as shown. You can use up to 38 feet of fence to make a border around the garden. What radius (in feet) can the garden have? Choose all that apply. Explain your reasoning.
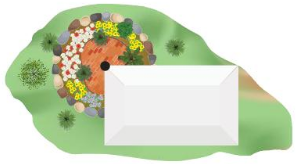
(A) 7
(B) 8
(C) 9
(D) 10
Answer:
None of the above is applied.
Explanation:
Given,
38 feet of fence to make a border around the garden.
C = 38 ft
C = 2πr
where as π is 22/7 or 3.141
38 = 2 x 3.141r
r = 38/6.282
r = 6.04
In Exercises 25 and 26, find the circumference of the circle with the given equation. Write the circumference in terms of π
Question 25.
x2 + y2 = 16
Answer:
8π units.
Explanation:
Given,
x2 + y2 = 16
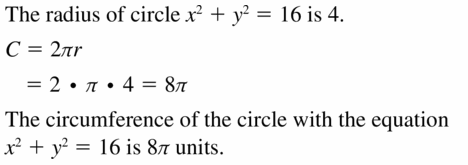
Question 26.
(x + 2)2 + (y – 3)2 = 9
Answer:
6π units.
Explanation:
Given,
(x + 2)2 + (y – 3)2 = 9
The radius of circle (x + 2)² + (y – 3)² = 9 is 3
C = 2πr
= 2π(3) = 6π
The circumference of the circle is 6π units.
Question 27.
USING STRUCTURE
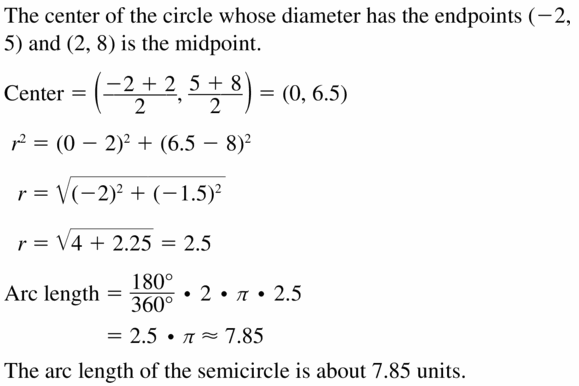
A semicircle has endpoints (- 2, 5) and (2, 8). Find the arc length of the semicircle.
Answer:
The arc length of the semicircle = 7.85
Explanation:
Question 28.
REASONING
\(\widehat{E F}\) is an arc on a circle with radius r. Let x° be the measure of \(\widehat{E F}\). Describe the effect on the length of \(\widehat{E F}\) if you (a) double the radius of the circle, and (b) double the measure of \(\widehat{E F}\).
Answer:
arc length of a circle = x/360 × 2πr
arc length of \(\widehat{E F}\) = x/360 × 2πr
(a) double the radius of the circle
x/360 × 2π(2r) = 2x/360 × 2πr
x/360 × 2π(2r) = 2arc length of \(\widehat{E F}\)
(b) double the measure of \(\widehat{E F}\)
2x/360 × 2πr = 2 × x/360 × 2πr
2x/360 × 2πr = 2arc length \(\widehat{E F}\)
Question 29.
MAKING AN ARGUMENT
Your friend claims that it is possible for two arcs with the same measure to have different arc lengths. Is your friend correct? Explain your reasoning.
Answer:
Question 30.
PROBLEM SOLVING
Over 2000 years ago, the Greek scholar Eratosthenes estimated Earth’s circumference by assuming that the Sun’s rays were Parallel. He chose a day when the Sun shone straight down into a well in the city of Syene. At noon, he measured the angle the Sun’s rays made with a vertical stick in the city of Alexandria. Eratosthenes assumed that the distance from Syene to Alexandria was equal to about 575 miles. Explain how Eratosthenes was able to use this information to estimate Earth’s circumference. Then estimate Earth’s circumference.
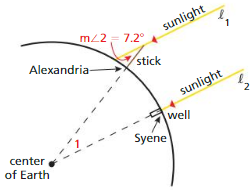
Answer:
∠1 and ∠2 are the alternate angles
m∠2 = m∠1 = 7.2°
2000 ÷ 575 = 3.47
Circumference = 2 × 3.14 × 3.47 = 21.8 + 7.2 = 29 (approx)
Question 31.
ANALYZING RELATIONSHIPS
In ⊙C the ratio of the length of \(\widehat{P Q}\) to the length of \(\widehat{R S}\) is 2 to 1. What is the ratio of m∠PCQ to m∠RCS?
(A) 4 to 1
(B) 2 to 1
(C) 1 to 4
(D) 1 to 2
Answer:
Option(B)
Explanation:
Given,
the ratio of the length of \(\widehat{P Q}\) to the length of \(\widehat{R S}\) is 2 to 1.
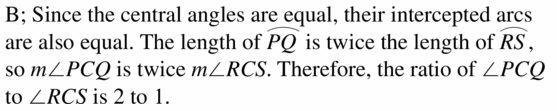
Question 32.
ANALYZING RELATIONSHIPS
A 45° arc in ⊙C and a 30° arc in ⊙P have the same length. What is the ratio of the radius r1 of ⊙C to the radius r2 of ⊙P? Explain your reasoning.
Answer:
A 45° arc in ⊙C and a 30° arc in ⊙P have the same length.
r1/r2 = 45/30 = 3/2
Thus, the ratio of the radius r1 of ⊙C to the radius r2 of ⊙P is 3/2.
Question 33.
PROBLEM SOLVING
How many revolutions does the smaller gear complete during a single revolution of the larger gear?

Answer:
2\(\frac {1}{3} \) revolutions.
Explanation:
Given,
with reference to the above information given in the figure,
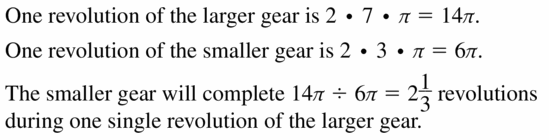
Question 34.
USING STRUCTURE
Find the circumference of each circle.
a. a circle circumscribed about a right triangle whose legs are 12 inches and 16 inches long
Answer:
Circumference = 62.83 in
Explanation:
Given,
a right triangle whose legs are 12 inches and 16 inches long.
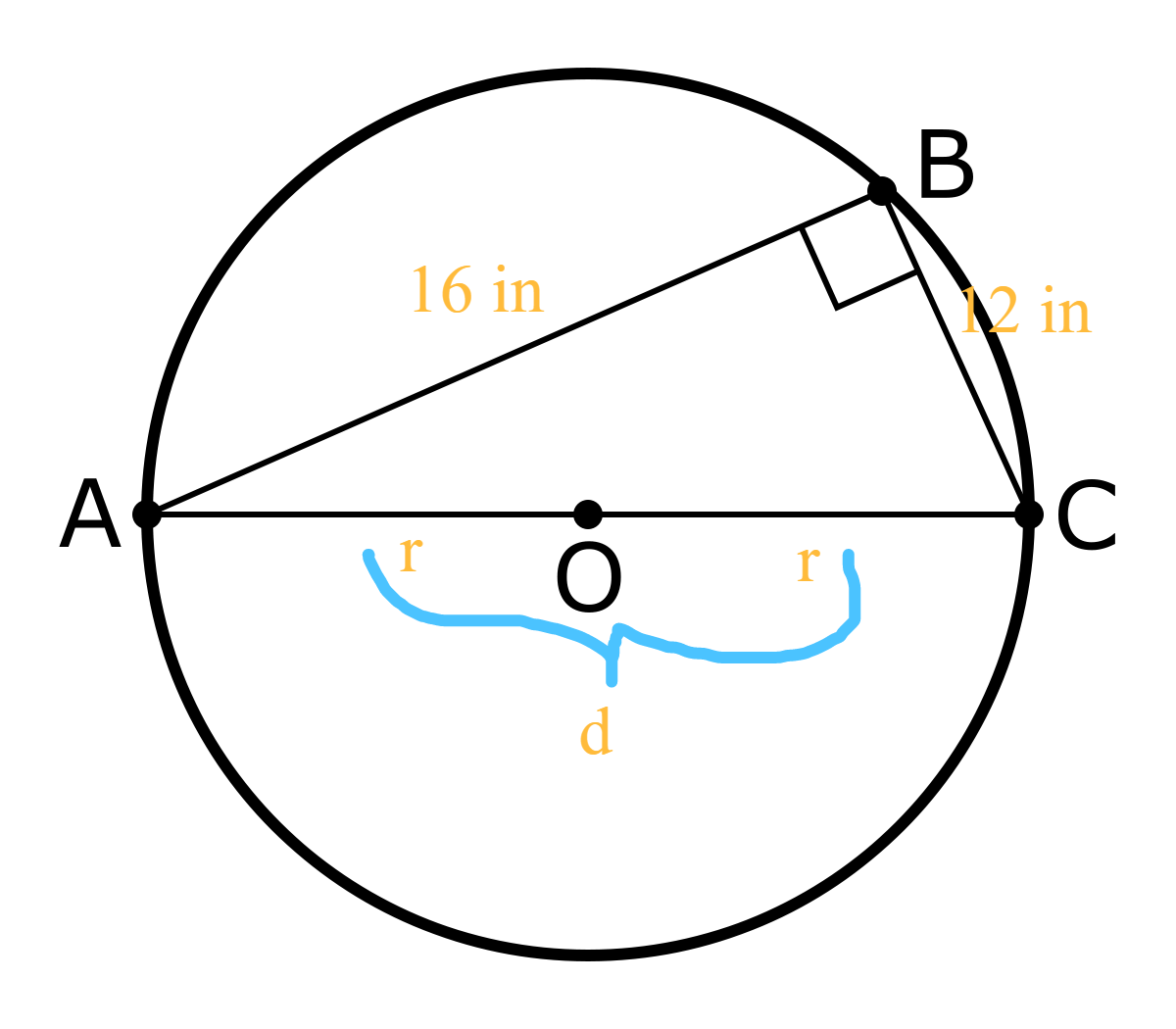
According to the Pythagoras theorem of right-angled triangle,
c² = a² + b²
c² = 12²+ 16²
c² = 144 + 256
c² = 400
c = 20 in
circumference c = dπ
where as π is 22/7 or 3.141
c = 20π
c = 62.83 in.
b. a circle circumscribed about a square with a side length of 6 centimeters
Answer:
Circumference = 26.67 cm
Explanation:
Given,
a square with a side length of 6 centimeters.
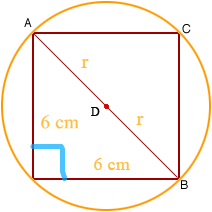
According to the Pythagoras theorem of right-angled triangle,
c² = a² + b²
d² = 6²+ 6²
d² = 36 + 36
d² = 72
d = 8.49 cm
C = dπ
C = 8.49π
where as π is 22/7 or 3.141
C = 26.67 cm
c. a circle inscribed in an equilateral triangle with a side length of 9 inches.
Answer:
Circumference = 32.67 in
Explanation:
Given,
an equilateral triangle with a side length of 9 inches.
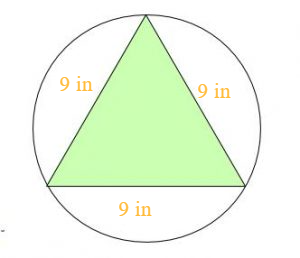
r = \(\frac { a√3 }{ 3 } \)
r = \(\frac { 9√3 }{ 3 } \)
r = 3√3 = 5.2
C = 2πr
where as π is 22/7 or 3.141
C = 2π (5.2) = 32.67 in
Question 35.
REWRITING A FORMULA
Write a formula in terms of the measure θ (theta) of the central angle in radians) that can he used to find the length of an arc of a circle. Then use this formula to find the length of an arc of a circle with a radius of 4 inches and a central angle of \(\frac{3 \pi}{4}\) radians.
Answer:
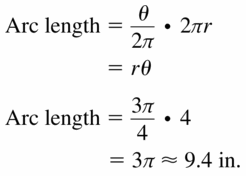
Question 36.
HOW DO YOU SEE IT?
Compare the circumference of ⊙P to the length of \(\widehat{D E}\). Explain your reasoning.
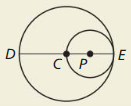
Answer:
The radius of C = 2r.
The arc length DE is subtended by a straight angle and so can be evaluated as
180/360 × 2π × 2r = 2πr
Comparing the circumference of P we can see that it is equal to the arc length of DE.
Question 37.
MAKING AN ARGUMENT
In the diagram. the measure of the red shaded angle is 30°. The arc length a is 2. Your classmate claims that it is possible to find the circumference of the blue circle without finding the radius of either circle. Is your classmate correct? Explain your reasoning.
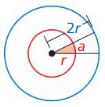
Answer:

Question 38.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
What is the measure (in radians) of the angle formed by the hands of a clock at each time? Explain your reasoning.
a. 1 : 30 P.M.
Answer:
5π/6
Explanation:
A circular clock of 12 parts of each measuring 30°
As, 360° = 2π radian
180°= π radian
in 1:30 P.M. we have 5 parts or 150°
now taking
= 150°/180° × π
=5/6π
b. 3:15 P.M.
Answer:
2π
Explanation:
As, 360° = 2π radian
180°= π radian
in 3:15 P.M. we have 12 parts or 360°
now taking
= 360°/180° × π
=2π
Hours Hand 3:15
= 3 + \(\frac {1}{4} \)
= \(\frac {12 + 1}{4} \)
= \(\frac {13}{4} \)
for 12 hr = 360
for \(\frac {13}{4} \) hr
= 360 x \(\frac {13}{4} \)
= \(\frac {13 x 360°}{4 x 12} \)
= \(\frac {13 x 15}{2} \)
= 97.5°
Minutes hand
60 minutes = 360°
15 minutes = \(\frac {360 x 15}{60} \) = 90°
97.5° – 90° = 7.5°
\(\frac {7.5 x π}{180} \)
= \(\frac {π}{180} \)
the measure (in radians) of the angle formed by the hands of a clock at each time
7.5 x
Question 39.
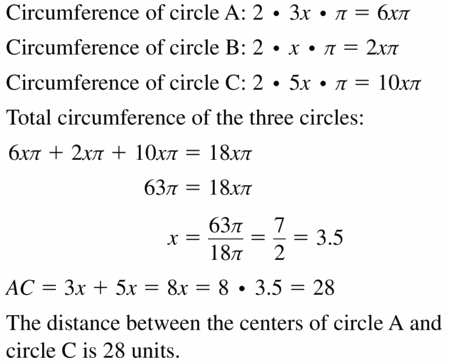
MATHEMATICAL CONNECTIONS
The sum of the circumferences of circles A, B, and C is 63π. Find AC.
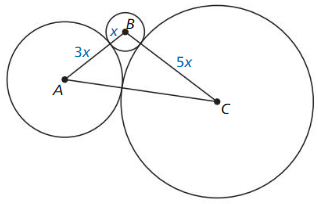
Answer:
AC = 28 units.
Explanation:
Based on the information given in the above figure,
Question 40.
THOUGHT PROVOKING
Is π a rational number? Compare the rational number \(\frac{355}{113}\) to π. Find a different rational number that is even closer π.
Answer:
No, π is not a rational number.
Explanation:
Because π can not be represented as an equivalent fraction.
where as, we know that
π = 3.14 and 355/113 = 3.14.
An accurate fraction will be starting by the value of 7 decimal places of π,
therefore 3.1415926 x x = a.
Question 41.
PROOF
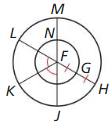
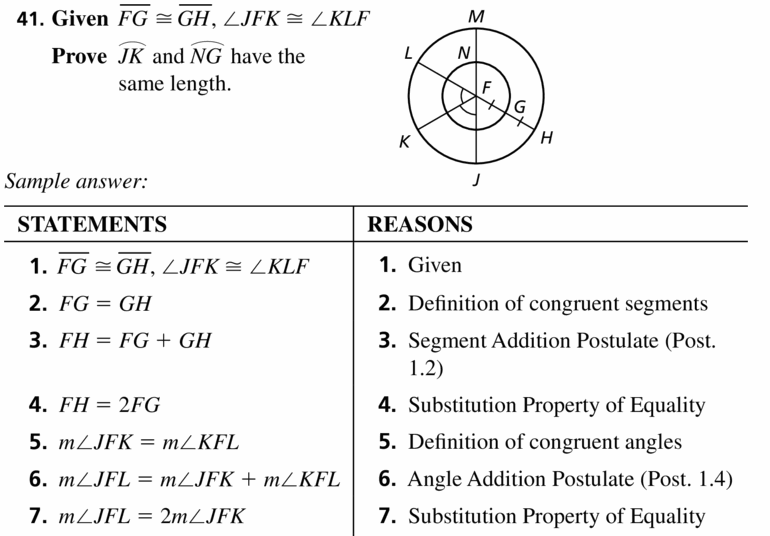
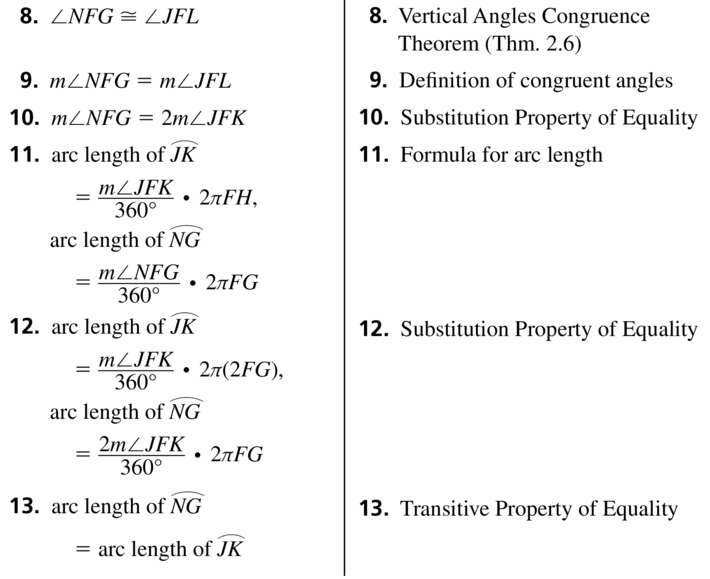
The circles in the diagram are concentric and \(\overrightarrow{F G}\) ≅ \(\overrightarrow{G H}\) Prove that \(\widehat{J K}\) and \(\widehat{N G}\) have the same length.
Answer:
Yes, the lengths are same.
Explanation:
Given,
\(\overrightarrow{F G}\) ≅ \(\overrightarrow{G H}\)
\(\widehat{J K}\) and \(\widehat{N G}\) have also the same length as
explained below,
Question 42.
REPEATED REASONING
\(\overline{A B}\) is divided into four congruent segments, and semicircles with radius r are drawn.
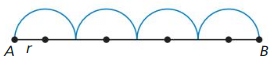
a. What is the sum of the four arc lengths?
Answer:
360/2 = 180 degrees
Then the arc length of 1 semicircle is
180/360 × 2πr
1/2 × 2πr = πr
Therefore the arc length of 4 semicircles is 4 × πr = 4πr
b. What would the sum of the arc lengths be if \(\overline{A B}\) was divided into 8 congruent segments? 16 congruent segments? n congruent segments? Explain your reasoning.
Answer:
360/2 = 180 degrees
Then the arc length of 1 semicircle is
180/360 × 2π(r/2)
1/2 × πr = πr/2
Therefore the arc length of 8 semicircles will be
8 × πr/2 = 4πr
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
Find the area of the polygon with the given vertices.
Question 43.
X(2, 4), Y(8, – 1), Z(2, – 1)
Answer:
Area = 15 sq units.
Explanation:
Given,
X(2, 4), Y(8, – 1), Z(2, – 1)
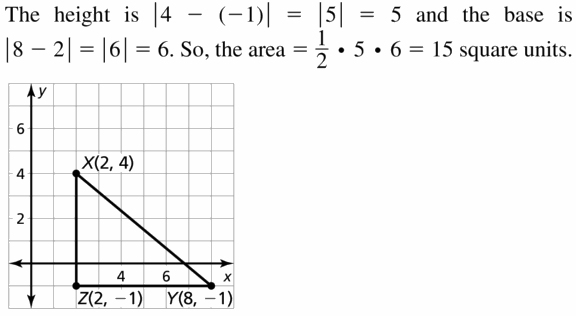
Question 44.
L(- 3, 1), M(4, 1), N(4, – 5), P(- 3, – 5)
Answer:
Area = 42 sq units.
Explanation:
Given,
L(- 3, 1), M(4, 1), N(4, – 5), P(- 3, – 5)
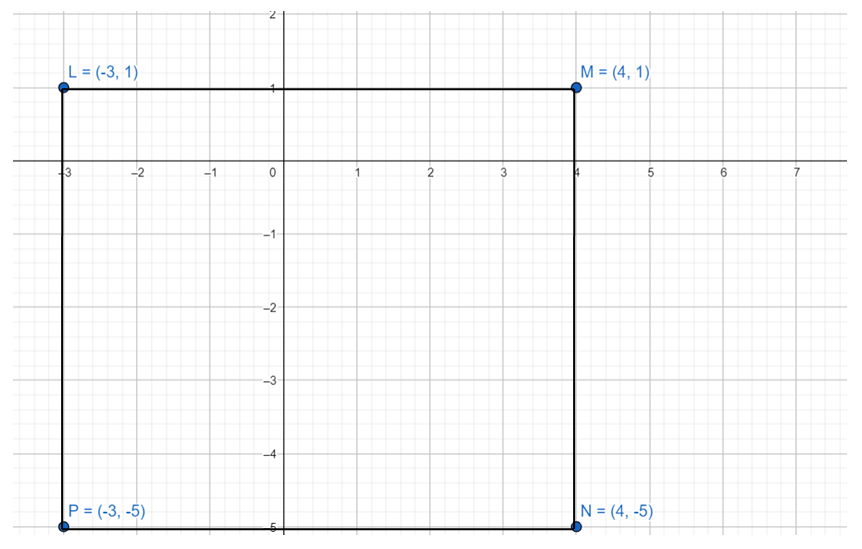
LP = √(-3 + 3)² + (-5 – 1)² = 6
PN = √(4 + 3)² + (-5 + 5)² = 7
MN = √(4 – 4)² + (-5 – 1)² = 6
LM = √(4 + 3)² + (1 – 1)²= 7
Area = 6 x 7 = 42 units.
11.2 Areas of Circles and Sectors
Exploration 1
Finding the Area of a Sector of a Circle
Work with a partner: A sector of a circle is the region bounded by two radii of the circle and their intercepted arc. Find the area of each shaded circle or sector of a circle.
a. entire circle
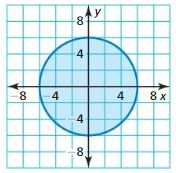
Answer:
The Formula for the area of the sector is πr²(θ/360)
r = 4
θ = 360 degrees.
Arc length = π(4)²(360/360)
= π(16)(360/360)
= 16π
= 50.24 sq. cm
b. one – fourth of a circle
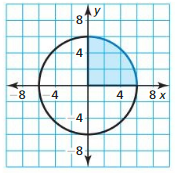
Answer:
The Formula for the area of the sector is πr²(θ/360)
r = 5
θ = 90 degrees.
Arc length = π(5)²(90/360)
= π(25)(90/360)
= 6.25π
= 19.625 sq. cm
c. seven – eighths of a circle.
Answer:
The Formula for the area of the sector is πr²(θ/360)
r = 2
θ = 315 degrees.
Arc length = π(4)²(360/360)
= π(4)(315/360)
= 3.5π
= 10.99 sq. cm
d. two – thirds of a circle
Answer:
The Formula for the area of the sector is πr²(θ/360)
r = 8
θ = 230 degrees.
Arc length = π(8)²(230/360)
= π(64)(230/360)
= 40.88π
= 128.36 sq. cm
Exploration 2
Finding the Area of a Circular Sector
Work with a partner: A center pivot irrigation system consists of 400 meters of sprinkler equipment that rotates around a central pivot point at a rate of once every 3 days to irrigate a circular region with a diameter of 800 meters. Find the area of the sector that is irrigated by this system in one day.
REASONING ABSTRACTLY
To be proficient in math, you need to explain to yourself the meaning of a problem and look for entry points to its solution.

Answer:
Communicate Your Answer
Question 3.
How can you find the area of a sector of a circle?
Answer:
The formula for sector area is simple, multiply the central angle by the radius squared, and divide by 2
Area of a sector = θ/360 × πr²
Question 4.
In Exploration 2, find the area of the sector that is irrigated in 2 hours.
Answer:
Lesson 11.2 Areas of Circles and Sectors
Monitoring progress
Question 1.
Find the area of a circle with a radius of 4.5 meters.
Answer:
A = π(4.5)² = 20.25π
Explanation:
Given,
radius = 4.5m
Area of circle = πr²
A = π(4.5)²
= 20.25π
Question 2.
Find the radius of a circle with an area of 176.7 square feet.
Answer:
r = 7.499 ft.
Explanation:
Given,
A = 176.7 sq ft.
Area of a circle = πr²
176.7 = πr²
where as π = 22/7
r² = 176.7 x 7/22
r² = 56.24
r = 7.499
Question 3.
About 58,000 people live in a region with a 2-mile radius. Find the population density in people per square mile.
Answer:
The population density is about 4615.49 people per square mile.
Explanation:
Given,
About 58,000 people live in a region with a 2-mile radius.
So, radius = 2 miles.
A = πr²
= π • 2²
= 4π
Population density = \(\frac { number of people }{ area of land } \)
= \(\frac { 58000 }{ 4π } \)
where as π = 22/7 or 3.141
= 4615.49 sq miles.
Question 4.
A region with a 3-mile radius has a population density of about 1000 people per square mile. Find the number of people who live in the region.
Answer:
The number of people who live in the region are 28274.
Explanation:
Given,
A region with a 3-mile radius has a population density of about 1000 people per sq mile.
So, radius = 3 miles.
A = πr²
= π • 3²
= 9π
Population density = \(\frac { number of people }{ area of land } \)
Number of people = 1000 x 9π
where as π = 22/7 or 3.141
Number of people = 9000 x 3.141
= 28274 people.
Find the indicated measure
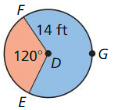
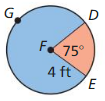
Question 5.
area of red sector
Answer:
The area of red sector = 205.25 sq ft.
Explanation:
Based on the information given in the above figure,
m∠FDE = 120°, FE = 120° and FGE = 360° – 120° = 240°
Area of red sector = \(\frac { FE }{ 360° } \) • πr²
= \(\frac { 120 }{ 360° } \) • π(14²)
where as π = 22/7 or 3.141
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \) • 3.141 x 196
= \(\frac { 615.636 }{ 3 } \)
= 205.25
Question 6.
area of blue sector
Answer:
Area of blue sector = 410.5 sq ft.
Explanation:
Based on the information given in the above figure,
Area of blue sector = \(\frac { FGE }{ 360° } \) • πr²
= \(\frac { 240 }{ 360° } \) • π(14²)
where as π = 22/7 or 3.141
= \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 } \) • 3.141 x 196
= 410.5 sq ft.
Question 7.
Find the area of ⊙H.
Answer:
Area of ⊙H = 907.92 sq cm
Explanation:
Based on the information given in the above figure,
Area of sector FHG =\(\frac { FG }{ 360° } \) • Area of ⊙H
214.37 = \(\frac { 85 }{ 360° } \) • Area of ⊙H
214.37 = \(\frac { 17 }{ 72 } \) • Area of ⊙H
Area of ⊙H = 907.92 sq cm
Question 8.
Find the area of the figure.
Answer:
A = 43.74 sq m
Explanation:
Based on the information given in the above figure,
Area of triangle = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) • 7 • 7
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) 49
= 24.5 sq m
Area of semi circle = πr²/2
radius = 3.5, π = 3.141
= π(3.5)²/2
= 19.242255
Area of the figure = Area of triangle + Area of semi circle
= 24.5 + 19.24 = 43.74 sq m
Question 9.
If you know the area and radius of a sector of a circle, can you find the measure of the intercepted arc? Explain.
Answer:
Exercise 11.2 Areas of Circles and Sectors
Vocabulary and Core Concept Check
Question 1.
VOCABULARY
A(n) ____________ of a circle is the region bounded by two radii of the circle and their intercepted arc.
Answer:

Question 2.
WRITING
The arc measure of a sector in a given circle is doubled. will the area of the sector also be doubled? Explain our reasoning.
Answer:
Yes,
Explanation:
Given that,
The arc measure of a sector in a given circle is doubled.
Area of sector with arc measure x and radius r is s = π/180(xr)
If x becomes double,
then s1 = π/180(2xr) = 2s
Therefore, the arc measure doubles, area of the sector also doubles.
Monitoring Progress and Modeling with Mathematics
In Exercise 3 – 10, find the indicated measure,
Question 3.
area of ⊙C
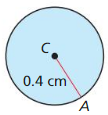
Answer:
Area = 0.50 sq cm
Explanation:
Given,
radius = 0.4 cm; π = 3.141
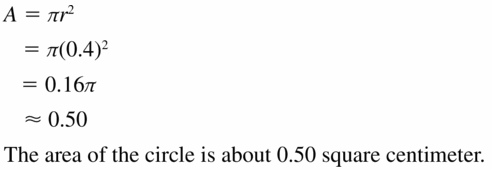
Question 4.
area of ⊙C
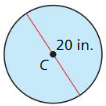
Answer:
Area of ⊙C = 100π sq in or 314.1 sq in.
Explanation:
Given, diameter = 20 in
Radius = d/2
r = 20/2 = 10 in.
Area of circle = πr²
A = π(10)²
A = 100π sq in or 314.1 sq in.
Question 5.
area of a circle with a radius of 5 inches
Answer:
Area of a circle = 78.54 sq in.
Explanation:
Given,
radius = 5 in
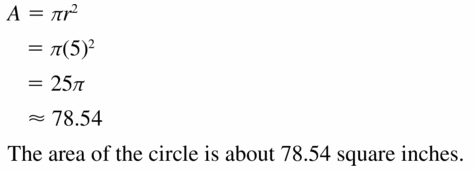
Question 6.
area of a circle with a diameter of 16 feet
Answer:
Area of a circle = 64π or 201.024 sq ft.
Explanation:
Given,
diameter = 16 ft.
d = 2r
Area of circle = πr²
= (π/4)d²
= (π/4)16² = 64π or 201.024 sq ft.
Question 7.
radius of a circle with an area of 89 square feet
Answer:
r = 5.32 ft
Explanation:
Given, A = 89 sq ft, π = 3.141

Question 8.
radius of a circle with an area of 380 square inches
Answer:
r = 10.99 in.
Explanation:
Given,
A = 380 sq in, π = 3.141 or 22/7
A = πr²
380 = 3.141r²
r² = (380 x 7)÷ 22
r² = 120.9
r = 10.99 in.
Question 9.
diameter of a circle with an area of 12.6 square inches
Answer:
d= 4 in.
Explanation:
Given,
A = 12.6 sq in, π = 3.141 or 22/7
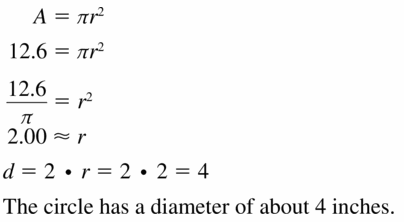
Question 10.
diameter of a circle with an area of 676π square centimeters
Answer:
diameter = 52 cm.
Explanation:
Given,
Area = 676π square centimeters, π = 3.141 or 22/7
A = (π/4)d²
d² = A ÷ (π/4)
d² = 676π ÷ (π/4)
d² = 676 x 4
d² = 2704
d = 52 cm
In Exercises 11 – 14, find the indicated measure.
Question 11.
About 210,000 people live in a region with a 12-mile radius. Find the population density in people per square mile.
Answer:

Question 12.
About 650,000 people live in a region with a 6-mile radius. Find the population density in people per square mile.
Answer:
The population density is about 5747 people per square mile.
Explanation:
Given,
About 650,000 people live in a region with a 6-mile radius.
So, radius = 6 mile.
Area of region = π(6)²
A = 36π
Population density = \(\frac { Number of people }{ area of land } \)
= \(\frac { 650,000 }{ 36π } \)
where π is 22/7 or 3.141
= 5747.2 people.
Question 13.
A region with a 4-mile radius has a population density of about 6366 people per square mile. Find the number of people who live in the region.
Answer:
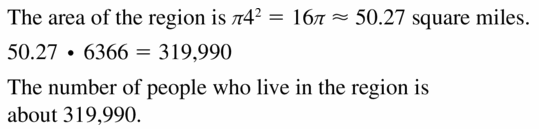
Question 14.
About 79,000 people live in a circular region with a population density of about 513 people per square mile. Find the radius of the region.
Answer:
The radius of the region is 7.
Explanation:
Given,
About 79,000 people live in a circular region,
with a population density of about 513 people per square mile.
Population density = \(\frac { Number of people }{ area of land } \)
513 = \(\frac { 79,000 }{ πr² } \)
πr² = 153.99
r² = 153.99π
where πis 3.141 or 22/7
r² = 49
r = 7
In Exercises 15-18 find the areas of the sectors formed by∠DFE.
Question 15.
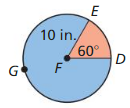
Answer:
Area = 261.80
Explanation:
Given,
with reference to the information given in the above figure,
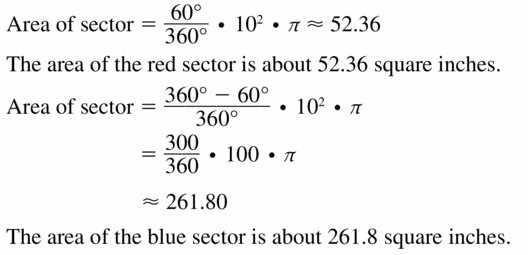
Question 16.
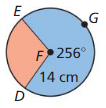
Answer:
Area of blue sector = 437.86 sq cm
Area of red sector = 177.88 sq cm
Explanation:
Given,
with reference to the information given in the above figure,
Area of sector = \(\frac { 104° }{ 360° } \) • π(14)²
where π = 22/7 or 3141
= \(\frac { 104° }{ 360° } \) • 3.141 x 49
= 0.288 x 50.256
= 177.88
Area of red region is 177.88 sq cm
Area of blue region = \(\frac { 256° }{ 360° } \) • π(14)²
= \(\frac { 256° }{ 360° } \) • 3.141 x 49
= 0.711 • 50.256
= 437.86 sq cm
Question 17.
Answer:

Question 18.
Answer:
Area of red region is 10.471 sq ft
Area of the blue region is 39.79 sq ft
Explanation:
Given,
with reference to the information given in the above figure,
Area of sector = \(\frac { 75° }{ 360° } \) • π(4)²
= \(\frac { 15° }{ 72° } \) • 3.141 x 16
= 0.2083 x 50.256
= 10.471
Area of red region is 10.471 sq ft
Area of blue region = \(\frac { 285° }{ 360° } \) • π(4)²
= \(\frac { 57° }{ 72° } \) • 3.141 x 16
= 0.7916 • 50.256
= 39.79 sq ft
Question 19.
ERROR ANALYSIS
Describe and correct the error in finding. the area of the circle.
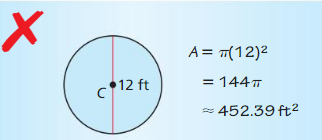
Answer:

Question 20.
ERROR ANALYSIS
Describe and correct the error in finding the area of sector XZY when the area of ⊙Z is 255 square feet.
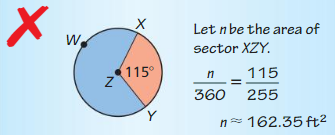
Answer:
n = 81.458 sq ft
Explanation:
Given,
Area of ⊙Z is 255 square feet
A = πr²
255 = πr²
where π is 22/7 or 3.141
So, r = 9
Area of sector XZY = \(\frac { 115 }{ 360 } \) • 255
A = 0.3194 x 255
n = 81.458 sq ft
In Exercises 21 and 22, the area of the shaded sector is show. Find the indicated measure.
Question 21.
area of ⊙M
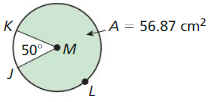
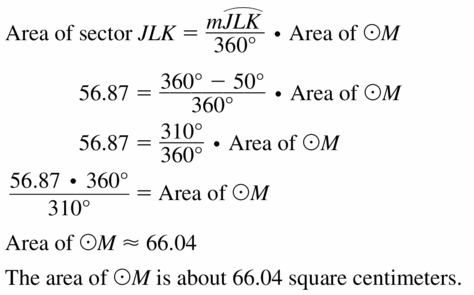
Answer:
Area = 66.04 sq cm
Explanation:
Based on the information given in the above figure,
Question 22.
radius of ⊙M
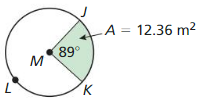
Answer:
radius of ⊙M = 3.98m
Explanation:
Based on the information given in the above figure,
Area of region = \(\frac { 89 }{ 360 } \) . Area of ⊙M
12.36 = \(\frac { 89 }{ 360 } \) . Area of ⊙M
Area of ⊙M = 49.99
πr² = 49.99
r = 3.98
In Exercises 23 – 28, find the area of the shaded region.
Question 23.
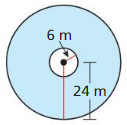
Answer:
Area of shaded region = 1696.46 sq m
Explanation:
Based on the information given in the above figure,

Question 24.
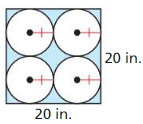
Answer:
The area of the shaded region is 85.840 sq in.
Explanation:
Given,
Area of square = 20² = 20 x 20 = 400
Diameter of one circle = 10
radius of one circle = d/2 = 10/ 2 = 5 in
Area of one circle = π(5)²
where π is 3.141 or 22/7
= 3.141 x 25 = 78.53
Areas of four circle = 314.159
Area of shaded region = 400 – 314.159 = 85.840
Question 25.
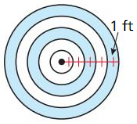
Answer:
The area of shaded region is 43.98 sq ft.
Explanation:
Based on the information given in the above figure,


Question 26.
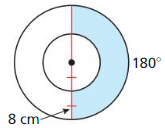
Answer:
The area of shaded region is 301.59
Explanation:
Based on the information given in the above figure,
The radius of smaller circle is 8 cm
The radius of bigger circle is 16 cm
Area of smaller semicircle = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(π(8)²)
where π is 3.141 or 22/7
= 0.5 x 3.141 x 64 = 100.53
Area of lager semicircle = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(π(16)²) = 402.123
= 0.5 x 3.141 x 256
Area of shaded region = 402.123 – 100.53 = 301.59
Question 27.
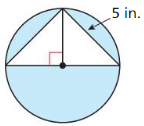
Answer:
The area of shaded region is 26.77 sq in.
Explanation:
Based on the information given in the above figure,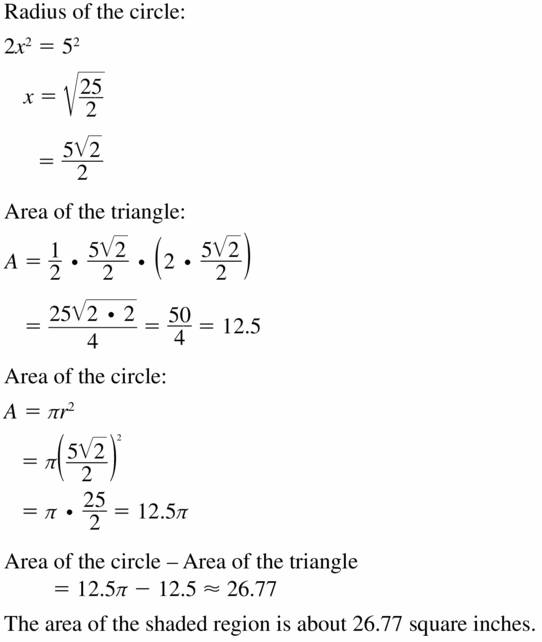
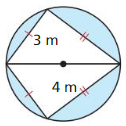
Question 28.
Answer:
Area of shaded region = 7.63 sq m.
Explanation:
According to the Pythagoras theorem,
c² = a² + b²
Given,
side lengths are 3 and 4.
c² = 3² + 4²
c² = 9 + 16
c² = 25
c = 5
Radius = 2.5
Area of circle = πr²
A = π(2.5)²
A = 19.63
where π 22/7 or 3.141
Area of triangle = (3 x 4)/2
= 12/2 = 6
Area of shaded region = 19.63 – 12 = 7.63 sq m.
Question 29.
PROBLEM SOLVING
The diagram shows the shape of a putting green at a miniature golf course. One part of the green is a sector of a circle. Find the area of the putting green.
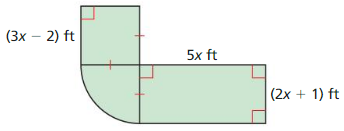
Answer:
Area = 192.48 sq ft.
Explanation:
Based on the information given in the above figure,

Question 30.
MAKING AN ARGUMENT
Your friend claims that if the radius of a circle is doubled, then its area doubles. Is your friend correct? Explain your reasoning.
Answer:
No, friend is not correct.
Explanation:
Given,
if the radius of a circle is doubled,
whether its area doubles.
Area of circle with radius r = πr²
Area of circle with radius 2r = π(2r)² = 4πr²
Therefore, doubling the radius quadruples the area.
Question 31.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
The diagram shows the area of a lawn covered by a water sprinkler.
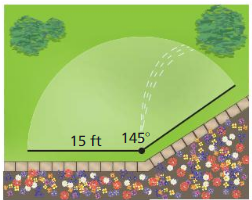
a. What is the area of the lawn that is covered by the sprinkler?
b. The water pressure is weakened so that the radius is 12 feet. What is the area of the lawn that will be covered?
Answer:

Question 32.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
The diagram shows a projected beam of light from a lighthouse.
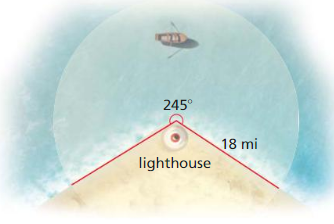
a. What is the area of water that can be covered by the light from the lighthouse?
Answer:
Area = 325.15 sq mi.
Explanation:
Based on the information given in the above figure,
Area = \(\frac { 115 }{ 360 } \) x π(18)²
where π is 3.141 or 22/7
= 0.3194 x 3.141 x 324
= 0.3194 x 1017.684
= 325.15 sq mi
b. What is the area of land that can be covered by the light from the lighthouse?
Answer:
Area =
692.72 sq mi
Explanation:
Based on the information given in the above figure,
Area = \(\frac { 245 }{ 360 } \) x π(18)²
where π is 3.141 or 22/7
= 0.6805 x 3.141 x 324
= 0.6805 x 1017.684
= 692.72 sq mi
Question 33.
ANALYZING RELATIONSHIPS
Look back at the Perimeters of Similar Polygons Theorem (Theorem 8.1) and the Areas of Similar PoIyons Theorem (Theorem 8.2) in Section 8.1. How would you rewrite these theorems to apply to circles? Explain your reasoning.
Answer:

Question 34.
ANALYZING RELATIONSHIPS
A square is inscribed in a circle. The same square is also circumscribed about a smaller circle. Draw a diagram that represents this situation. Then find the ratio of the area of the larger circle to the area of the smaller circle.
Answer:
The ratio of the area of larger circle to the smaller circle = 2.
Explanation:
Assigning a variable to the radius of the inner circle.
The area of the circle is πr²
It can be seen that the side length of square is twice this radius.
So, the side length of the square is 2r.
We observe that the diagonal of the square is diameter of outer circle.
So, length of the diagonal of the circle = 2r√2.
outer circle radius = r√2
Area of outer circle 2πr²
Therefor the ratio of the area of larger circle to the smaller circle = 2.
Question 35.
CONSTRUCTION
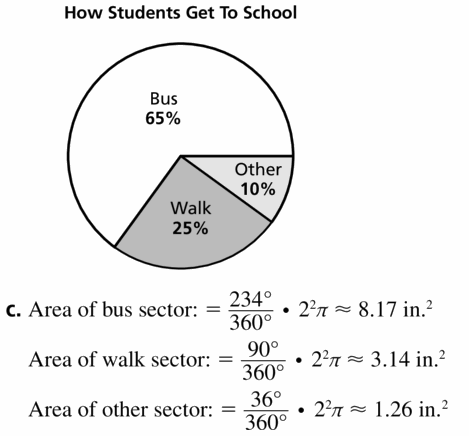
The table shows how students get to school.
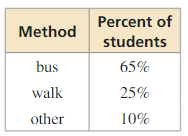
a. Explain why a circle graph is appropriate for the data.
b. You will represent each method by a sector of a circle graph. Find the central angle to use for each sector. Then construct the graph using a radius of 2 inches.
c. Find the area of each sector in your graph.
Answer:

Question 36.
HOW DO YOU SEE IT?
The outermost edges of the pattern shown form a square. If you know the dimensions of the other square, is it possible to compute the total colored area? Explain.

Answer:
Question 37.
ABSTRACT REASONING
A circular pizza with a 12-inch diameter is enough for you and 2 friends. You want to buy pizzas for yourself and 7 friends. A 10-inch diameter pizza with one topping Costs $6.99 and a 14-inch diameter pizza with one topping Costs $12.99. How many 10-inch and 14-inch pizzas should you buy in each situation? Explain.
a. You want to spend as little money as possible.
b. You want to have three pizzas. each with a different topping, and spend as little money as possible.
C. You want to have as much of the thick outer crust as possible.
Answer:

Question 38.
THOUGHT PROVOKING
You know that the area of a circle is πr2. Find the formula for the area of an ellipse, shown below.
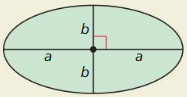
Answer:
Ellipse area = πab
Explanation:
The area of the ellipse is the product of π, the length of the semi-major axis, and the length of the semi-minor axis. Let us explore a bit more about this shape while discussing its area, and the formula for the area of the ellipse
Question 39.
MULTIPLE REPRESENTATIONS
Consider a circle with a radius of 3 inches.
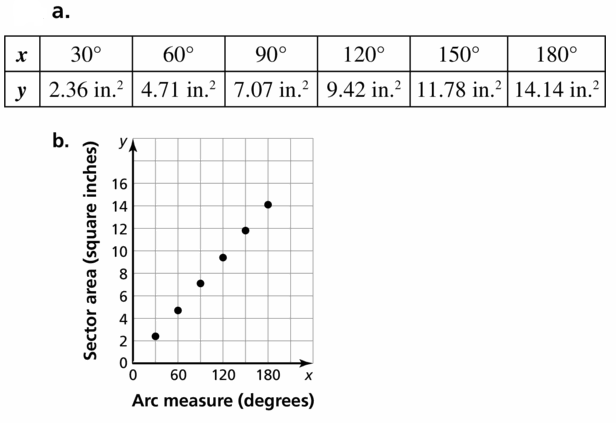
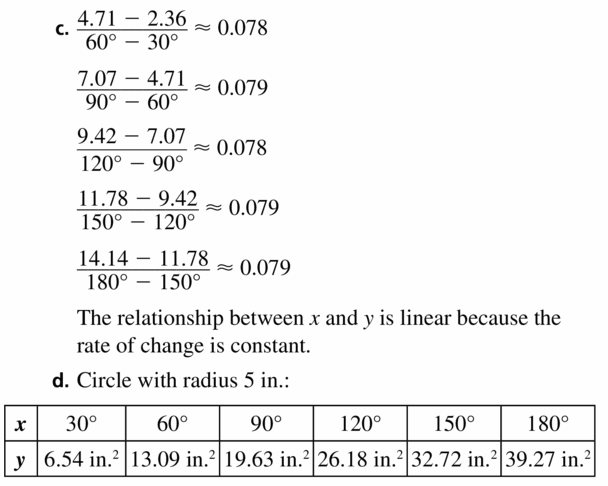
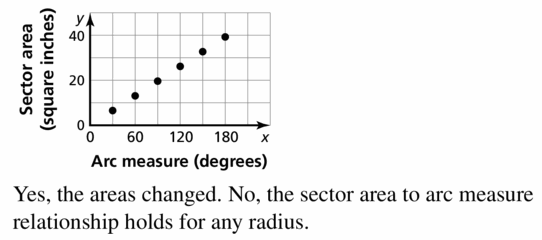
a. Complete the table, where x is the measure of the arc and is the area of the corresponding sector. Round your answers to the nearest tenth.

b. Graph the data in the table.
c. Is the relationship between x and y linear? Explain.
d. If parts (a) – (c) were repeated using a circle with a radius of 5 inches, would the areas in the table change? Would your answer to part (c) change? Explain your reasoning.
Answer:
Question 40.
CRITICAL THINKING
Find the area between the three congruent tangent circles. The radius of each circle is 6 inches.
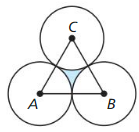
Answer:
Question 41.
PROOF
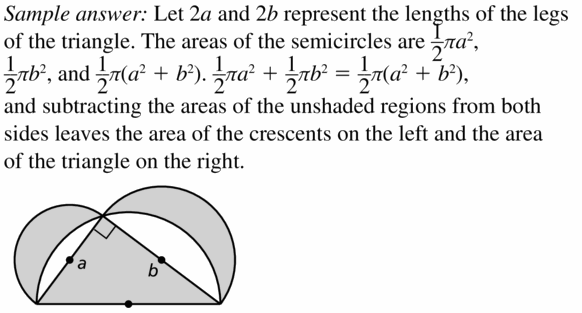
Semicircles with diameters equal to three sides of a right triangle are drawn, as shown. Prove that the sum of the areas of the two shaded crescents equals the area of the triangle.
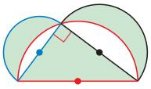
Answer:
Maintaining Mathematical proficiency
Find the area of the figure.
Question 42.
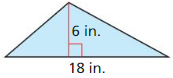
Answer:
Area = 54 sq in.
Explanation:
Given,
base = 18 in; height = 6 in
Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(base x height)
Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(18 x 6)
A = 0.5 x 108
A = 54 sq in
Question 43.
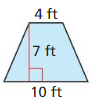
Answer:
Area = 49 sq ft.
Explanation:
Given, b1 = 4ft; b2 = 10 ft and h = 7 ft
b1 and b2 are the bases of the trapezoid and h is the height.

Question 44.
Answer:
Area = 58.5 sq in.
Explanation:
Given,
base = 18 in; height = 6 in
Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(base x height)
A = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(13 x 9)
A = 0.5 x 117
A = 58.5 sq in
Question 45.
Answer:
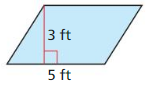
Area = 15 sq ft.
Explanation:
Given,
base = 5ft; height = 3ft

11.3 Areas of Polygons
Exploration 1
Finding the Area of a Regular Polygon
Work with a partner: Use dynamic geometry software to construct each regular polygon with side lengths of 4, as shown. Find the apothem and use it to find the area of the polygon. Describe the steps that you used.
a.
Answer:
Length = 4.
Height = 3.5
The formula for the area of the triangle is ½ x b x h
= 1/2 x 4 x 3.5
= 14/2
= 7 square cm
b.
Answer:
A = 1/4 x square root of 5(5 + 2 square root(5) x (4)²
= 1/4 x square root of 5 + 4.47 x 16
= 1/4 x square root of (9.47) x 16
= 1/4 x 3.077 x 16
= 1/4 x 49.232
= 12.308 square cm
c.
Answer:
The formula for the area of the hexagon is 3 square root(3) x s²/2
= 3 square root(3) x 16/2
= 41.56 square cm
d.
Answer:
The formula for the area of the octagon is A = 8/2 x a x h
a = length
h = height
= 8/2 x 4 x 3.5
= 8/2 x 14
= 56 square cm
Exploration 2
Writing a Formula for Area
Work with a partner: Generalize the steps you used in Exploration 1 to develop a formula for the area of a regular polygon.
REASONING ABSTRACTLY
To be proficient in math, you need to know and flexibly use different properties of operations and objects.
Answer:
Communicate Your Answer
Question 3.
How can you find the area of a regular polygon?
Answer:
The formula for the regular pentagon if only the side is known is A = 1/4 x square root of 5(5 + 2 square root(5) x (a)².
The formula for the area of the regular pentagon is 1/2 x p x a.
Where a = apothem
P = perimeter
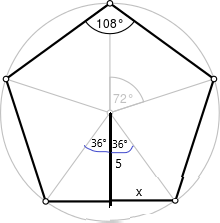
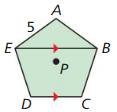
Question 4.
Regular pentagon ABCDE has side lengths of 6 meters and an apothem of approximately 4.13 meters. Find the area of ABCDE.
Answer:
The side length of the regular pentagon ABCDE is 6 meters.
The apothem of the regular pentagon is 4.13 meters.
The formula for the area of the regular pentagon is 1/2 x p x a.
Where
a = apothem
P = perimeter
The formula for the perimeter of a regular pentagon is = 5a
= 5(6) = 30
= 1/2 x 30 x 4.13
= 1/2 x 123.9
= 61.95 square cm
Lesson 11.3 Areas of Polygons
Monitoring Progress
Question 1.
Find the area of a rhombus with diagonals d1 = 4 feet and d2 = 5 feet.
Answer:
Area = 5 sq ft
Explanation:
Given,
diagonals d1 = 4 feet and d2 = 5 feet.
A = ½ × d1 × d2
Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(d₁d₂)
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(4 x 5)
= \(\frac { 20 }{ 2 } \)
= 5 sq ft.
Question 2.
Find the area of a kite with diagonals d1 = 12 inches and d1 = 9 inches.
Answer:
54 sq in.
Explanation:
Given,
diagonals d1 = 12 inches and d1 = 9 inches.
Area of kite = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(d₁d₂)
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(12 x 9)
= \(\frac { 108 }{ 2 } \)
= 54 sq in.
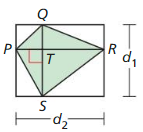
In the diagram. WXYZ is a square inscribed in ⊙P.
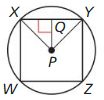
Question 3.
Identify the center, a radius, an apothem, and a central angle of the polygon.
Answer:
P is the center, PY or PX is the radius, PQ is apothem, ∠XPY is the central angle.
Explanation:
The center of a circle is the point where all the distances to the points on the circle are equal as shown in the above given figure.
So, P is the center is the center of the given figure.
The apothem of a regular polygon is a line segment connecting the center of the polygon to a midpoint of one of the sides.
So, PQ is apothem in the above given figure.
The radius of a regular polygon is a line segment connecting the center of the polygon to one of the vertices.
So, PY or PX is the radius of the given figure.
A central angle of a regular polygon is an angle whose vertex is the center and whose rays, or sides, contain the endpoints of a side of the regular polygon.
So, ∠XPY is the central angle in the above given figure.
Question 4.
Find m∠XPY, m∠XPQ, and m∠PXQ.
Answer:
m∠XPY = 90°
m∠XPQ = 45°
m∠PXQ = 45°
Explanation:
Given to find m∠XPY, m∠XPQ, and m∠PXQ.
m∠XPY = \(\frac { 360 }{ 4 } \) = 90
m∠XPQ = 90/2 = 45
m∠PXQ = 180 – (90 + 45) = 45
So, the sum of the angles in a triangle,
90° + 45° + 45° = 180°
Find the area of regular polygon
Question 5.
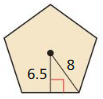
Answer:
Area = 730.8 sq units.
Explanation:
Based on the information given in the above figure,
c = √(8² + 6.5²) = 10.3
a = 20.61
Area = 0.25(√5(5+2√5) a²
Area = 0.25(√5(5+2√5) 20.61² = 730.8
Question 6.
Answer:
Area = 55377 sq units.
Explanation:
Given,
a = 7 units.
where ‘a’ is the distance from the center.
Area = \(\frac { 5a² }{ 2 } \)√(5+2√5)
= \(\frac { 5(7²) }{ 2 } \)√(5+2√5)
Area = 55377
Exercise 11.3 Areas of Polygons
Vocabulary and Core Concept Check
Question 1.
WRITING
Explain how to find the measure of a central angle of a regular polygon.
Answer:

Question 2.
DIFFERENT WORDS, SAME QUESTION
Which is different? Find “both” answers.
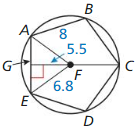
Find the radius of ⊙F.
Answer:
EF = radius = 6.8
Explanation:
We know that,
The radius of a regular polygon is a line segment connecting the center of the polygon to one of the vertices.
So, EF is the radius and ⊙F is 6.8
Find the apothem of polygon ABCDE.
Answer:
GF = apothem = 5.5
Explanation:
The apothem of a regular polygon is a line segment connecting the center of the polygon to a midpoint of one of the sides.
So, GF is apothem in the above given figure.
Therefore, the apothem of polygon ABCDE is 5.5
Find AF.
Answer:
AF = √4² + 5.5²
AF = 6.8
Find the radius of polygon ABCDE.
Answer:
AF = radius = 6.8
Explanation:
We know that,
The radius of a regular polygon is a line segment connecting the center of the polygon to one of the vertices.
So, AF is the radius of the given figure.
Monitoring Progress and Modeling with Mathematics
In Exercises 3 – 6, find the area of the kite or rhombus.
Question 3.
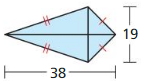
Answer:
Area = 361 sq units.
Explanation:
The formulae for both the kite and rhombus are same,
The given diagonals are 19 and 38.

Question 4.
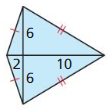
Answer:
Area = 72 sq units.
Explanation:
Given,
d₁ = 6 + 6 = 12
d₂ = 2 + 10 = 12
A = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(d₁ x d₂)
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(12 x 12)
= \(\frac { 144 }{ 2 } \)
= 72 sq units.
Question 5.
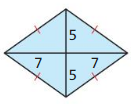
Answer:
Area = 70 sq units.
Explanation:
The formulae for both the kite and rhombus are same,
Given,
d₁ = 5 + 5 = 10
d₂ = 7 + 7 = 14

Question 6.
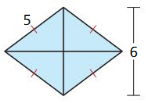
Answer:
Area = 15 sq units.
Explanation:
Given,
d₁ = 6; d₂ = 5
A = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(d₁ x d₂)
A = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(5 x 6)
= \(\frac { 30 }{ 2 } \)
= 15 sq units.
In Exercises 7 – 10, use the diagram
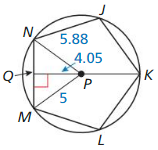
Question 7.
Identify the center of polygon JKLMN?
Answer:
![]()
Explanation:
The center of a circle is the point where all the distances to the points on the circle are equal as shown in the above given figure.
So, P is the center is the center of the given figure.
Question 8.
Identify a central angle of polygon JKLMN.
Answer:
∠NPM is the central angle of polygon JKLMN.
Explanation:
A central angle of a regular polygon is an angle whose vertex is the center and whose rays, or sides, contain the endpoints of a side of the regular polygon.
So, ∠NPM is the central angle of polygon JKLMN.
Question 9.
What is the radius of polygon JKLMN?
Answer:
![]()
Explanation:
The radius of a regular polygon is a line segment connecting the center of the polygon to one of the vertices.
So, PN and PM are the radius of the polygon JKLMN.
Question 10.
What is the apothem of polygon JKLMN?
Answer:
QP is the apothem of polygon JKLMN.
Explanation:
The apothem of a regular polygon is a line segment connecting the center of the polygon to a midpoint of one of the sides.
So, QP is apothem of the given polygon JKLMN>
In Exercises 11 – 14, find the measure of a central angle of a regular polygon with the given number of sides. Round answers to the nearest tenth of a degree, if necessary.
Question 11.
10 sides
Answer:
36 degrees.
Explanation:

Question 12.
18 sides
Answer:
20 degrees.
Explanation:
Given,
18 sides.
The measure of central angle = \(\frac { 360 }{ 18 } \) = 20
Question 13.
24 sides
Answer:
15 degrees.
Explanation:

Question 14.
7 sides
Answer:
51 degrees.
Explanation:
Given,
7 sides.
The measure of central angle = \(\frac { 360 }{ 7 } \) = 51.42
In Exercises 15 – 18, find the given angle measure for regular octagon ABCDEFGH.
Question 15.
m∠GJH
Answer:
45 degrees.
Explanation:
Given, to find the angle measure for regular octagon ABCDEFGH.
So, the number of sides in octagon is 8.
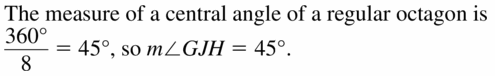
Question 16.
m∠GJK
Answer:
m∠GJK = 22.5
Explanation:
From the above we know that the angle measure for regular octagon ABCDEFGH is 45°.
m∠GJK = m∠GJH/2
m∠GJK is half of the m∠GJH
m∠GJK = 45/ 2
m∠GJK = 22.5
Question 17.
m∠KGJ
Answer:
m∠KGJ = 67.5°
Explanation:
From the above we know that the angle measure for regular octagon ABCDEFGH is 45°.
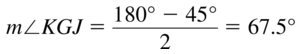
Question 18.
m∠EJH
Answer:
m∠EJH = 135
Explanation:
From the above we know that the angle measure for regular octagon ABCDEFGH is 45°.
m∠EJH = 3 x 45
m∠EJH = 135°
In Exercises 19 – 24, find the area of the regular polygon.
Question 19.
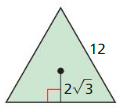
Answer:
Area = 62.35 sq units.
Explanation:
Given,
length of one side = 12 units
‘n’ is number of sides of a polygon.
So, n = 3
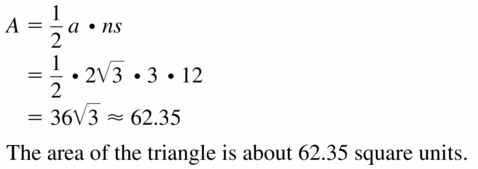
Question 20.
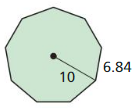
Answer:
Area = 359.9784 sq units.
Explanation:
Given,
a = 6.84
where a is distance from center of sides to the center of polygon.
Area = \(\frac { 5a² }{ 2 } \)√(5+2√5)
Area = \(\frac { 5(6.84)² }{ 2 } \)√(5+2√5)
A = \(\frac { 233.928 }{ 2 } \)√(5+2√5)
A = 116.964 x √(5+2√5)
A = 359.9784 sq units.
Question 21.
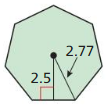
Answer:
Area = 20.83 sq units.
Explanation:

Question 22.
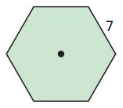
Answer:
Area = 127.30 sq units.
Explanation:
a = distance from center of sides to the center of hexagon.
Area = \(\frac { 3√3 a²}{ 2 } \)
A = \(\frac { 3√3 (7)²}{ 2 } \)
A = \(\frac { 3√3 (49)}{ 2 } \)
A = 127.30 sq units.
Question 23.
an octagon with a radius of 11 units
Answer:
Area = 341.38 sq units.
Explanation:
Given,
Radius of octagon as 11 units.
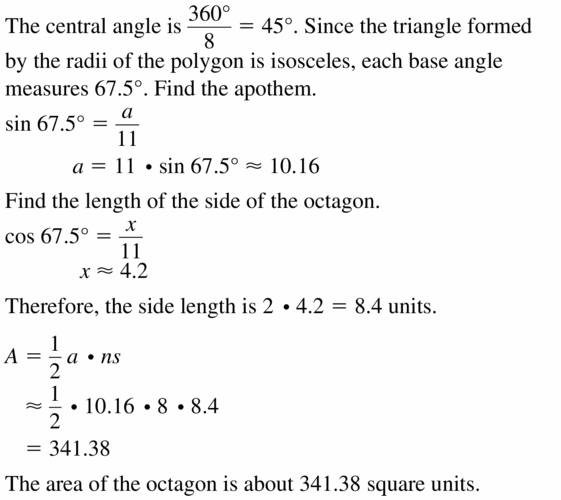
Question 24.
a pentagon with an apothem of 5 units
Answer:
A = 90.75 sq units.
Explanation:
Given,
an apothem of a pentagon is 5 units.
We know apothem (a) = 360/5 = 72
Then, divided the angle into 2 halves,
we get 2 right triangles with x = 44 and y = 36.
we know one side and all three angles of the triangle,
then find p with the tangent function.
tan y = p/a
tan 36 = p/5
tan 36 = 0.726
p = 0.726 x 5
p = 3.63
Since p is just half of the length of the side, we have to multiply it by 2.
2p = 2 x 3.63
p = 7.26 = s
Area = \(\frac { a . s. n }{ 2 } \)
‘n’ is the number of sides.
A = \(\frac { 15 x 7.26 x 5 }{ 2 } \)
A = \(\frac { 544.5 }{ 2 } \)
A = 90.75 sq units.
Question 25.
ERROR ANALYSIS
Describe and correct the error in finding the area of the kite.
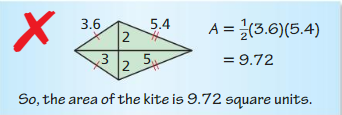
Answer:
Question 26.
ERROR ANALYSIS
Describe and correct the error in finding. the area of the regular hexagon.
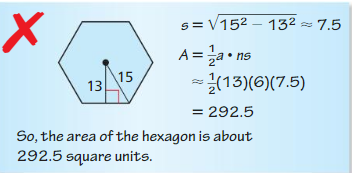
Answer:
Area = 291.72 sq units.
Explanation:
Given,
s = √15² – 13² = 7.48 or 7.5
Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(a . ns)
where ‘n’ is the number of side and ‘a’ is the distance from the center to the end point.
So, n = 6, a = 13
A = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(13 x 6 x 7.48)
A = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) x 583.44
A = 291.72 sq units.
In Exercises 27 – 30, find the area of the shaded region.
Question 27.
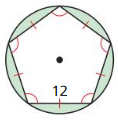
Answer:
Area = 77.85 sq units.
Explanation:
Question 28.
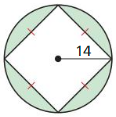
Answer:
Area of the shaded region = 223.75 sq units.
Explanation:
Given,
side length = 14 units.
Square side = diagonal/√2
d = 14 x 2 = 28 units.
s = 28/√2 = 19.79 units.
Area of square = s²
A = 19.79²
A = 392 sq units.
Area of circle = πr²
where π is 3.141 or 22/7
A = 3.141(14)²
A = 615.75
Area of the shaded region = 615.75 – 392 = 223.75 sq units.
Question 29.
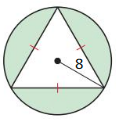
Answer:
Area of shaded region = 117.92 sq units.
Explanation:

Question 30.
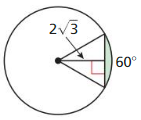
Answer:
Question 31.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
Basaltic columns arc geological formations that result from rapidly cooling lava. Giant’s Causeway in Ireland contains many hexagonal basaltic columns. Suppose the top of one of the columns is in the shape of a regular hexagon with a radius of 8 inches. Find the area of the top of the column to the nearest square inch.

Answer:
Area = 166 sq in.
Explanation:
Given, the radius of hexagon is 6 in.
where ‘n’ is the number of sides.
So, n = 6
Question 32.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
A watch has a circular surface on a background that is a regular octagon. Find the area of the octagon. Then find the area of the silver border around the circular face.
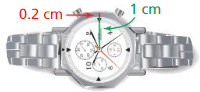
Answer:
CRITICAL THINKING
In Exercises 33 – 35, tell whether the statement is true or false. Explain your reasoning
Question 33.
The area of a regular n-gon of a fixed radius r increases as n increases.
Answer:

Question 34.
The apothem of a regular polygon is always less than the radius.
Answer:
True,
Explanation:
We know that the radius of a circle always reaches to the end of the circle,
but the apothem never does.
So, the apothem of a regular polygon is always less than the radius.
Question 35.
The radius of a regular polygon is always less than the side length.
Answer:

Question 36.
REASONING
Predict which figure has the greatest area and which has the least area. Explain your reasoning. Check by finding the area of each figure.
(A) 
(B) 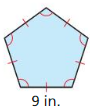
(C) 
Answer:
(B) has the highest area and (C) has the lowest area.
Explanation:
(A) area = πr²
where π is 3.141 or 22/7
r is the radius = 6.5
A = 3.141(6.5)²
A = 132.73 sq units.
(B) Area of polygon A =\(\frac {n x s x a}{2} \)
a = apothem to be calculated first
a = s/tan(36)
a = 4.5/ 0.7265 =6.2
a = 0.7265 x 4.5 = 6.2
A =\(\frac {n x s x a}{2} \)
A =\(\frac {5 x 9 x 6.2}{2} \)
area = 139.25 sq units.
(C) area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(18 x 15)
A = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) 270
A = 135 sq units.
Question 37.
USING EQUATIONS
Find the area of a regular
pentagon inscribed in a circle whose equation is given by (x – 4)2 + y + 2)2 = 25.
Answer:
Area = 59.5 sq units.
Explanation:
Given,
(x – 4)2 + y + 2)2 = 25.

Question 38.
REASONING
What happens to the area of a kite if you double the length of one of the diagonals? if you double the length of both diagonals? Justify your answer.
Answer:
If you double the length of one diagonal, then the area becomes halve.
If you double length of both diagonals, then area becomes 4 times.
Explanation:
Given, to double the length of one of the diagonals and both the diagonals.
Area of a kite = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(d₁d₂)
If you double the length of one diagonal, then d₁ = 2d₁
Area of kite = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(d₁d₂)
If you double length of both diagonals
Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(2d₁2d₂) = d₁d₂
MATHEMATICAL CONNECTIONS
In Exercises 39 and 40, write and solve an equation to find the indicated lengths. Round decimal answers to the nearest tenth.
Question 39.
The area of a kite is 324 square inches. One diagonal is twice as long as the other diagonal. Find the length of each diagonal.
Answer:

Question 40.
One diagonal of a rhombus is four times the length of the other diagonal. The area of the rhombus is 98 square feet. Find the length of each diagonal.
Answer:
The length of each diagonal is 9.89, 2.47.
Explanation:
Given,
One diagonal of a rhombus is four times the length of the other diagonal.
The area of the rhombus is 98 square feet.
d₁ = 4d₂
Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(d₁d₂)
98 = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(d₁(4d₁))
d₁ = 9.89
d₂ = 2.47
Question 41.
REASONING
The perimeter of a regular nonagon. or 9-gon, is 18 inches. Is this enough information to find the area? If so, find the area and explain your reasoning. If not, explain why not.
Answer:

Question 42.
MAKING AN ARGUMENT
Your friend claims that it is possible to find the area of any rhombus if you only know the perimeter of the rhombus. Is your friend correct? Explain your reasoning.
Answer:
No,
Explanation:
A rhombus is not a regular polygon.
So, we can not find the area of any rhombus simply by knowing the perimeter.
Question 43.
PROOF
Prove that the area of any quadrilateral with perpendicular diagonals is A = \(\frac{1}{2}\)d1d2, where d1 and d2 are the lengths of the diagonals.
Answer:
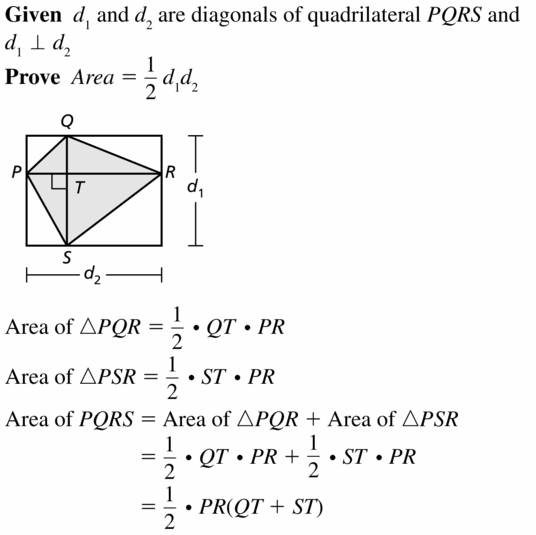
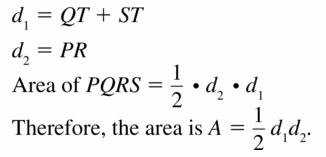
Question 44.
HOW DO YOU SEE IT?
Explain how to find the area of the regular hexagon by dividing the hexagon into equilateral triangles.
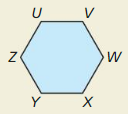
Answer:
The hexagon has 6 sides.
The hexagon is divided into 6 equilateral triangles.
The area of the equilateral triangle is (square root of 3)/4 x a²
a = side length
= (square root of 3)/4 x (6)²
= (square root of 3)/4 x 36
= 15.588 square cm.
Question 45.
REWRITING A FORMULA
Rewrite the formula for the area of a rhombus for the special case of a square with side length s. Show that this is the same as the formula for the area of a square, A = s2.
Answer:
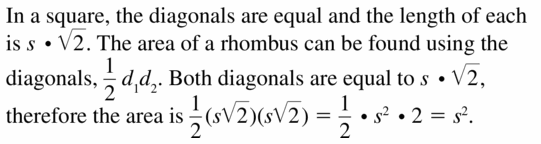
Question 46.
REWRITING A FORMULA
Use the formula for the area of a regular polygon to show that the area of an equilateral triangle can be found by using the formula A = \(\frac{1}{4}\)s2√3 where s is the side length.
Answer:
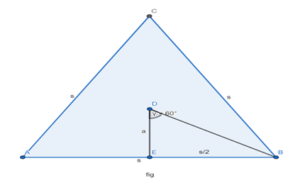
BE/ED = tan θ
Substitute θ as 60 degrees
BE/ED = tan 60°
BE = tan 60°(ED)
s/2 = (√3)a
a = s/2√3
A = 1/2 . a. (n . s)
A = 1/2 . s/2√3 . (3 . s)
A = 1/4 . √3 . s²
A = √3/4 s²
Question 47.
CRITICAL THINKING
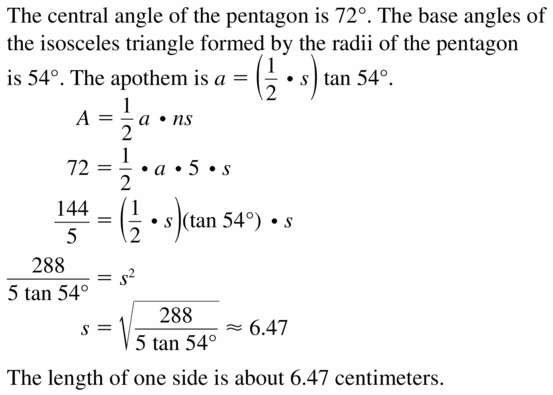
The area of a regular pentagon is 72 square centimeters. Find the length of one side.
Answer:
Question 48.
CRITICAL THINKING
The area of a dodecagon, or 12-gon, is 140 square inches. Find the apothem of the polygon.
Answer:
Apothem = 1.768 units.
Explanation:
Given,
The area of a dodecagon, or 12-gon, is 140 square inches.
Let the side length of dodecagon be 2x.
So, the measure of each interior angle of a regular 12-agon is 150 degrees.
The base angle of C and A is equal to 150/2 = 75.
The adjacent to this angle is the length 2x/2 = x inches,
while the opposite to it is the blue apothem in the right triangle BDC formed.
Therefore,
a = x tan 75.
Area = 1/2 (x tan75)(n . s)
140 = 1/2 (x tan75)(12 . 2x)
140 = 44.785 x²
x² = 3.126
x = 1.768 sq units.
Question 49.
USING STRUCTURE
In the figure, an equilateral triangle lies inside a square inside a regular pentagon inside a regular hexagon. Find the approximate area of the entire shaded region to the nearest whole number.
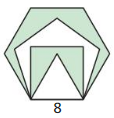
Answer:
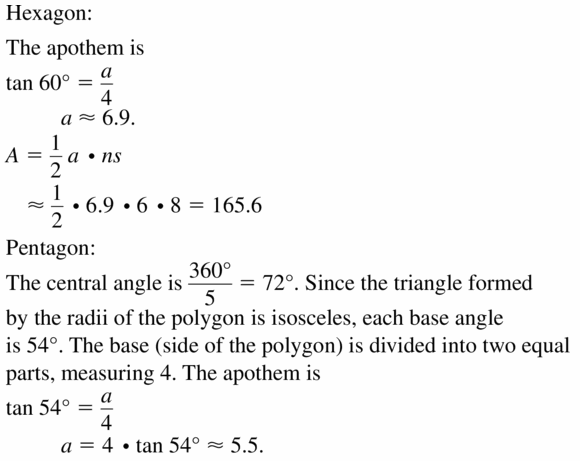

Question 50.
THOUGHT PROVOKING
The area of a regular n-gon is given by A = \(\frac{1}{2}\)aP. As n approaches infinity, what does the n-gon approach? What does P approach? What does a approach? What can you conclude from your three answers? Explain your reasoning.
Answer:
Question 51.
COMPARING METHODS
Find the area of regular pentagon ABCDE by using the formula A = \(\frac{1}{2}\)aP, or A = \(\frac{1}{2}\)a • ns. Then find the area by adding the areas of smaller polygons. Check that both methods yield the same area. Which method do you prefer? Explain your reasoning.
Answer:

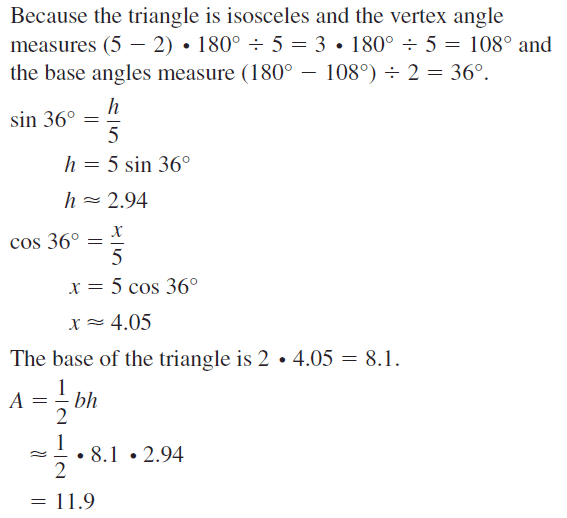

Question 52.
USING STRUCTURE
Two regular polygons both have n sides. One of the polygons is inscribed in, and the other is circumscribed about, a circle of radius r. Find the area between the two polygons in terms of n and r.
Answer:
The radius of the smaller polygon is equal to the apothem of the larger polygon.
The central angle is 360/n,
We know that,
The apothem of a regular polygon is a line segment connecting the center of the polygon to a midpoint of one of the sides.
So, the apothem makes an angle of 180/n.
Use sine and cosine to find the apothem and side length of the smaller polygon.
asmall = r sin\(\frac { 180 }{ n } \)
ssmall = 2r cos\(\frac { 180 }{ n } \)
Use tangent to find the side length of the large polygon.
Slarge = 2r tan\(\frac { 180 }{ n } \)
Use the formula to find the area of the smaller polygon.
Asmall = 1/2 . asmall . n . ssmall
Asmall = 1/2 . r sin\(\frac { 180 }{ n } \) . n . 2r cos\(\frac { 180 }{ n } \)
Asmall = nr² sin \(\frac { 180 }{ n } \) cos\(\frac { 180 }{ n } \)
Use the formula to find the area of the larger polygon.
ALarge = 1/2 . alarge . n . slarge
= nr² tan\(\frac { 180 }{ n } \)
The area between the polygons is equal to the area of the larger polygon minus the area of the smaller polygon.
A = Alarge – Asmall
Use some trig identities to simplify the expression.
A = nr² tan\(\frac { 180 }{ n } sin²[latex]\frac { 180 }{ n }
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
Determine whether the figure has line symmetry, rotational symmetry, both, or neither. If the
figure has line symmetry. determine the number of lines of symmetry. It the figure has rotational
symmetry, describe any rotations that map the figure onto itself.
Question 53.
Answer:
![]()
Explanation:
A line of symmetry is an imaginary line that divides a shape or an object into two equal and symmetrical parts.
So, the above given figure divides the shape into two identical halves, vertically.
Question 54.

Answer:
The figure has rotational symmetry.
Explanation:
If a figure is rotated around a center point and it still appears exactly as it did before the rotation, it is said to have rotational symmetry.
Question 55.

Answer:
![]()
Explanation:
If a figure is rotated around a center point and it still appears exactly as it did before the rotation, it is said to have rotational symmetry.
Question 56.
Answer:
The figure has one line symmetry.
Explanation:
A line of symmetry is an imaginary line that divides a shape or an object into two equal and symmetrical parts.
11.4 Three-Dimensional Figures
Exploration 1
Analyzing a Property of Polyhedra
Work with a partner: The five Platonic solids are shown below. Each of these solids has congruent regular polygons as faces. Complete the table by listing the numbers of vertices, edges, and faces of each Platonic solid.
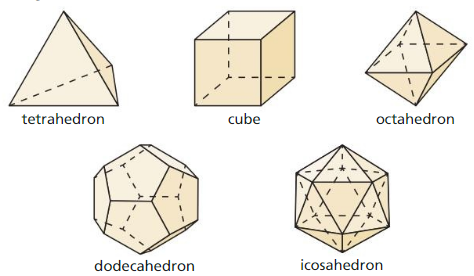
Answer:
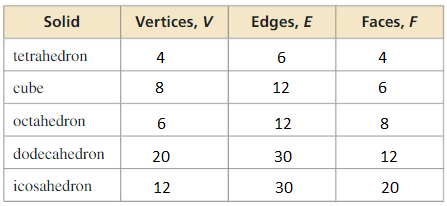
Communicate Your Answer
Question 2.
What is the relationship between the numbers of vertices V, edges E, and faces F of a polyhedron? (Note: Swiss mathematician Leonhard Euler (1707 – 1783) discovered a formula that relates these quantities.)
CONSTRUCTING VIABLE ARGUMENTS
To be proficient in math, you need to reason inductively about data.
Answer:
The relationship between the vertices, edges, and faces of a polyhedron according to Euler’s formula is F + V = E + 2.
Where F = number of faces.
V = number of vertices.
E = number of edges.
Question 3.
Draw three polyhedra that are different from the Platonic solids given in Exploration 1. Count the numbers of vertices, edges, and faces of each polyhedron Then verify that the relationship you found in Question 2 is valid for each polyhedron.
Answer:
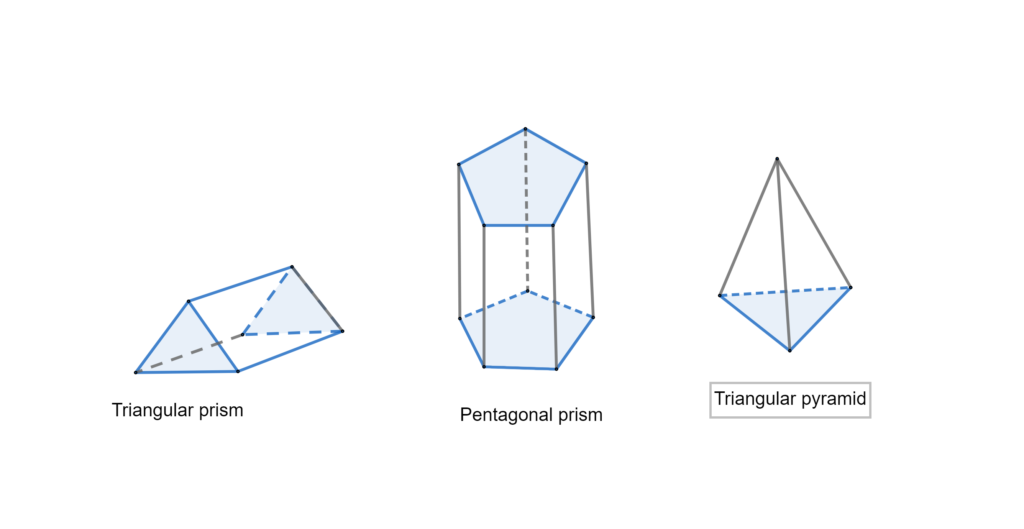
Lesson 11.4 Three-Dimensional Figures
Monitoring progress
Tell whether the solid is a polyhedron. If it is, name the polyhedron.
Question 1.
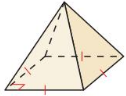
Answer:
yes, the solid is a polyhedron.
Explanation:
We know that,
A three-dimensional shape with flat polygonal faces, straight edges, and sharp corners or vertices is called a polyhedron.
So, the above solid figure is formed by polygons and the base is a square.
Therefore, the given figure is square pyramid.
Question 2.
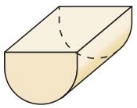
Answer:
No, it is not a polyhedron.
Explanation:
We know that,
A three-dimensional shape with flat polygonal faces, straight edges, and sharp corners or vertices is called a polyhedron.
But the above solid have curved faces.
So, it is not a polyhedron.
Question 3.
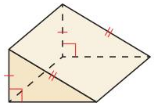
Answer:
Yes, it is not a polyhedron.
Explanation:
We know that,
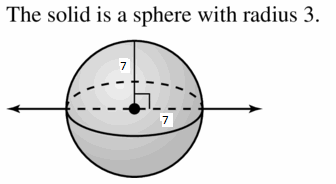
A three-dimensional shape with flat polygonal faces, straight edges, and sharp corners or vertices is called a polyhedron.
The above given figure has two triangles, one rectangle and two squares.
Describe the shape formed by the intersection of the plane and the solid.
Question 4.
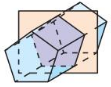
Answer:
The cross-section is a pentagon.
Explanation:
When a pentagonal prism is sliced with a plane parallel to the base,
then the cross section of the plane is a pentagon.
Question 5.
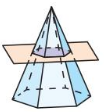
Answer:
The cross-section is a hexagon.
Explanation:
When a hexagonal prism is sliced with a plane parallel to the base,
then the cross section of the plane is a hexagon.
Question 6.
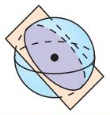
Answer:
The cross-section is a circle.
Explanation:
When a circle is sliced with a plane parallel to the base,
then the cross section of the plane is a circle.
Sketch the solid produced by rotating the figure around the given axis. Then identify and describe the solid.
Question 7.
Answer:
Cone.
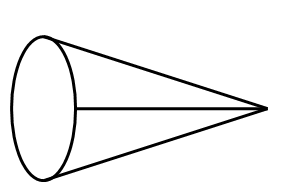
Explanation:
A cone has a circular base and smooth curved sides ending in a point at the top.
It has 1 vertex, 1 edge,1 face and 1 curved surface as shown in the above figure.
Question 8.
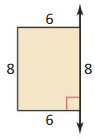
Answer:
Cylinder.
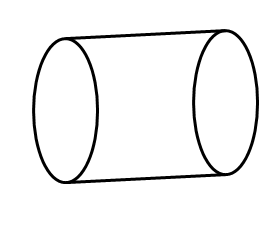
Explanation:
A cylinder is a three-dimensional solid figure which has two identical circular bases joined by a curved surface at a particular distance from the center.
It has has no vertices, 2 edges, 2 faces and 1 curved surface.
Question 9.
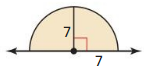
Answer:
Exercise 11.4 Three-Dimensional Figures
Vocabulary and Core Concept Check
Question 1.
VOCABULARY
A(n) ___________ is a solid that is bounded by polygons.
Answer:
![]()
Question 2.
WHICH ONE DOESN’T BELONG?
Which solid does not belong with the other three? Explain your reasoning.
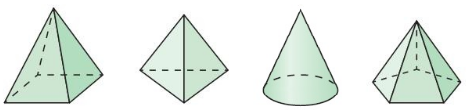
Answer:
Cone.
Explanation:
We know that,
A three-dimensional shape with flat polygonal faces, straight edges, and sharp corners or vertices is called a polyhedron.
But cone does not belong with the other three as it has a curved surface.
Monitoring Progress and Modeling with Mathematics
In Exercises 3 – 6, match the polyhedron with its name.
3.  |
A. triangular Prism |
4.  |
B. rectangular pyramid |
5.  |
C. hexagonal pyramid |
6.  |
D. Pentagonal prism |
Answer:
![]()
![]()
In Exercises 7 – 10, tell whether the solid is a polyhedron. If it is, name the polyhedron.
Question 7.
Answer:
![]()
Explanation:
We know that,
A three-dimensional shape with flat polygonal faces, straight edges, and sharp corners or vertices is called a polyhedron.
So, the given figure is pentagon.
It 7 faces, 15 edges, and 10 vertices.
Question 8.
Answer:
Yes, it is a polyhedron.
It is a hexagonal prism.
Explanation:
We know that,
A three-dimensional shape with flat polygonal faces, straight edges, and sharp corners or vertices is called a polyhedron.
So, the given figure is hexagon.
It has 8 faces, 18 edges, and 12 vertices.
Question 9.
Answer:
![]()
Explanation:
We know that,
A three-dimensional shape with flat polygonal faces, straight edges, and sharp corners or vertices is called a polyhedron.
So, the above given figure is not a polyhedron due to curved faces.
Question 10.
Answer:
Yes, it is a polyhedron, truncated square pyramid.
Explanation:
We know that,
A three-dimensional shape with flat polygonal faces, straight edges, and sharp corners or vertices is called a polyhedron.
If two of its faces are non-congruent squares, and four are congruent trapezoids,
then it is said to be a truncated square pyramid.
It has 12 edges – where 3 faces meet.
7 vertices – 6 at the base and 1 above.
9 diagonals – at the base.
6 slant heights.
So, the above given figure is a polyhedron.
In Exercises 11 – 14, describe the cross section formed by the intersection of the plane and the solid.
Question 11.
Answer:
![]()
Explanation:
If a plane intersects a solid 3-dimensional shape,
then the region common to the plane and the solid is called a cross-section of the solid.
So, the cross-section of the above solid figure is circle.
Question 12.
Answer:
The cross-section is a square.
Explanation:
If a plane intersects a solid 3-dimensional shape,
then the region common to the plane and the solid is called a cross-section of the solid.
So, the cross-section of the above solid figure is square.
Question 13.
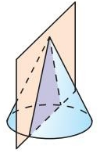
Answer:
![]()
Explanation:
If a plane intersects a solid 3-dimensional shape,
then the region common to the plane and the solid is called a cross-section of the solid.
So, the cross-section of the above solid figure is triangle.
Question 14.
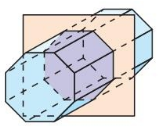
Answer:
The cross-section is a hexagon.
Explanation:
If a plane intersects a solid 3-dimensional shape,
then the region common to the plane and the solid is called a cross-section of the solid.
So, the cross-section of the above solid figure is hexagon.
In Exercises 15 – 18, sketch the solid produced by rotating the figure around the given axis. Then identify and describe the solid.
Question 15.
Answer:
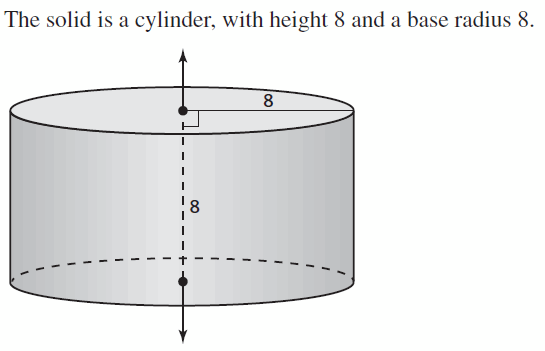
Question 16.
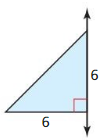
Answer:
Explanation:
The solid produced by rotating the given figure around the given axis is a cone,
with a height of 6 and a base radius is 6.
Question 17.
Answer:
Question 18.
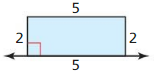
Answer:

Explanation:
The solid produced by rotating the given figure around the given axis is a cylinder.
with a height of 5 and a base radius is 2.
Question 19.
ERROR ANALYSIS
Describe and correct the error in identifying the solid.
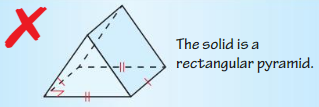
Answer:

Question 20.
HOW DO YOU SEE IT?
Is the swimming pool shown a polyhedron? If it is, name the polyhedron. If not, explain why not.

Answer:
An octagonal polyhedron.
Explanation:
We know that,
A three-dimensional shape with flat polygonal faces, straight edges, and sharp corners or vertices is called a polyhedron.
The above given figure is an octagonal polyhedron,
because it has 8 sides, 10 faces, 24 edges, and 16 vertices.
In Exercises 21 – 26, sketch the polyhedron.
Question 21.
triangular prism
Answer:
Explanation:
A triangular prism is a prism composed of two triangular bases and three rectangular sides.
A triangular prism is also called as pentahedron.
Question 22.
rectangular prism
Answer:
Explanation:
A rectangular prism is a polyhedron with two congruent and parallel bases.
It is also called a cuboid.
Question 23.
pentagonal prism
Answer:
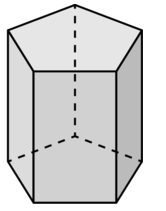
Explanation:
A pentagonal prism is a prism that has two pentagonal bases and five rectangular sides.
We know that penta means five and gonia means angles.
It is a type of heptahedron.
Question 24.
hexagonal prism
Answer:
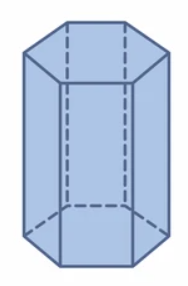
Explanation:
A hexagonal prism is a prism with hexagonal base and top.
We know that Hexa means six and gonia means angles.
Question 25.
square pyramid
Answer:
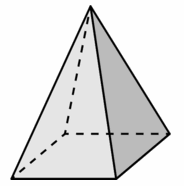
Explanation:
A square pyramid is a pyramid that has a square base and four lateral faces.
Question 26.
pentagonal pyramid
Answer:
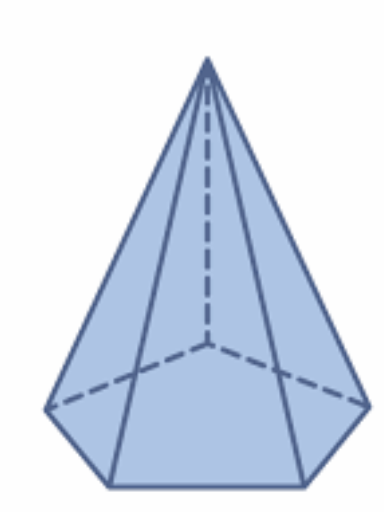
Explanation:
A pentagonal pyramid is a pyramid that has a pentagonal base and five lateral faces.
Question 27.
MAKING AN ARGUMENT
Your Friend says that the polyhedron shown is a triangular prism. Your cousin says that it is a triangular pyramid. Who is correct? Explain your reasoning.
Answer:

Question 28.
ATTENDING TO PRECISION
The figure shows a plane intersection a cube through four of its vertices. The edge length of the cube is 6 inches.
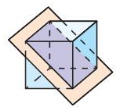
a. Describe the shape of the cross section.
Answer:
The cross-section is a rectangle.
b. What is the perimeter of the cross section?
Answer:
We know that, the above cross-section is rectangle.
The perimeter of the cross-section = 2(l + b)
where l is length and b is the breadth.
c. What is the area of the cross section?
Answer:
We know that, the above cross-section is rectangle.
Area of the cross-section = lb.
where l is length and b is the breadth.
REASONING
In Exercises 29 – 34, tell whether it is possible for a cross section of a cube to have the given shape. If it is, describe or sketch how the plane could intersect the cube.
Question 29.
circle
Answer:
![]()
Explanation:
It is not possible for a cross section of a cube,
because if the plane cuts at an angle through the base the cross section includes a straight line along the base.
Question 30.
pentagon
Answer:
yes, cross-section of the cube can be a pentagon.
Explanation:
The cross-section of the cube can be a pentagon,
if the plane touches exactly 5 faces of the cube.
Question 31.
rhombus
Answer:
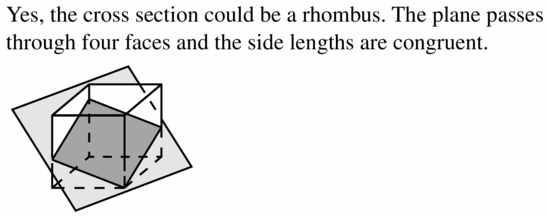
Question 32.
isosceles triangle
Answer:
Yes, the cross-section can be an isosceles triangle.
Explanation:
If the plane is tilted and it intersects 2 adjacent faces at the same distance from the vertex, then cross section forms an isosceles triangle.
Question 33.
hexagon
Answer:
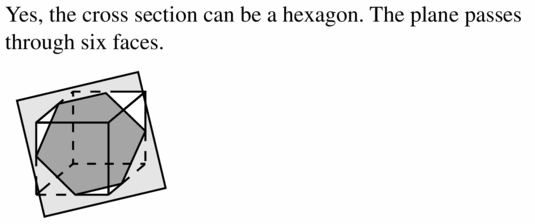
Question 34.
scalene triangle
Answer:
Yes, the cross-section can be scalene triangle.
Explanation:
If the plane is tilted and it intersects all 3 adjacent faces at different distances from the vertex, then the cross-section can be scalene triangle.
Question 35.
REASONING
Sketch the composite solid produced by rotating the figure around the given axis. Then identify and describe the composite solid.
a.
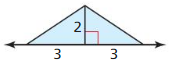
b.
Answer:
Question 36.
THOUGHT PROVOKING
Describe how Plato might have argued that there are precisely five Platonic Solids (see page 617). (Hint: Consider the angles that meet at a vertex.)
Answer:
Maintaining Mathematical proficiency
Decide whether enough information is given to prove that the triangles are congruent. It so, state the theorem you would use.
Question 37.
∆ABD, ∆ CDB
Answer:
Explanation:
According to SSS Triangle Congruence Theorem,
If all the three sides of one triangle are equivalent to the corresponding three sides of the second triangle, then the two triangles are said to be congruent by SSS rule.
When we observe the above given figure,
∆ABD is similar ∆ CDB.
Question 38.
∆JLK, ∆JLM
Answer:
∆JLK ≅ ∆JLM by SAS congruence theorem.
Explanation:
According to SAS Triangle Congruence Theorem,
If two sides and the included angle of one triangle are equal to two sides and the included angle of another triangle, then the triangles are congruent.
When we observe the above given figure,
∆JLK ≅ ∆JLM
Question 39.
∆RQP, ∆RTS
Answer:

Explanation:
According to ASA Triangle Congruence Theorem,
If any two angles and side included between the angles of one triangle are equivalent to the corresponding two angles and side included between the angles of the second triangle, then the two triangles are said to be congruent.
When we observe the above given figure,
∆RPQ ≅ ∆RTS
11.1 – 11.4 Quiz
Find the indicated measure.
Question 1.
m[latex]\widehat{E F}\)
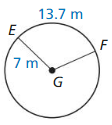
Answer:
m\(\widehat{E F}\) = 112.13°
Explanation:
Given,
radius = 7m; circumference = 13.7 m
C = πd or C = 2πr,
m\(\widehat{E F}\)
13.7 = \(\frac { m[latex]\widehat{E F}\) }{ 360 } [/latex] • 2π(7)
where π is 3.141 or 22/7
m\(\widehat{E F}\) = 112.13
Question 2.
arc length of \(\widehat{Q S}\)
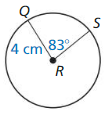
Answer:
arc length of \(\widehat{Q S}\) = 5.79cm
Given,
radius = 4cm, angle measure = 83°
s = 2 π r (θ/360°)
arc length of \(\widehat{Q S}\) = \(\frac { 83 }{ 360 } \) • 2π(4)
where π is 3.141 or 22/7
So, arc length of \(\widehat{Q S}\) = 5.79
Question 3.
circumference of ⊙N
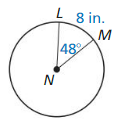
Answer:
circumference = 60 in.
Explanation:
Given,
angle = 48°, s = 8
s = 2 π r (θ/360°)
8 = \(\frac { 48 }{ 360 } \) • 2πr
where π is 3.141 or 22/7
C = 60
Question 4.
Convert 26° to radians and \(\frac{5 \pi}{9}\) radians to degrees.
Answer:
26° = \(\frac { 13π }{ 90 } \) radians.
\(\frac{5 \pi}{9}\) = 100°
Explanation:
To convert the value of the angle in degree to its equivalent radians,
we need to multiply the given value with π/180.
Given to convert 26° to radians,
26° = \(\frac { π }{ 180 } \) = \(\frac { 13π }{ 90 } \) radians.
Convert \(\frac{5 \pi}{9}\) radians to degrees,
\(\frac{5 \pi}{9}\) x \(\frac { 180 }{ π } \)
cross multiply
So, \(\frac{5 \pi}{9}\) = 100°
Use the figure to find the indicated measure.
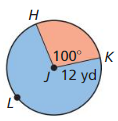
Question 5.
area of red sector
Answer:
Area of red sector = 125.66 sq yd.
Explanation:
With to the above given figure,
angle = 100°, radius = 12 yd.
Area of red sector = \(\frac { 100 }{ 360 } \) . π(12)²
where π is 3.141 or 22/7
A = \(\frac { 5 }{ 18 } \) x 3.141 x 144
A = 5 x 3.141 x 8
A = 125.66 sq yd.
Question 6.
area of blue sector
Answer:
Area of blue sector = 326.72 sq yd.
Explanation:
Explanation:
With to the above given figure,
angle of blue sector = 360 – angle of red sector
angle = 360 – 100 = 260°,
radius = 12 yd.
area of blue sector = \(\frac { 260 }{ 360 } \) . π(12)²
where π is 3.141 or 22/7
A = \(\frac {13 }{ 18 } \) x 3.141 x 144
A = 13 x 3.141 x 8
A = 326.72 sq yd.
In the diagram, RSTUVWXY is a reuIar octagon inscribed in ⊙C.
Question 7.
Identify the center, a radius, an apothem, and a central angle of the polygon.
Answer:
C is center,
CY is radius,
CZ is apothem,
∠YCR is central angle of the polygon.
Explanation:
The center of a circle is the point where all the distances to the points on the circle are equal as shown in the above given figure.
So, C is the center is the center of the given figure.
The apothem of a regular polygon is a line segment connecting the center of the polygon to a midpoint of one of the sides.
So, CZ is apothem in the above given figure.
The radius of a regular polygon is a line segment connecting the center of the polygon to one of the vertices.
So, CY or CX is the radius of the given figure.
A central angle of a regular polygon is an angle whose vertex is the center and whose rays, or sides, contain the endpoints of a side of the regular polygon.
So, ∠YCR is the central angle in the above given figure.
Question 8.
Find m∠RCY, m∠RCZ, and m∠ZRC.
Answer:
m∠RCY = 45°
m∠RCZ = 22.5°
m∠ZRC = 67.5°
Explanation:
Given to Find m∠RCY, m∠RCZ, and m∠ZRC.
m∠RCY = 360/8 = 45
m∠RCZ = 45/2 = 22.5
m∠ZRC = 180 – (22.5 + 90) = 67.5
So, the sum of the angles in a triangle,
45° + 22.5° + 67.5° = 180°
Question 9.
The radius of the circle is 8 units. Find the area of the octagon.
Answer:
Area = 22.62 sq units.
Explanation:
Given,
The radius of the circle is 8 units.
The area of the octagon = 1/2 (r)² sin 45
sin 45 = 0.7071
Area of octagon = 0.5 x 8 x 8 x 0.7071
A = 22.62 sq units.
Tell whether the solid is a polyhedron. If it is, name the polyhedron.
Question 10.
Answer:
No, it is not a polyhedron.
Explanation:
We know that,
A three-dimensional shape with flat polygonal faces, straight edges, and sharp corners or vertices is called a polyhedron.
But the above solid have curved faces.
So, it is not a polyhedron.
Question 11.
Answer:
Yes, it is an octagonal pyramid.
Explanation:
We know that,
A three-dimensional shape with flat polygonal faces, straight edges, and sharp corners or vertices is called a polyhedron.
Therefore, the above given figure is a octagonal pyramid.
Question 12.
Answer:
The solid is a polyhedron. It is a pentagonal prism.
Explanation:
A three-dimensional shape with flat polygonal faces, straight edges, and sharp corners or vertices is called a polyhedron.
So, the given solid is a pentagonal prism with two pentagonal bases like top and bottom and five rectangular sides.
Question 13.
Sketch the composite solid produced by rotating the figure around the given axis. Then identify and describe the composite solid.
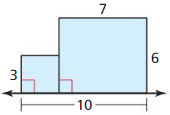
Answer:
Cylinder.
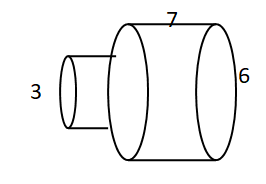
Explanation:
A cylinder is a three-dimensional solid figure which has two identical circular bases joined by a curved surface at a particular distance from the center.
It has has no vertices, 2 edges, 2 faces and 1 curved surface.
Question 14.
The two white congruent circles just fit into the blue circle. What is the area of the blue region?
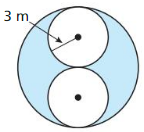
Answer:
Area of blue region = 56.541 sq m.
Explanation:
Given that,
The two white congruent circles just fit into the blue circle.
radius of white circle = 3m
radius of the blue circle = 3 + 3 = 6m
Firstly find,
White circle diameter = radius of the blue circle.
Area of blue circle = π6²
where π = 3.141 or 22/7
A = 3.141 x 36
A = = 113.09 sq m.
Area of white circle = π3²
A = 3.141 x 9 =
A = 28.27 sq m.
Area of blue region = 113.09 – 2(28.27)
A = 113.09 – 56.54
A = 56.541 sq m.
Question 15.
Find the area of each rhombus tile. Then find the area of the pattern.
Answer:
Area of pattern = 2070.09 sq mm
Explanation:
Given, area of each rhombus tile in the above figures,
Area of rhombus = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(d1 x d2)
Area of yellow tile = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(15.7 x 11.4) = 44.745 sq mm.
area of red tile = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(18.5 x 6) = 27.75 sq mm.
From the above information there are,
32 yellow tiles and 23 red tiles.
Area of pattern = 32(44.745) + 23(27.75) = 2070.09 sq mm
11.5 Volumes of Prisms and Cylinders
Exploration 1
Finding volume
Work with a partner: Consider a stack of square papers that is in the form of a right prism.
a. What is the volume the prism?
Answer:
The volume of the prism is B = 1/2 x h(b1 + b2)
h = 8
b1 = 2
b2 = 2
= 1/2 x 8(2 + 2)
= 1/2 x 8(4)
= 1/2 x 32
= 16 cube inches.
b. When you twist the slack of papers, as shown at the right, do you change the volume? Explain your reasoning.
Answer: The volume of the prism and the twist of the slack of paper volume are the same. Because the different shapes of the prism have the same volume.
c. Write a carefully worded conjecture that describes the conclusion you reached in part (b).
ATTENDING TO PRECISION
To be proficient in math, you need to communicate precisely to others.
Answer: The conjecture is that the different shapes of the prism have the same volume but are different in surface area.
d. Use your conjecture to find the volume of the twisted stack of papers.
Answer:
V = 1/2 x h(b1 + b2)
h = 8
b1 = 2
b2 = 2
= 1/2 x 8(2 + 2)
= 1/2 x 8(4)
= 1/2 x 32
= 16 cu. inches.
Exploration 2
Finding volume
Work with a partner: Use the conjecture you wrote in Exploration I to find the volume of the cylinder.
a.
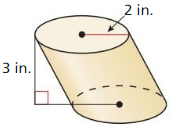
Answer:
V = πr² h.
h = 3
r = 2
= π(2)² x 3
= π(4) x 3
= 12π
= 37.68 cu. cm
b.
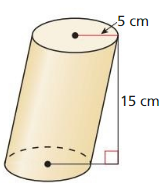
Answer:
V = πr² h.
h = 15
r = 5
= π(5)² x 15
= π(25) x 15
= 375π
= 1,177.5 cu. cm
Communicate Your Answer
Question 3.
How can you find the volume of a prism or cylinder that is not a right prism or right cylinder?
Answer:
Using π we can find the volume of the prism or cylinder that is not the right prism of the right cylinder.
The cylinder and the prism have the same cross-sectional area of πr².
Both the cylinder and prism have the same volume it is V = πr²h
Question 4.
In Exploration 1, would the conjecture you wrote change if the papers in each stack were not squares? Explain your reasoning.
Answer:
Lesson 11.5 Volumes of Prisms and Cylinders
Monitoring Progress
Find the volume of the solid.
Question 1.
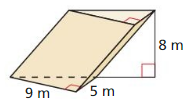
Answer:
V= 180 cubic m.
Explanation:
Given,
height = 8m, length = 5m and breadth = 9m.
Volume = Area x height
Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)lb
Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(5 x 9)
A = 45 x 05
A = 22.5 sq m.
Volume = 22. 5 x 8
V= 180 cubic m.
Question 2.
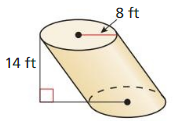
Answer:
V = 2814.86 cubic ft.
Explanation:
Given,
radius = 8ft, height = 14 ft.
Area of circle = πr²
= π(8)² = 64π
Volume = Area x height
Volume = 64π x 14
where π is 3.1471 or 22/7
V = 2814.86 cubic ft.
Question 3.
The diagram shows the dimensions of a concrete cylinder. Concrete has a density of 2.3 grams per cubic centimeter. Find the mass of the concrete cylinder to the nearest gram.
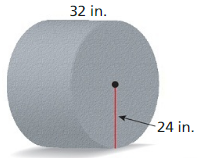
Answer:
V = 18432π cubic in.
Explanation:
Given,
Concrete has a density of 2.3 grams per cubic centimeter.
height = 32 in, radius = 24 in.
V = πr²h.
Mass of the concrete cylinder = 32 x π(24)²
where π is 3.1471 or 22/7
V = 32 x 3.141 x 576
V = 18432π cubic in.
Question 4.
WHAT IF?
In Example 4, you want the length to be 5 meters, the width to be 3 meters. and the volume to be 60 cubic meters. What should the height be?
Answer:
h = 4 m
Explanation:
Given,
length to be 5 meters, the width to be 3 meters and the volume to be 60 cubic meters.
volume = lbh
60 = 5 x 3 x h
h = 60/15
h = 4 m
Question 5.
WHAT IF?
In Example 5, you want the height to be 5 meters and the volume to be 75 cubic meters. What should the area of the base be? Give a possible length and width.
Answer:
b = 15 sq m.
Explanation:
Given,
the height to be 5 meters and the volume to be 75 cubic meters.
volume V = base x height
75 = base x 5
b = 75/5
b = 15 sq m.
Question 6.
Prism C and prism D are similar. Find the volume of prism D.
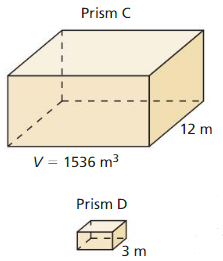
Answer:
Volume of prism D = 384 cubic m.
Explanation:
Given,
Prism C and prism D are similar.
\(\frac { 12 }{ 3 } \) = \(\frac { 1536 }{ v } \)
cross multiply on both sides.
3v = 12 x 1536
v = 18432/3
v = 384
Volume of prism D = 384 cubic m.
Question 7.
Find the volume of the composite solid.
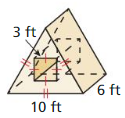
Answer:
V = = 90 cubic ft.
Explanation:
Based on the information given in the above figure,
l = 3 ft, b = 10ft, h = 6ft
Volume = area x height
Volume = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(10 x 3 x 6)
V = 180/2
V = 90 cubic ft.
Exercise 11.5 Volumes of Prisms and Cylinders
Vocabulary and Core Concept Check
Question 1.
VOCABULARY
In what type of units is the volume of a solid measured?
Answer:
![]()
Question 2.
COMPLETE THE SENTENCE
Density is the amount of _______ that an object has in a given unit of __________ .
Answer:
mass
Explanation:
Density is the mass of the object divided by its volume.
d = M/V
d = density,
m = mass,
v = volume.
Monitoring Progress and Modeling with Mathematics
In Exercises 3 – 6, find the volume of the prism.
Question 3.
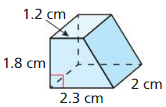
Answer:

Question 4.
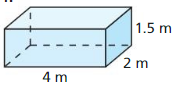
Answer:
V = 12 m³
Explanation:
Given,
l = 1.5m, b = 2m, h = 4m
Volume V = lbh
V = 1.5 x 2 x 4
V = 12 m³
Question 5.
Answer:

Question 6.
Answer:
V = 924 m³
Explanation:
Given,
l = m, b = 2m, h = 4m
Volume V = lbh
Volume = 11 x 6 x 14
V = 924 m³
In Exercises 7 – 10. find the volume of the cylinder.
Question 7.
Answer:

Question 8.
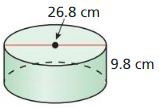
Answer:
V = 1759.6π cm³
Explanation:
Given,
h = 9.8 cm, d = 26.8 cm
radius = d/2
r = 26.8/2
r = 13.4
Volume = πr²h
V = π(13.4)² x 9.8
V = π x 179.56 x 9.8
V = 1759.6π cm³
Question 9.
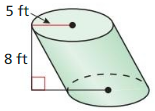
Answer:

Question 10.
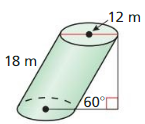
Answer:
V = 1763 m³
Explanation:
Given,
Volume V = πr²h
Shorter side = 18/2 = 9
Height h = √18² – 9² = 15.588
V = π6² x 15.588
V = 36 π x 15.588
V = 1763 m³
In Exercises 11 and 12. make a sketch of the solid and find its volume. Round your answer to the nearest hundredth.
Question 11.
A prism has a height of 11.2 centimeters and an equilateral triangle for a base, where each base edge is 8 centimeters.
Answer:
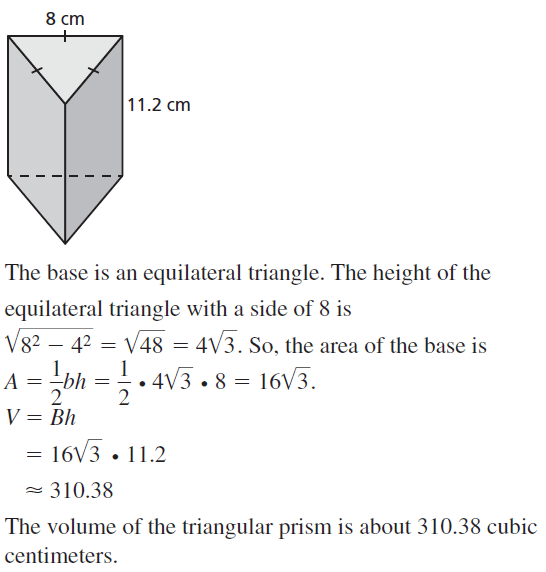
Question 12.
A pentagonal prism has a height of 9 feet and each base edge is 3 feet.
Answer:
volume is 139.32 ft³
Explanation:
Given,
Area = 15.48
Height = 9 ft
Volume = area x height
V = 15.48 x 9
V = 139.32 ft³
Question 13.
PROBLEM SOLVING
A piece of copper with a volume of 8.25 cubic centimeters has a mass of 73.92 grams. A piece of iron with a volume of 5 cubic centimeters has a mass of 39.35 grams. Which metal has the greater density?

Answer:

Question 14.
PROBLEM SOLVING
The United States has minted one-dollar silver coins called the American Eagle Silver Bullion Coin since 1986. Each coin has a diameter of 40.6 millimeters and is 2.98 millimeters thick. The density of silver is 10.5 grams per cubic centimeter. What is the mass of an American Eagle Silver Bullion Coin to the nearest grain?

Answer:
V = 3856 mm³
Explanation:
Given,
Each coin has a diameter of 40.6 millimeters and is 2.98 millimeters thick.
The density of silver is 10.5 grams per cubic centimeter.
V = πr²h
where π is 3.141 or 22/7
radius = d/2
r = 40.6/2 = 20.3 mm
V = π(20.3)² x (2.98)
V = 3.141 x 412.09 x 2.98
V = 3856 mm³
Question 15.
ERROR ANALYSIS
Describe and correct the error in finding the volume of the cylinder.
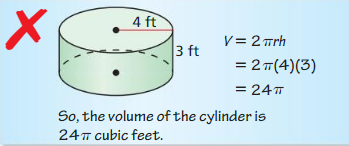
Answer:

Question 16.
ERROR ANALYSIS
Describe and correct the error in finding the density of an object that has a mass of 24 grams and a volume of 28.3 cubic centimeters.

Answer:
Density = 0.8480 cu.cm
Explanation:
Given,
The density of an object that has a mass of 24 grams and a volume of 28.3 cubic centimeters.
Density = mass / volume
Density = \(\frac { 24 }{ 28.3 } \)
Density = 0.8480 cu.cm
In Exercises 17 – 22, find the missing dimension of the prism or cylinder.
Question 17.
Volume = 500 ft3
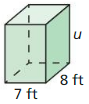
Answer:
Question 18.
Volume = 2700 yd3
Answer:
v = 15 yd
Explanation:
Given,
Volume = 2700 yd3
l = 15yd, b = 12 yd, h = v
V = lbh
12 x 5 x v = 2700
60 v = 2700
v = 2700/60
v = 15 yd
Question 19.
Volume = 80 cm3
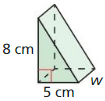
Answer:

Question 20.
Volume = 72.66 in.3
Answer:
x = 6.9 in.
Explanation:
Given,
Volume = 72.66 in.3
V = area x height
Area . x = 72.66
10.39 x = 72.66
x = 72.66/10.39
x = 6.9 in
Question 21.
Volume = 3000 ft3
Answer:

Question 22.
Volume = 1696.5 m3
Answer:
z = 6m
Explanation:
Given,
radius = z
Volume = 1696.5m3
V = πr²h
where π is 3.141 or 22/7
1696.5 = 3.141
z² x 15 = 1696.5
z² = 1696.5/47.115
z² = 36.00
z = 6m
In Exercises 23 and 24, find the area of the base of the rectangular prism with the given volume and height. Then give a possible length and width.
Question 23.
V= 154 in.3, h = 11 in.
Answer:

Question 24.
V = 27 m3,h = 3m
Answer:
b = 9m
Explanation:
Given,
V = 27 m3,h = 3m
V = bh
27 = b x 3
b = 27/3
b = 9m
In Exercises 25 and 26, the solids are similar. Find the volume of solid B.
Question 25.
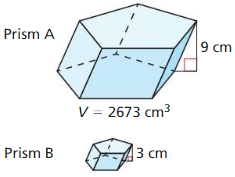
Answer:
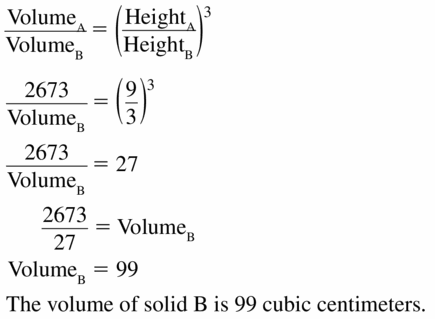
Question 26.
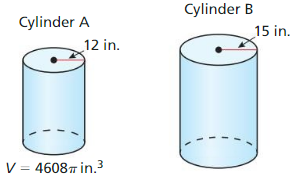
Answer:
Cylinder B = 5760π cu in.
Explanation:
Given,
V = 4608π cu in
Cylinder A = 12 in; cylinder B = 15 in
Compare both the cylinders,
\(\frac { 12 }{ 15 } \) = \(\frac { 4608π }{ V } \)
Cross multiply on both sides.
V = \(\frac { 15 x 4608π }{ 12 } \)
V = \(\frac { 69120π }{ 12 } \)
Volume of cylinder B = 5760π
In Exercises 27 and 28, the solids are similar. Find the indicated measure.
Question 27.
height x of the base of prism A
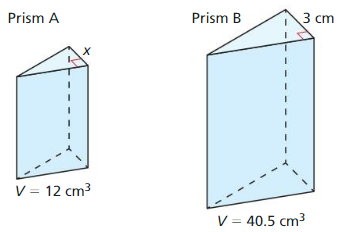
Answer:
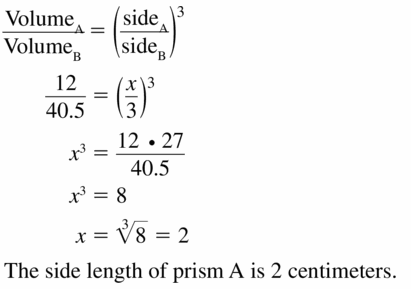
Question 28.
height h of cylinder B
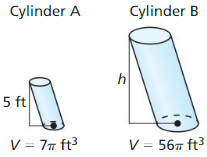
Answer:
height of cylinder B is 40 ft.
Explanation:
Given,
Volume of cylinder A = 7π cu ft.
Volume of cylinder A = 56π cu ft.
height of cylinder A = 5ft
Compare both the cylinders,
\(\frac { 7π }{ 5 } \) = \(\frac { 56π }{ h } \)
cross multiply on both sides.
h = \(\frac { 56π × 5 }{ 7π } \)
h = \(\frac { 280π }{ 7π } \)
h = 40
In Exercises 29 – 32. find the volume of the composite solid.
Question 29.
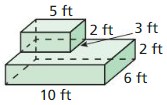
Answer:

Question 30.
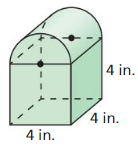
Answer:
Volume V = 89 cu in.
Explanation:
Given,
side length of square = 4 in.
Volume of square = s³
V = 4³
V = 4 x 4 x 4
V = 64 cu in.
Volume of semicircle = πr²
radius = d/2
radius = 4/2 = 2 in.
V = π(2)² x 4
V = 8π
V = 25.128 cu in.
Volume of of the given solid shape = 64 + 25 = 89 cu in.
Question 31.
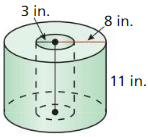
Answer:

Question 32.
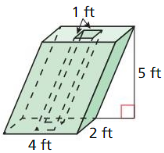
Answer:
The volume of composite solid is 35 cubic ft.
Explanation:
Given,
measurement so of larger prism,
h = 5ft, b = 4 ft, l = 2ft
Volume of larger prism = lwh
V = 4 x 2 x 5 = 40 cubic ft.
measurement of smaller prism,
h = 5ft, b = 1ft, l = 1ft
Volume of the smaller prism = lwh
1 x 1 x 5 = 5 cubic ft.
Volume of composite solid = Volume of larger prism – volume of the smaller prism
V = 40 – 5
V = 35 cubic ft.
Question 33.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
The Great Blue Hole is a cylindrical trench located off the coast of Belize. It is approximately 1000 feet wide and 400 feet deep. About how many gallons of water does the Great Blue Hole contain? (1 ft3 ≈ 7.48 gallons)

Answer:

Question 34.
COMPARING METHODS
The Volume Addition Postulate states that the volume of a solid is the sum of the volumes of all its non overlapping parts. Use this postulate to find the volume of the block of concrete in Example 7 by subtracting the volume of each hole from the volume of the large rectangular prism. Which method do you prefer? Explain your reasoning.
Answer:
REASONING
In Exercises 35 and 36, you are melting a rectangular block of wax to make candles. how many candles of the given shape can be made using a block that measures 10 centimeters by 9 centimeters by 20 centimeters?
Question 35.

Answer:

Question 36.
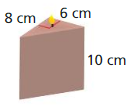
Answer:
7 triangular prism.
Explanation:
Given,
h = 10 cm, l = 8 cm, b = 6 cm
Volume of block = 1800 cu cm.
V = 1/2 x lbh
The volume of triangular prism = 4 x 6 x 10 = 240
1800/240 = 7.5
Question 37.
PROBLEM SOLVING
An aquarium shaped like a rectangular prism has a length of 30 inches, a width of 10 inches, and a height of 20 inches. You fill the aquarium \(\frac{3}{4}\) fill with water. When you submerge a rock in the aquarium, the water level rises 0.25 inch.
a. Find the volume of the rock.
b. How many rocks of this size can you place in the aquarium before water spills out?
Answer:

Question 38.
PROBLEM SOLVING
You drop an irregular piece of metal into a container partially filled with water and measure that the waler level rises 4.8 centimeters. The square base of the container has a side length of 8 centimeters. You measure the mass of the metal to be 450 grams. What is the density of the metal?
Answer:
The density of metal is 1.4648 gm /cu cm.
Explanation:
Given,
waler level rises = 4.8 centimeters.
side length = 8 centimeters.
The mass of the metal = 450 grams.
Density = \(\frac { Mass }{ Volume } \)
Volume V = 4.8 x 64 = 307.2 cu cm.
Density = \(\frac { 450 }{ 307.2 } \) = 1.4648 gm /cu cm.
Question 39.
WRITING
Both of the figures shown arc made up of the same number of congruent rectangles. Explain how Cavalieri’s Principle can be adapted to compare the areas of these figures.
Answer:

Question 40.
HOW DO YOU SEE IT?
Each stack of memo papers contains 500 equally-sized sheets of paper. Compare their volumes. Explain your reasoning.

Answer:
Question 41.
USING STRUCTURE
Sketch the solid formed by the net. Then find the volume of the solid.
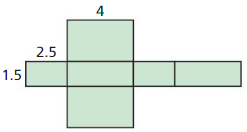
Answer:
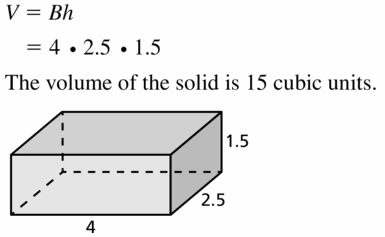
Question 42.
USING STRUCTURE
Sketch the solid with the given views. Then find the volume of the solid.
Answer:
Volume = 52.5 cu units.
Explanation:
with reference to the above figures,
Volume = 2.5 x 3.5 x 6
Volume = 52.5 cu units.
Question 43.
OPEN-ENDED
Sketch two rectangular prisms that have volumes of 1000 cubic inches hut different surface areas. Include dimensions in your sketches.
Answer:
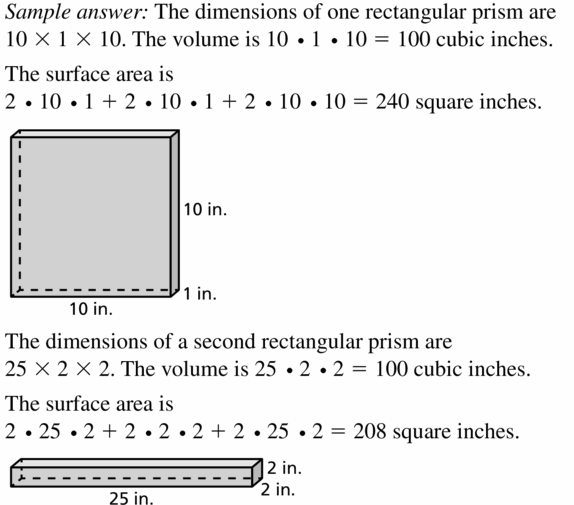
Question 44.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
Which box gives you more cereal for your money? Explain.

Answer:
First one gives more cereal.
Explanation:
Given,
measures of bigger volumes,
h = 16 in, l = 4 in, b = 10 in
Volume = lbh
Bigger volume = 16 x 4 x 10 = 640
measures of smaller volumes,
Smaller volume = 2 x 8 x 10 = 160
$6 – 640 then $1 = 106.66
$2 – 160 then $1 = 80
Question 45.
CRITICAL THINKING
A 3-inch by 5-inch index card is rotated around a horizontal line and a vertical line to produce two different solids. Which solid has a greater volume? Explain your reasoning.
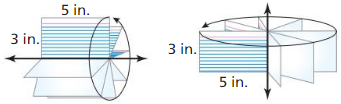
Answer:

Question 46.
CRITICAL THINKING
The height of cylinder X is twice the height of cylinder Y. The radius of cylinder X is half the radius of cylinder Y. Compare the volumes of cylinder X and cylinder Y. Justify your answer.
Answer:
Let the height of cylinder X be h, radius be r and its volume is πr²h.
So, the height of cylinder Y is h/2 and radius is 2r, then the volume is 2πr²h.
By comparing both expressions,
observe that the volume of cylinder y is twice that of cylinder X.
Question 47.
USING STRUCTURE
Find the volume of the solid shown. The bases of the solid are sectors of circles.
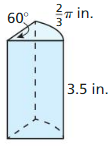
Answer:
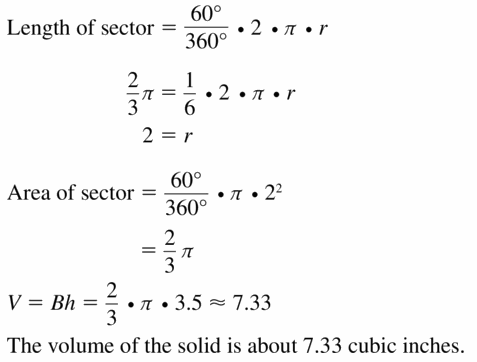
Question 48.
MATHEMATICAL CONNECTIONS
You drill a circular hole of radius r through the base of a cylinder of radius R. Assume the hole is drilled completely through to the other base. You want the volume of the hole to be half the volume of the cylinder. Express r as a function of R.
Answer:
r = √R²/2
Explanation:
The radius of a solid cylinder without a hole is R.
We know that,
volume is πR²h
As per the given condition,
the volume of the hole must be half of that of the solid cylinder,
hole volume is πR²h/2
Volume of cylinder V = πr²h
πR²h/2 = πr²h
R²/2 = r²
r = √R²/2
r = \(\frac { R√2 }{ 2 } \)
Question 49.
ANALYZING RELATIONSHIPS
How can you change the height of a cylinder so that the volume is increased by 25% but the radius remains the same?
Answer:
![]()
Question 50.
ANALYZING RELATIONSHIPS
How can you change the edge length of a cube so that the volume is reduced by 40%?
Answer:
Volume of a cube = s x s x s
We know that the volume of a cube is directly proportional to one of its side length.
If the volume is to be reduced by 40%,
then its the length of one of its side must be reduced by 40%,
without changing the 2 other of its sides.
Question 51.
MAKING AN ARGUMENT
You have two objects of equal V0lume. Your friend says you can compare the densities of the objects by comparing their mass, because the heavier object will have a greater density. Is your friend correct? Explain your reasoning.
Answer:
Question 52.
THOUGHT PROVOKING
Cavalieri’s Principle states that the two solids shown below have the same volume. Do they also have the same surface area? Explain your reasoning.
Answer:
Question 53.
PROBLEM SOLVING
A barn is in the shape of a pentagonal prism with the dimensions shown, The volume of the barn is 9072 cubic feel. Find the dimensions of each half of the root.

Answer:

Question 54.
PROBLEM SOLVING
A wooden box is in the shape of a regular pentagonal prism. The sides, top, and bottom of the box are 1 centimeter thick. Approximate the volume of wood used to construct the box. Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
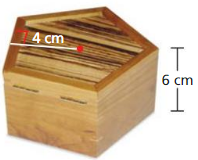
Answer:
V = 228 cu cm.
Explanation:
Pentagon area = \(\frac { 5 }{ 2 } \)(4)² sin 72
A = \(\frac { 5 }{ 2 } \)16 x 0.9511
A = 5 x 8 x 0.9511
A = 38, h = 6 cm
Volume = Area x height
Volume = 38 x 6 = 228 cu cm.
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
Find the surface area of the regular pyramid.
Question 55.
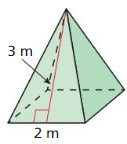
Answer:

Question 56.
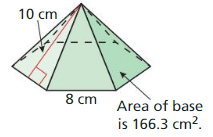
Answer:
SA = 406.3 sq cm.
Explanation:
Given,
Area of base = 166.3 sq cm,
base = 8 cm, side length = 10 cm
Surface area = base area + 3bs
Surface area = 166.3 + 3(8)(10)
SA = 406.3 sq cm.
Question 57.
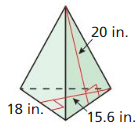
Answer:

11.6 Volumes of Pyramids
Exploration 1
Finding the Volume of a Pyramid
Work with a partner: The pyramid and the prism have the same height and the same square base.
When the pyramid is filled with sand and poured into the prism, it takes three pyramids to fill the prism.
Use this information to write a formula for the volume V of a pyramid.
LOOKING FOR STRUCTURE
To be proficient in math, you need to look closely to discern a pattern or structure.
Answer:
Ab × h = 3V
V = Ab . h/3
where Ab = Area of the square pyramid as well as prism
h = height of the prism
Exploration 2
Finding the Volume of a Pyramid
Work with a partner: Use the formula you wrote in Exploration 1 to find the volume of the hexagonal pyramid.
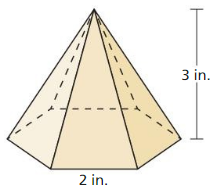
Answer:
V = √3/2 × a² × h
V = √3/2 × 4 × 3
V = 10.39 cubic. in
Communicate Your Answer
Question 3.
How can you find the volume of a pyramid?
Answer:
The volume of a pyramid is found using the formula V = (1/3) Bh, where ‘B’ is the base area and ‘h’ is the height of the pyramid. As we know the base of a pyramid is any polygon, we can apply the area of polygons formulas to find ‘B’.
Question 4.
In Section 11 .7, you will study volumes of cones. How do you think you could use a method similar to the one presented in Exploration 1 to write a formula for the volume of a cone? Explain your reasoning.
Answer:
Lesson 11.6 Volumes of Pyramids
Monitoring Progress
Find the volume of the pyramid.
Question 1.
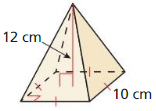
Answer:
The volume of the pyramid is 400 cm³
Explanation:
Given,
w = 10cm, h = 12 cm, l = 10cm.
Volume = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)lwh
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(10 x 10 x 12)
V = \(\frac { 1200 }{ 3 } \)
V = 400cm³
Question 2.
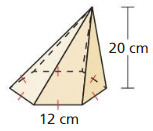
Answer:
The volume of the pyramid is 2494.13 cm³
Explanation:
Given,
Volume V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)bh
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(374.12 x 20)
V = \(\frac { 7482.4 }{ 3 } \)
V = 2494.13cm³
Question 3.
The volume of a square pyramid is 75 cubic meters and the height is 9 meters. Find the side length of the square base.
Answer:
The side length of the square base is 5 m
Explanation:
Given,
volume = 75 cubic meters and height = 9 meters.
b = √\(\frac { 3v }{ h } \)
b = √\(\frac { 3 . 75 }{ 9 } \)
B = √25
s = 5m
Question 4.
Find the height of the triangular pyramid at the left.
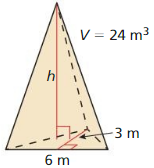
Answer:
The height of the triangular pyramid is 8 m.
Explanation:
Given,
V = 24m³, b = 6m, l = 3m
24 = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh
24 = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(3 x 6)h
24 = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(9)h
h = \(\frac { 24 }{ 3 } \)
h = 8m.
Question 5.
Pyramid C and pyramid D are similar. Find the volume of pyramid D.
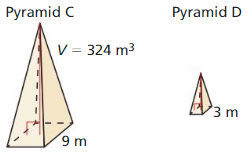
Answer:
The volume of pyramid D is 12 m³
Explanation:
Given,
v = 324³, b = 9, 3
Compare the pyramid C and pyramid D.
\(\frac { volume of pyramid C }{ volume of pyramid D } \) = (\(\frac { pyramid C base }{ pyramid D base } \))³
\(\frac { 324 }{ V } \) = (\(\frac { 9 }{ 3 } \))³
\(\frac { 324 }{ V } \) = \(\frac { 729 }{ 27 } \)
\(\frac { 324 }{ V } \) = 27
V = 324 / 27
V = 12 m³.
Question 6.
Find the volume of the composite solid.
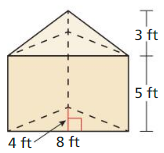
Answer:
The volume of solid = 96 cu ft.
Explanation:
Given,
B = 8 x 2 = 16ft
h = 5ft and 3ft
Volume of prism = Bh
V = 16 x 5 = 80
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(16 x 3)
V = 16 cu ft.
The volume of composite solid = 16 + 80 = 96cu ft.
Exercise 11.6 Volumes of Pyramids
Vocabulary and Core Concept Check
Question 1.
VOCABULARY
Explain the difference between a triangular prism and a triangular pyramid.
Answer:

Question 2.
REASONING
A square pyramid and a cube have the same base and height. Compare the volume of the square pyramid to the volume of the cube.
Answer:
The volume of the square pyramid is 1/3 of the volume of the cube.
Explanation:
Given,
Square pyramid = 1/3 Bh
Cube = Bh
If we compare the volume of the square pyramid to the volume of the cube,
then the volume of the square pyramid is 1/3 of the volume of the cube.
Monitoring Progress and Modeling with Mathematics
In Exercises 3 and 4, find the volume of the pyramid.
Question 3.
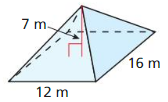
Answer:

Question 4.
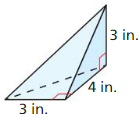
Answer:
V = 6 in³
Explanation:
B = 2 x 3 = 6in.
h = 3 in.
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(6 x 3)
V = 6 in³
In Exercises 5 – 8, find the indicated measure.
Question 5.
A pyramid with a square base has a volume of 120 cubic meters and a height of 10 meters. Find the side length of the square base.
Answer:
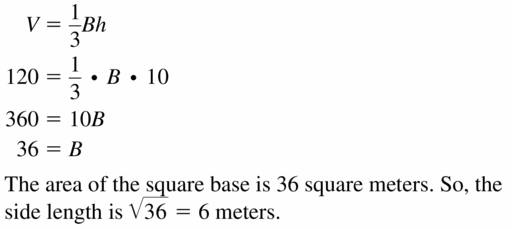
Question 6.
A pyramid with a square base has a volume of 912 cubic feet and a height of 19 feet. Find the side length of the square base.
Answer:
The side length of the square base is 12 ft.
Explanation:
Given,
A pyramid with a square base has a volume of 912 cubic feet.
h = 19 ft
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh
912 = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)B(19)
B = \(\frac { 912 . 3}{ 19 } \)
B = \(\frac { 2736 }{ 19 } \)
B = 144 ft
s = 12 ft.
Question 7.
A pyramid with a rectangular base has a volume of 480 cubic inches and a height of 10 inches. The width of the rectangular base is 9 inches. Find the length of the rectangular base.
Answer:
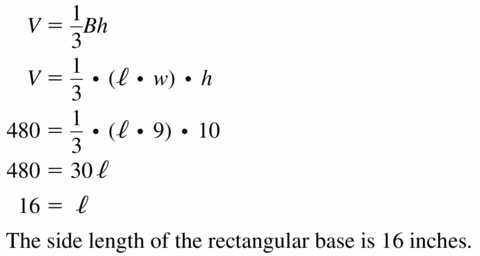
Question 8.
A pyramid with a rectangular base has a volume of 105 cubic centimeters and a height of 15 centimeters. The length of the rectangular base is 7 centimeters. Find the width of the rectangular base.
Answer:
The width of the rectangular base is 3 cm.
Explanation:
Given,
A pyramid with a rectangular base has a volume of 105 cubic centimeters.
h = 15 cm
l = 7 cm
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)lbh
105 = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(7 x 15 x b)
105 = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \) 105 b
105 = 35b
b = 105/35
b = 3 cm.
Question 9.
ERROR ANALYSIS
Describe and correct the error in finding the volume of the pyramid.
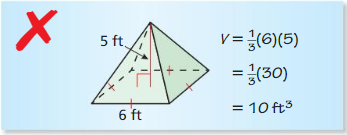
Answer:

Question 10.
OPEN-ENDED
Give an example of a pyramid and a prism that have the same base and the same volume. Explain your reasoning.
Answer:
The volume of the pyramid is 1/3 of the volume of the prism.
Explanation:
A pyramid takes up 1/3 of the volume of a prism when their bases and height are equal. Therefore, the volume of a pyramid is 1/3 multiplied by the volume of a prism.
So, Volume of a pyramid = 1/3 (area of the base) x height.
Let us take the rectangular pyramid with the base dimensions 4 x 2 and a height of 5.
We know that volume = lbh
Therefore, its volume is 4 x 2 x 5 = 40 cubic units.
Know we take the rectangular prism also have the same dimensions of 4 x 2 and a height of 5 x 3 = 15 units.
We know that the volume = 1/3 x l x b x h
Therefore, its volume V = 1/3 x 4 x 2 x 15 = 40 cubic units.
In Exercises 11 – 14, find the height of the pyramid.
Question 11.
Volume = 15 ft3
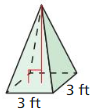
Answer:

Question 12.
Volume = 224 in.3
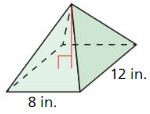
Answer:
The height of the pyramid is 10.5 in
Explanation:
Given,
Volume = 224in.3
B = 8² = 64 in
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh
224 = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(64)h
h = \(\frac { 224 }{ 21.3 } \)
h = 10.5 in
Question 13.
Volume = 198 yd3
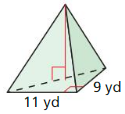
Answer:
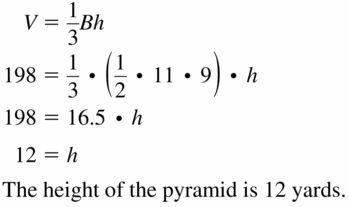
Question 14.
Volume = 392 cm3
Answer:
The height of the pyramid is 12 cm.
Explanation:
Given,
Volume = 392cm3
B = 14 x 7 = 98 cm
\(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh = 392
\(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(98)h = 392
h = \(\frac { 1176 }{ 98 } \)
h = 12 cm.
In Exercises 15 and 16, the pyramids are similar. Find the volume of pyramid B.
Question 15.
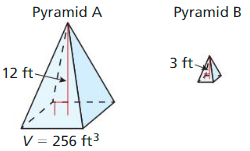
Answer:
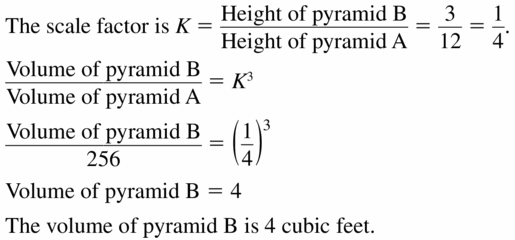
Question 16.
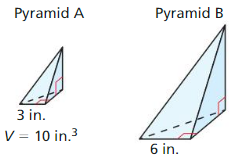
Answer:
Volume of A = 80 in3
Explanation:
Given,
pyramid A measures as,
V = 10 in3, 3 in
measures of pyramid B,
b = 6 in.
Compare both the pyramids.
\(\frac {Volume of B}{Volume of A} \) = (\(\frac {Side of B}{side of A} \))³
\(\frac { V }{ 10 } \) = (\(\frac { 6 }{ 3 } \))³
V = 8 x 10
Volume of A = 80 in3
In Exercises 17 – 20, find the volume of the composite solid.
Question 17.
Answer:

Question 18.
Answer:
Composite solid volume = 306 cm3
Explanation:
Given,
b = 9 cm, h = 12 cm and 10 cm
Base area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)bh
B = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(12 x 9)
B = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)108
B = 54 cm.
Bottom solid volume V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(54 x 10)
V = \(\frac { 540 }{ 3 } \)
V = 180 cm3
Top solid volume v = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(54 x 7)
V = \(\frac { 378 }{ 3 } \)
= 126 cm3
So, the volume of composite solid = 180 + 126 = 306 cm3
Question 19.
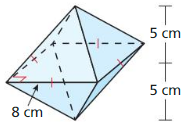
Answer:
Question 20.
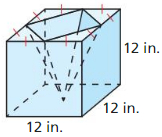
Answer:
Composite solid volume = 1152 in3
Explanation:
Given,
l x b = 12 x 12 = 144 in
h = 12 in
Volume of Box = 12 x 12 x 12 = 1728 in3
Square pyramid volume = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(144 x 12)
V = 144 x 4
V = 576 in3
Volume of composite solid = 1728 – 576 = 1152 in3
Question 21.
ABSTRACT REASONING
A pyramid has a height of 8 feet and a square base with a side length of 6 feet.
a. How does the volume of the pyramid change when the base slays the same and the height is doubled?
b. How does the volume of the pyramid change when the height stays the same and the side length of the base is doubled?
C. Are your answers 10 parts (a) and (b) true for any square pyramid? Explain your reasoning.
Answer:

Question 22.
HOW DO YOU SEE IT?
The cube shown is formed by three pyramids. each with the same square base and the same height. How could you use this to verify the formula for the volume of a pyramid?

Answer:
Question 23.
CRITICAL THINKING
Find the volume of the regular pentagonal pyramid. Round your answer to the nearest hundredth. In the diagram. m∠ABC = 35°
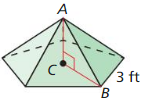
Answer:
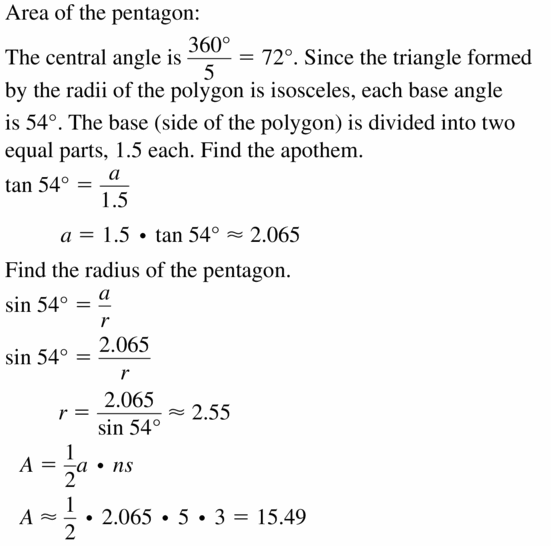

Question 24.
THOUGHT PROVOKING
A frustum of a pyramid is the part of the pyramid that lies between the base and a plane parallel to the base, as shown. Write a formula for the volume of the frustum of a square pyramid in terms of a, b, and h. (Hint: Consider the “missing” top of the pyramid and use similar triangles.)
Answer:
The frustum of a square pyramid is shown in the figure. The question requires creating a formula for the volume of the frustum. To create the required formula, draw the complete pyramid by creating the missing top on the frustum. Then, using similar triangles, find the total height of the pyramid in terms of h, b, and a. Finally, write an equation for the volume of the frustum and use the formula for the volume of the pyramid to create the formula.
Question 25.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
Nautical deck prisms were used as a safe way to illuminate decks on ships. The deck prism shown here is composed of the following three solids: a regular hexagonal prism with an edge length of 3.5 inches and a height of 1.5 inches, a regular hexagonal prism with an edge length of 3.25 inches arid a height of 0.25 inch, and a regular hexagonal pyramid with an edge length of 3 inches and a height of 3 inches. Find the volume of the deck prism.

Answer:


Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
Find the value of X. Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
Question 26.
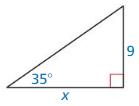
Answer:
x = 12.8
Explanation:
Given,
angle = 35, one of the side length = 9
tan 35 = \(\frac { 9 }{ x } \)
tan 35 = 0.7
0.7 = \(\frac { 9 }{ x } \)
x = 12.8
Question 27.
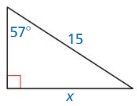
Answer:
Question 28.
Answer:
x = 5.77
Explanation:
given,
angle = 30, one of the side length = 10
tan 30 = \(\frac { x }{ 10 } \)
tan 30 = 0.577
0.577 = \(\frac { x }{ 10 } \)
x = 5.77
Question 29.
Answer:
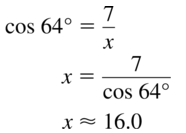
11.7 Surface Areas and Volumes of Cones
Exploration 1
Finding the Surface Area of a Cone
Work with a partner: Construct a circle with a radius of 3 inches. Mark the circumference of the circle into six equal parts, and label the length of each part. Then cut out one sector of the circle and make a cone.
a. Explain why the base of the cone is a circle. What are the circumference and radius
of the base?
Answer:
b. What is the area of the original circle? What is the area with one sector missing?
Answer:
c. Describe the surface area of the cone, including the base. Use your description to find the surface area.
Answer:
Exploration 2
Finding the Volume of a Cone
Work with a partner: The cone and the cylinder have the same height and the same circular base.
When the cone is filled with sand and poured into the cylinder. it takes three cones to fill the cylinder.
Use this information to write a formula for the volume V of a cone.
CONSTRUCTING VIABLE ARGUMENTS
To be proficient in math, you need to understand and use stated assumptions, definitions, and previously established results in constructing arguments.
Answer:
Communicate Your Answer
Question 3.
How can you find the surface area and the volume of a cone?
Answer:
Question 4.
In Exploration 1, cut another sector from the circle and make a cone. Find the radius of the base and the surface area of the cone. Repeat this three times, recording your results in a table. Describe the pattern.
Answer:
Lesson 11.7 Surface Areas and Volumes of Cones
Monitoring progress
Question 1.
Find the surface area of the right cone.
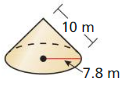
Answer:
The surface area of the right cone is 436.17 m²
Explanation:
Given,
r = 7.8m
l = 10m
S = πr² + πrl
S = π(7.8)² + π(7.8 x 10)
where π is 3.141 or 22/7
S = 3.141 x 60.84 + 3.141 x 78
S = 191.09 + 244.99
S = 436.17m²
Find the volume of the cone.
Question 2.
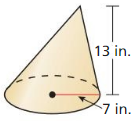
Answer:
The volume of the cone is 667.3in³
Explanation:
Given,
r = 7, h = 13
l = √13² – 7²= 10.95
S = πr² + πrl
S = π7² + π(7 x 10.95)
where π is 3.141 or 22/7
S = 3.141 x 49 + 3.141 x 76.65
S = 153.90 + 240.75
S = 394.65
Volume V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h)
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 7² x 13)
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(22 x 7 x 13)
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)2002
V = 667.3in³
Question 3.
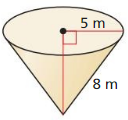
Answer:
The volume of the cone is 163.4 m³
Explanation:
Given,
radius = 5m
h = √8² – 5² = 6.24
Volume V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h)
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 5² x 6.24)
V = \(\frac { 489.99 }{ 3 } \)
V = 163.4m³
Question 4.
Cone C and cone D are similar. Find the volume of cone D.
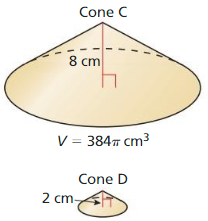
Answer:
Volume of cone D = 18.84 cm³
Explanation:
Given,
measures of cone C,
radius = 8cm, v = 384πcm³
measures of cone D,
radius = 2cm
compare both the cones,
\(\frac { Volume of cone C }{ Volume of cone D } \) = (\(\frac { height of C }{ height of D } \))³
\(\frac { 384π }{ Volume of cone D } \) = (\(\frac { 8 }{ 2 } \))³
Volume of cone D = \(\frac { 8 . 384π }{ 512 } \))³
where π is 3.141 or 22/7
Volume = \(\frac { 9649.152}{ 512 } \)
Volume D = 18.84cm³
Question 5.
Find the volume of the composite solid.
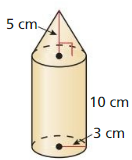
Answer:
Composite solid volume = 329.86 cm³
Explanation:
Given,
radius = 3 cm, π = 3.141 or 22/7, h = 10 cm
Volume of cylinder = πr²h
V = π(3)² x 10
V = 90π
Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h)
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 3² x 5)
= 15π
Volume of composite solid = 15π + 90π = 105π or 329.86 cm³
Exercise 11.7 Surface Areas and Volumes of Cones
Vocabulary and Core Concept Check
Question 1.
WRITING
Describe the differences between pyramids and cones. Describe their similarities.
Answer:

Question 2.
COMPLETE THE SENTENCE
The volume of a cone with radius r and height h is \(\frac{1}{3}\) the volume of a(n) __________ with radius r and height h.
Answer:
Monitoring Progress and Modeling with Mathematics
In Exercises 3 – 6, find the surface area of the right cone.
Question 3.
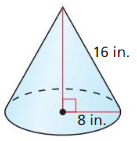
Answer:

Question 4.
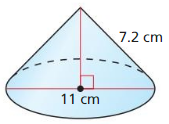
Answer:
The surface area of cone is 219.44 sq cm.
Explanation:
Given,
diameter = 11 cm
radius = d/2
r = 11/2
r = 5.5 cm
l = 7.2 cm
S = πr² + πrl
S = π(5.5)² + π(5.5 x 7.2)
where π is 3.141 or 22/7
S = 30.25 x 3.141 + 39.6 x 3.141
S = 95.01 + 135.03
S = 219.44 sq cm.
Question 5.
A right cone has a radius of 9 inches and a height of 12 inches.
Answer:

Question 6.
A right cone has a diameter of 11.2 feet and a height of 19.2 feet.
Answer:
The surface area is 418.25 sq ft.
Explanation:
Given,
r = 5.6 ft
h = 19.2 ft
l = √19.2² – 5.6² = 18.36 ft
Surface area S = πr² + πrl
S = π(5.6)² + π(5.6 x 18.36)
where π is 3.141 or 22/7
S = 3.141 x 31.36 + 3.141 x 102.81
S = 98.50 + 319.75
S = 418.25 sq ft.
In Exercises 7 – 10, find the volume of the cone.
Question 7.
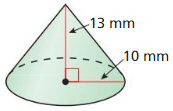
Answer:
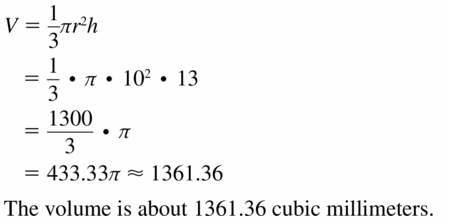
Question 8.
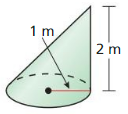
Answer:
The volume is 2.07 cubic meter.
Explanation:
Given,
h = 2m, r = 1m
Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h)
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π(1)² x 2)
where π is 3.141 or 22/7
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)3.141 x 2
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)6.22
V = \(\frac { 6.22 }{ 3 } \)
V = 2.07 cubic meter
Question 9.
A cone has a diameter of 11.5 inches and a height of 15.2 inches.
Answer:
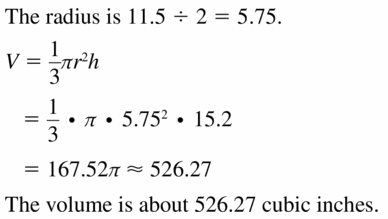
Question 10.
A right cone has a radius of 3 feet and a slant height of 6 feet.
Answer:
The volume is 56.54 cubic ft.
Explanation:
Given,
radius = 3 feet, height = 6 feet.
Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h)
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 3² x 6)
where π is 3.141 or 22/7
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)54π
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)169.614
V = 56.54 cu ft.
In Exercises 11 and 12, find the missing dimension(s).
Question 11.
Surface area = 75.4 cm2
Answer:
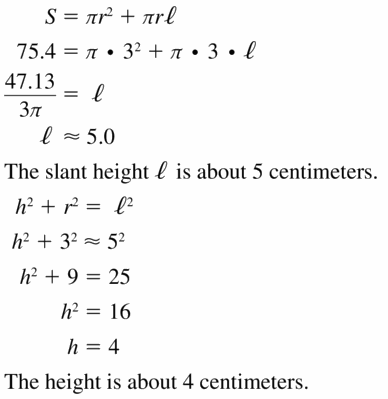
Question 12.
Volume = 216π in.3
Answer:
The radius is 3.41 in.
Explanation:
Given,
Volume = 216π in.3
height = 18 in.
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h)
\(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr² x 18) = 216
r² = \(\frac { 216 }{ 6π } \)
where π is 3.141 or 22/7
r² = \(\frac { 216 }{ 18.84 } \)
r² = 11.45
r = 3.41 in
In Exercises 13 and 14, the cones are similar. Find the volume of cone B.
Question 13.
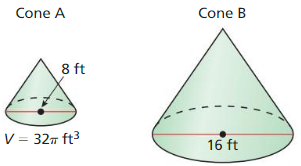
Answer:
Question 14.
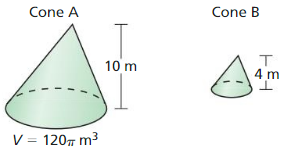
Answer:
Volume of cone B = 24.127cum3
Explanation:
Given,
Measures of cone A,
V = 120π m3, h = 10 m
measures of cone B,
h = 4m
compare both the cones,\(\frac { Volume of cone A }{ Volume of cone B } \) = (\(\frac { height of A }{ height of B } \))³
\(\frac { 120π }{ Volume of cone B } \) = (\(\frac { 10 }{ 4 } \))³
where π is 3.141 or 22/7
\(\frac { 120 . 3.141 }{ Volume of cone B } \) = \(\frac { 1000 }{ 64 } \)
\(\frac { 376.92 }{ Volume of cone B } \) = \(\frac { 1000 }{ 64 } \)
cross multiply on both sides,
Volume B = \(\frac { 376.92 . 64 }{ 1000 } \)
Volume B = \(\frac { 24122.88 }{ 1000 } \)
Volume of cone B = 24.127cum3
In Exercises 15 and 16, find the volume of the composite solid.
Question 15.
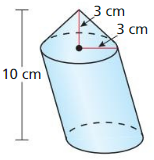
Answer:
Question 16.
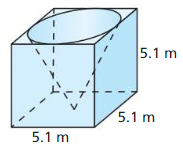
Answer:
Volume of the composite solid = 97.93 cubic m.
Explanation:
Given,
Volume of box = lbh
V = 51 x 5.1 x 5.1 = 132.651cubic m
Cone volume = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h)
where π is 3.141 or 22/7
v = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(3.141 x 2.55² x 5.1)
v = \(\frac { 104.16 }{ 3 } \)
v = 34.72
Volume of the composite solid = 132.651 – 34.72 = 97.93cubic m.
Question 17.
ANALYZING RELATIONSHIPS
A cone has height h and a base with radius r. You warn to change the cone so its volume is doubled. What is the new height if you change only the height? What is the new radius if you change only the radius? Explain.
Answer:
Question 18.
HOW DO YOU SEE IT
A snack stand serves a small order of popcorn in a cone-shaped container and a large order of popcorn in a cylindrical container. Do not perform any calculations.

a. How many small containers of popcorn do you have to buy to equal the amount of popcorn in a large container? Explain.
Answer:
3 small containers.
Explanation:
Given,
radius = 3in, h = 8 in,
cost of cone = $1.25
cost of cylinder = $2.50
Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h)
where π is 3.141 or 22/7
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(3.141 x 3² x 8)
V = \(\frac { 226.152 }{ 3 } \)
V = 75.39cubic in.
Volume of cylinder = πr²h
V = 3.141 x 3² x 8
V = 226.19
Volume of cylinder / Volume of cone = \(\frac { 226.19 }{ 75.39 } \) = 3
So, You have to buy 3 small containers of popcorn to equal the amount of popcorn in a large container.
b. Which container gives you more popcorn for your money? Explain.
Answer:
large containers gives you more popcorn for your money.
Explanation:
From the above information,
small container with a price $1.25 contains 75.39 cu in popcorn.
So, $1 = 60.312 cu in
large container with a price $2.50 contains 226.19 cu in popcorn.
So, $1 = 90.47 cu in.
when we compare both large containers gives more popcorn for your money.
In Exercises 19 and 20. find the volume of the right cone.
Question 19.
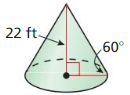
Answer:
Question 20.
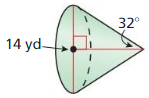
Answer:
Volume of cone is 575.62 cubic yd.
Explanation:
Given,
angle = 32,
diameter = 14 yd
radius = d/2
r = 14/2 = 7 yd.
tan 32 = \(\frac { 7 }{ h } \)
tan 32 = 0.62
h = \(\frac { 7 }{ 0.62 } \)
h = 11.21
Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h)
where π is 3.141 or 22/7
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(22 x 7 x 11.21)
V = \(\frac { 1726.34 }{ 3 } \)(22 x 7 x 11.21)
V = 575.62 cubic yd.
Question 21.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
A cat eats hail a cup of food, twice per day. Will the automatic pet feeder hold enough food for 10 days? Explain your reasoning. (1 cup ≈ 14.4 in.3)

Answer:

Question 22.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
During a chemistry lab, you use a funnel to pour a solvent into a flask. The radius of the funnel is 5 centimeters and its height is 10 centimeters. You pour the solvent into the funnel at a rate of 80 milliliters per second and the solvent flows out of the funnel at a rate of 65 milliliters per second. How long will it be before the funnel overflows? (1 mL = 1 cm3)
Answer:
17.45 seconds.
Explanation:
Given,
radius = 5 cm, h = 10 cm
pour the solvent into the funnel at a rate of 80 milliliters per second and,
the solvent flows out of the funnel at a rate of 65 milliliters per second.
(1 mL = 1 cm3)
Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h)
where π is 3.141 or 22/7
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(3.141 x 5² x 10)
V = \(\frac { 785.25 }{ 3 } \)
V = 261.8 cu cm.
solvent = 80 – 65 = 15 milliliters per second.
So, \(\frac { 261.8 }{ 15 } \) = 17.45 sec.
Question 23.
REASONING
To make a paper drinking cup, start with a circular piece of paper that has a 3-inch radius, then follow the given steps. How does the surface area of the cup compare to the original paper circle? Find m∠ABC.

Answer:

Question 24.
THOUGHT PROVOKING
A frustum of a cone is the part of the cone that lies between the base and a plane parallel to the base, as shown. Write a formula for the volume of the frustum of a cone in terms of a, b, and h. (Hint: Consider the “missing” top of the cone and use similar triangles.)
Answer:
Volume V = (1/3) * π * h * (r1² + r2² + (r1 * r2))
where,
‘r’ is the radius,
‘h’ is the height.
Question 25.
MAKING AN ARGUMENT
In the figure, the two cylinders are congruent The combined height of the two smaller cones equals the height of the larger cone. Your friend claims that this means the total volume of the two smaller cones is equal to the volume of the larger cone. Is your friend correct? Justify your answer.
Answer:
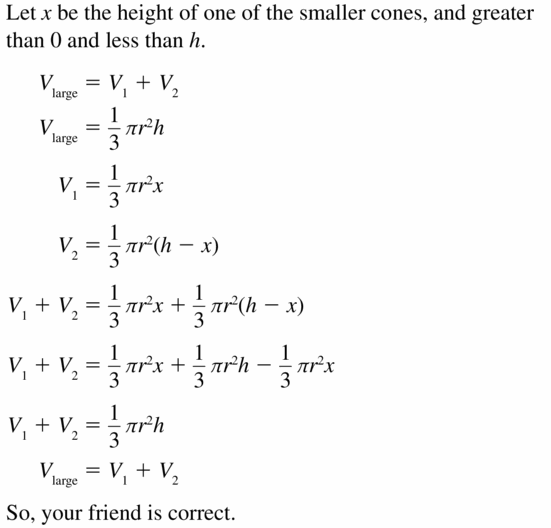
Question 26.
CRITICAL THINKING
When the given triangle is rotated around each of its sides. solids of revolution are formed. Describe the three solids and find their volumes. Give your answers in terms of π.
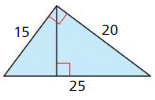
Answer:
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
Find the indicated measure.
Question 27.
area of a circle with a radius of 7 feet
Answer:
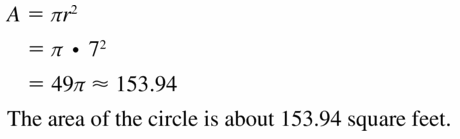
Question 28.
area of a circle with a diameter of 22 centimeters
Answer:
121π or 380.28 sq cm.
Explanation:
Given,
d = 22 cm
r = d/2
r = 22/2 = 11 cm
A = πr²
where π is 22/7 or 3.141
A = 121π or 380.28 sq cm.
Question 29.
diameter of a circle with an area of 256 square meters
Answer:
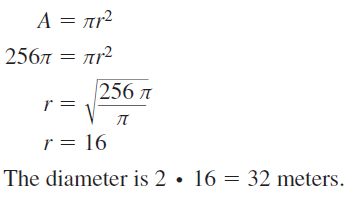
Question 30.
radius of a circle with an area of 529 π square inches
Answer:
r = 23 in.
Explanation:
Given,
Area = 529 π square inches
A = πr²
529π = πr²
r² = 529π/π
r = 23
11.8 Surface Areas and Volumes of Spheres
Exploration 1
Finding the Surface Area of a Sphere
Work with a partner: Remove the covering from a baseball or softball.

You will end up with two “figure 8” pieces of material, as shown above. From the amount of material it takes to cover the ball, what would you estimate the surface area S of the ball to be? Express your answer in terms of the radius r of the ball.
![]()
Use the Internet or some other resource to confirm that the formula you wrote for the surface area of a sphere is correct.
USING TOOLS STRATEGICALLY
To be proficient in math, you need to identify relevant external mathematical resources, such as content located on a website.
Answer:
Exploration 2
Finding the volume of a sphere
Work with a partner: A cylinder is circumscribed about a sphere, as shown. Write a formula for the volume V of the cylinder in terms of the radius r.
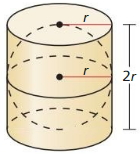
![]()
When half of the sphere (a hemisphere) is filled with sand and poured into the cylinder, it takes three hemispheres to till the cylinder. Use this information to write a formula for the volume V of a sphere in terms of the radius r.
![]()
Answer:
Communicate Your Answer
Question 3.
How can you find the surface area and the volume of a sphere?
Answer:
Question 4.
Use the results of Explorations 1 and 2 to find the surface area and the volume of a sphere with a radius of(a) 3 inches and (b) 2 centimeters.
Answer:
Lesson 11.8 Surface Areas and Volumes of Spheres
Monitoring Progress
Find the surface area of the sphere.
Question 1.
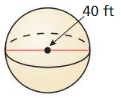
Answer:
The surface area of the sphere is 5026.54 ft²
Explanation:
Given,
D = 40
r = d/2
r = 40/2
r = 20 ft
The surface area of the sphere = 4πr²
Where π is 3.141 or 22/7
S = 4 x π x (20)²
S = 4 x 3.141 x 400
S = 5026.54 ft²
Question 2.
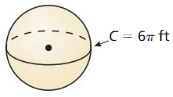
Answer:
The surface area of the sphere is 113.09 ft²
Explanation:
Given,
r = 3
Circumference C = 2πr
Circumference C = 6π
Where π is 3.141 or 22/7
2πr = 6π
The surface area of the sphere = 4πr²
S = 4π x 3²
S = 113.09 ft²
Question 3.
Find the radius of the sphere.
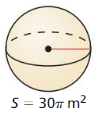
Answer:
The radius of the sphere is 2.73 m.
Explanation:
Given,
Where π is 3.141 or 22/7
s = 30πm²
The surface area of the sphere = 4πr²
30π = 4πr²
r = 2.73 m
Question 4.
The radius of a sphere is 5 yards. Find the volume of the sphere.
Answer:
The volume of the sphere is 523.59 yards³
Explanation:
Given,
r = 5 yd
The volume of the sphere V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³
V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 5³
Where π is 3.141 or 22/7
V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \) 3.141 x 125
V = 523.59 yards³
Question 5.
The diameter of a sphere is 36 inches. Find the volume of the sphere.
Answer:
The volume of the sphere is 24429.02 in³
Explanation:
Given,
D = 36
r = d/2
r = 36/2
r = 18 in.
The volume of the sphere V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³
Where π is 3.141 or 22/7
V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 18³
V = 24429.02
Question 6.
The surface area of a sphere is 576π square centimeters. Find the volume of the sphere.
Answer:
The volume of the sphere is 2304π cm³
Explanation:
Given,
r = 12
The surface area of the sphere = 4πr²
576π = 4πr²
The volume of the sphere V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³
V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 12³
V = 2304π
Question 7.
Find the volume of the composite solid at the left.
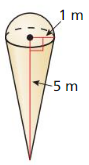
Answer:
The volume of the composite solid is 7.324 m³
Explanation:
Given,
h = 5m, r = 1 m
The volume of cone = πr²\(\frac { h }{ 3 } \)
= π x 1² x \(\frac { 5 }{ 3 } \) = 5.23
The volume of sphere = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³
= \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 1³ = 4.188
The volume of the composite solid = The volume of cone + The volume of sphere/2
= 5.23 + 4.188/2
= 7.324 m³
Exercise 11.8 Surface Areas and Volumes of Spheres
Question 1.
VOCABULARY
When a plane intersects a sphere. what must be true for the intersection to be a great circle?
Answer:

Question 2.
WRITING
Explain the difference between a sphere and a hemisphere.
Answer:
Hemisphere is a related term of the sphere. Sphere and hemisphere are three-dimensional solids. The volume of sphere is \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ and hemisphere volume is \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 } \)πr³. The surface area of the sphere is 4πr² and hemisphere surface area is 3πr².
Monitoring progress and Modeling with Mathematics
In Exercises 3 – 6, find the surface area of the sphere.
Question 3.
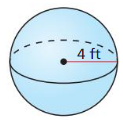
Answer:

Question 4.
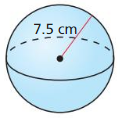
Answer:
The surface area of the sphere is 225π cm²
Explanation:
Given,
r = 7.5 cm.
The surface area of the sphere = 4πr²
S = 4π x 7.5²
S = 225π
Question 5.
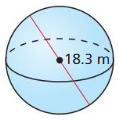
Answer:

Question 6.
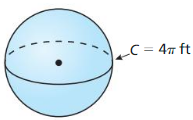
Answer:
The surface area of the sphere is 8π ft²
Explanation:
Given,
r = 2
C = 4π
2πr = 4π
The surface area of the sphere = 4πr²
S = 4π x 2²
S = 8π ft²
In Exercises 7 – 10. find the indicated measure.
Question 7.
Find the radius of a sphere with a surface area of 4π square feet.
Answer:

Question 8.
Find the radius of a sphere with a surface area of 1024π square inches.
Answer:
The radius of a sphere is 16 in.
Explanation:
Given,
Surface area of the sphere = 1024π
SA = 4πr²
1024π = 4 x πr²
r² = 1024/4
r² = 256
r = 16 in.
Question 9.
Find the diameter of a sphere with a surface area of 900π square meters.
Answer:

Question 10.
Find the diameter of a sphere with a surface area of 196π square centimeters.
Answer:
The diameter of a sphere is 14 cm.
Explanation:
Given,
The surface area of the sphere = 196π
SA = 4πr²
196π = 4πr²
r² = 196/4
r² = 49
r = 7
D = 2r
D = 2 x 7 = 14 cm.
In Exercises 11 and 12, find the surface area of the hemisphere.
Question 11.
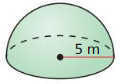
Answer:
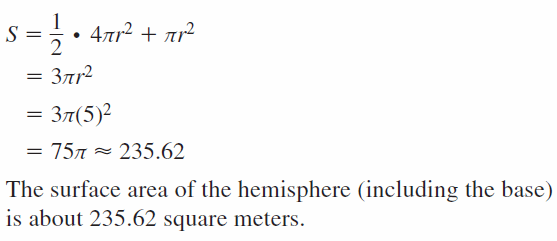
Question 12.
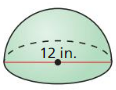
Answer:
The surface area of the hemisphere is 108π in²
Explanation:
Given,
D = 12in, r = 6in
The surface area of the sphere = 3πr²
SA = 3π x 6²
S = 108πin²
In Exercises 13 – 18. find the volume of the sphere.
Question 13.
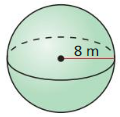
Answer:

Question 14.
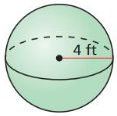
Answer:
The volume of the sphere is 268.08 ft³
Explanation:
Given,
r = 4 ft
Volume of the sphere V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³
V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 4³
Where π is 3.141 or 22/7
V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)64π
V = 268.08 ft
Question 15.
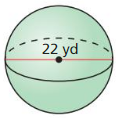
Answer:

Question 16.
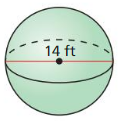
Answer:
The volume of the sphere is 1436.75 ft³
Explanation:
Given,
D = 14 ft
r = 7 ft
Volume of the sphere V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³
V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 7³
Where π is 3.141 or 22/7
V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)343π
V = 1436.75 ft
Question 17.
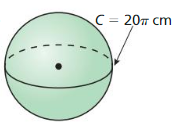
Answer:

Question 18.
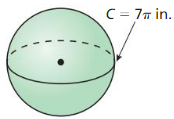
Answer:
The volume of the sphere is 179.89 in³
Explanation:
Given,
C = 7π
2πr = 7π
r = 3.5
Volume of the sphere V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³
V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 3.5³
Where π is 3.141 or 22/7
V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)42.875π
V = 179.89 in³
In Exercises 19 and 20, find the volume of the sphere with the given surface area.
Question 19.
Surface area = 16π ft2
Answer:

Question 20.
Surface area = 484π cm2
Answer:
The volume of the sphere is 5575.27 cm³
Explanation:
Given,
Surface area = 484π
4πr² = 484π
r = 11
Volume of the sphere V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³
V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 11³
Where π is 3.141 or 22/7
V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)121π
V = 5575.27 cm³
Question 21.
ERROR ANALYSIS
Describe and correct the error in finding the volume of the sphere.
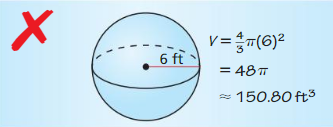
Answer:

Question 22.
ERROR ANALYSIS
Describe and correct the error in finding the volume of the sphere.
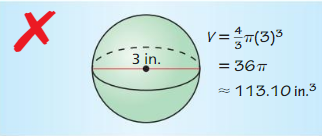
Answer:
V = 14.137 cubic in³
Explanation:
Given,
Diameter = 3 in
r = d/2
radius = 3/2
r = 1.5 in
Volume of the sphere V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³
V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x (1.5)³
Where π is 3.141 or 22/7
V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \) 3.375π
V = 14.137 cubic in³
In Exercises 23 – 26, find the volume of the composite solid.
Question 23.
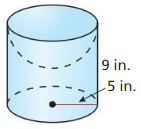
Answer:
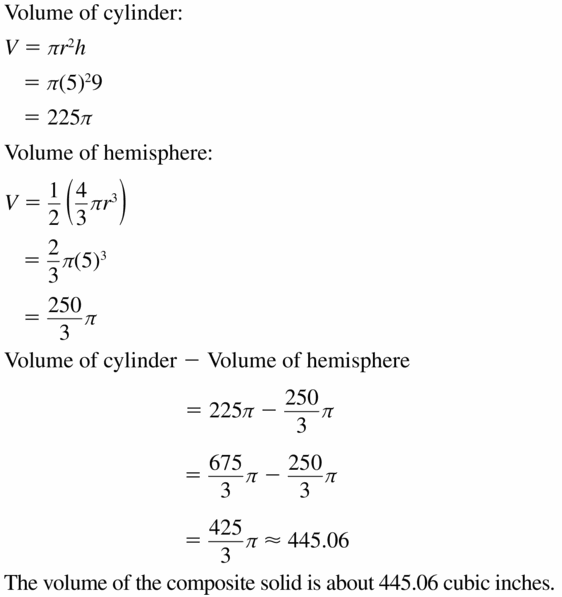
Question 24.
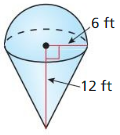
Answer:
Volume is 288π ft³
Explanation:
Given,
r = 6ft, h = 12 ft.
Volume of hemisphere = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 } \)πr³
= \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 } \)π x 6³ = 144π
volume of the cone = πr²\(\frac { h }{ 3 } \)
= π x 6² x \(\frac { 12 }{ 3 } \) = 144π
Area of circle = πr² = π x 6² = 36π
Volume of hemisphere + volume of the cone = 144π + 144π = 288π
Question 25.
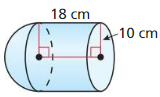
Answer:
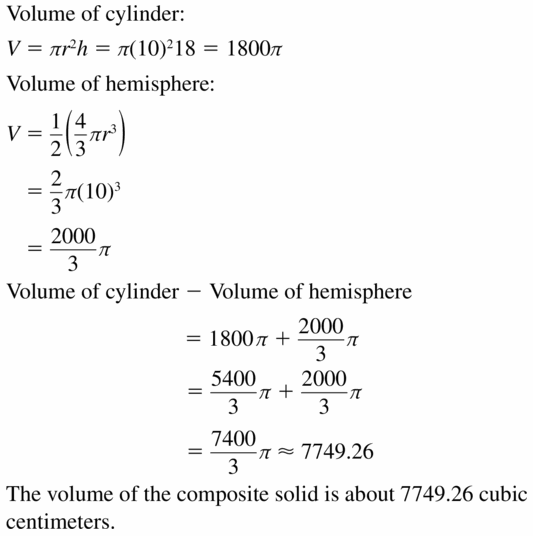
Question 26.
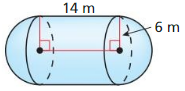
Answer:
The volume of solid is 296π m³
Explanation:
Given,
r = 6m, h = 14m
Volume of hemisphere = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 } \)πr³
= \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 } \)π x 6³ = 144π
Volume of cylinder = πr²h
= π x 6² x 14 = 504π
Volume of solid = 504π – 2(144π) = 296π
In Exercises 27 – 32, find the surface area and volume of the ball.
Question 27.
bowling ball

d = 8.5 in.
Answer:

Question 28.
basketball

C = 29.5 in.
Answer:
The surface area is 277 in², volume is 43212.27 in³
Explanation:
Given,
C = 29.5 in
r = d/2
r = 29.5/2
r = 14.75 in
2πr = C
Surface area = 4πr²
SA = 4π x 4.69² = 277 in²
Volume V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³
V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 4.69³
where π is 3.141 or 22/7
V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)103.16π
V = 43212.27 in³
Question 29.
softball

C = 12 in.
Answer:

Question 30.
golf ball
![]()
d = 1.7 in.
Answer:
The surface area is 10.68 in², volume is 2.57 in³
Explanation:
Given,
d = 1.7
r = d/2
r = 1.7/2
r = 0.85
Surface area = 4πr²
SA = 4π x 0.85²
SA = 3.4 x 3.141
SA = 10.68 in²
Volume V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³
where π is 3.141 or 22/7
V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)0.6141π
V = 2.57 in³
Question 31.
volleyball

C = 26 in.
Answer:

Question 32.
baseball

C = 9 in.
Answer:
The surface area is 25.78 in², volume is 12.24 in³
Explanation:
Given,
C = 9
r = 1.43 in
2πr = C
Surface area = 4πr²
S = 4π x 1.43²
S = 25.78 in²
Volume V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³
where π is 3.141 or 22/7
V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \) 2.92π
V = 12.24 in³
Question 33.
MAKING AN ARGUMENT
You friend claims that if the radius of a sphere is doubled, then the surface area of the sphere will also be doubled. Is our friend correct? Explain your reasoning.
Answer:

Question 34.
REASONING
A semicircle with a diameter of 18 inches is rotated about its diameter. Find the surface area and the volume of the solid formed.
Answer:
The surface area is 1018 in², volume is 3054.02 in³
Explanation:
Given,
Diameter = 18
r = d/2
r = 18/2
r = 9 in
Volume V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³
V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 9³
V = 3054.02 in³
Surface area = 4πr²
S = 4π x 9²
Where π is 3.141 or 22/7
S = 4 x 3.141 x 81
S = 1018 in²
Question 35.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
A silo has the dimensions shown. The top of the silo is a hemispherical shape. Find the volume of the silo.

Answer:
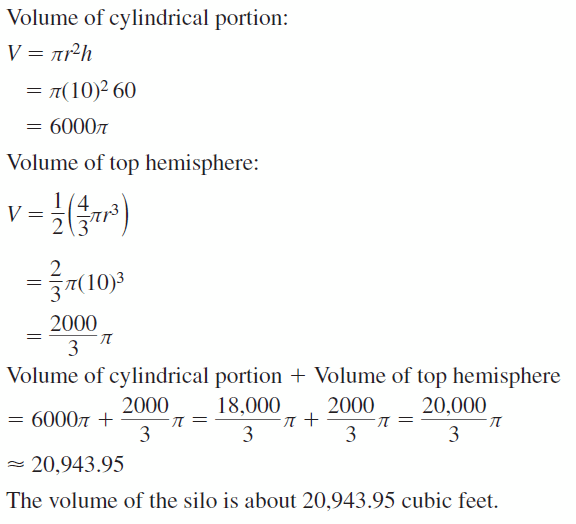
Question 36.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
Three tennis balls are stored in a cylindrical container with a height of 8 inches and a radius of 1.43 inches. The circumference of a tennis ball is 8 inches.

a. Find the volume of a tennis ball.
Answer:
V = 8.64 in³
Explanation:
Given,
C = 8 in
2πr = c
2 x 3.141r = 8
r = 1.27 in
Volume V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³
V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 1.27³
Where π is 3.141 or 22/7
V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 1.27³
V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)2.048π
V = 8.64 in³
The volume of tennis ball = 8.64 in³
b. Find the amount of space within the cylinder not taken up by the tennis balls.
Answer:
Remaining space = 64.46 in²
Explanation:
Given,
r = 1.27 in
The surface area of tennis ball (S) = 4πr²
S = 4π x 1.27² = 20.26
Area of cylinder s = 2πrh + 2πr²
s = 2π x 1.43 x 8+2π x 1.43²
Where π is 3.141 or 22/7
s = 84.72
Remaining space = 84.72 – 20.26 = 64.46 in²
Question 37.
ANALYZING RELATIONSHIPS
Use the table shown for a sphere.
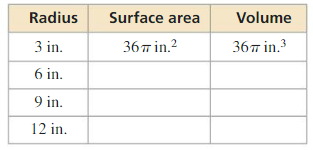
a. Copy and complete the table. Leave your answers in terms of π.
b. What happens to the surface area of the sphere when the radius is doubled? tripled? quadrupled?
c. What happens to the volume of the sphere when the radius is doubled? tripled? quadrupled?
Answer:

Question 38.
MATHEMATICAL CONNECTIONS
A sphere has a diameter of 4(x + 3) centimeters and a surface area of 784 π square centimeters. Find the value of x.
Answer:
x =11
Explanation:
Given,
4(x + 3) centimeters.
surface area of 784 π square centimeters
Surface area = 4πr²
784π = πr²
r = 28
2r = diameter = 4(x + 3)
r = 2(x + 3)
28 = 2(x + 3)
x = 11
Question 39.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
The radius of Earth is about 3960 miles. The radius of the moon is about 1080 miles.
a. Find the surface area of Earth and the moon.
b. Compare the surface areas of Earth and the moon.
c. About 70% of the surface of Earth is water. How many square miles of water are on Earth’s surface?
Answer:

Question 40.
MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS
The Torrid Zone on Earth is the area between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn. The distance between these two tropics is about 3250 miles. You can estimate the distance as the height of a cylindrical belt around the Earth at the equator.
a. Estimate the surface area of the Torrid Zone. (The radius of Earth is about 3960 miles.)
Answer:
Surface Area = 197086348.8
Explanation:
Given,
The radius of Earth is about 3960 miles.
h = 3250 mi
Surface area of cylinder = 2πrh
S = 2π x 3960 x 3250
Where π is 3.141 or 22/7
S = 80875080
surface area of earth = 4πr²
= 4π x 3960²
= 197086348.8
b. A meteorite is equally likely to hit anywhere on Earth. Estimate the probability that a meteorite will land in the Torrid Zone.
Answer:
0.4104 or 41%
Explanation:
Given,
A meteorite is equally likely to hit anywhere on Earth.
From the above information,
SA of cylinder = 80875080
SA of earth = 197086348.8
Probability of meteorites hitting the torrid zone = 80875080/197086348.8 = 0.4104
Question 41.
ABSTRACT REASONING
A sphere is inscribed in a cube with a volume of 64 cubic inches. What is the surface area of the sphere? Explain your reasoning.
Answer:

Question 42.
HOW DO YOU SEE IT?
The formula for the volume of a hemisphere and a Cone are shown. If each solid has the same radius and r = h, which solid will have a greater volume? Explain your reasoning.
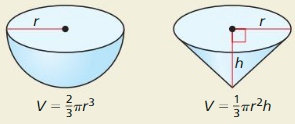
Answer:
The hemisphere has the highest volume.
Explanation:
According to the information given in the figure,
Volume of hemisphere v = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 } \)πr³
Volume of cone V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)πr²h
If r = h
Volume of cone V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)πr² x r = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)πr³
So, the hemisphere has the highest volume.
Question 43.
CRITICAL THINKING
Let V be the volume of a sphere. S be the surface area of the sphere, and r be the radius of the sphere. Write an equation for V in terms of r and S. (Hint: Start with the ratio \(\frac{V}{S}\).)
Answer:
V = \(\frac{Sr}{3}\).
Explanation:
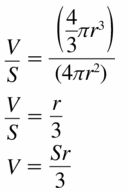
Question 44.
THOUGHT PROVOKING
A spherical lune is the region between two great circles of a sphere. Find the formula for the area of a lune.
Answer: The surface area of a spherical lune is 2θ R²,
where R is the radius of the sphere and θ is the dihedral angle in radians between the two half-great circles.
Question 45.
CRITICAL THINKING
The volume of a right cylinder is the same as the volume of a sphere. The radius of the sphere is 1 inch. Give three possibilities for the dimensions of the cylinder.
Answer:
r = \(\frac{1}{3}\), h = 12
Explanation:
Given,
The radius of the sphere is 1 inch.
We know that ,
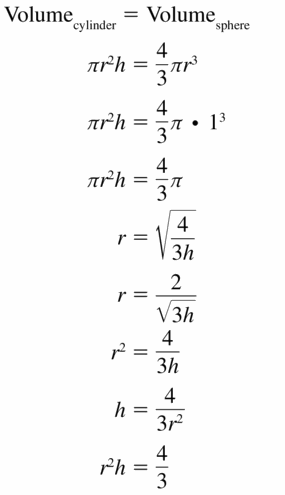
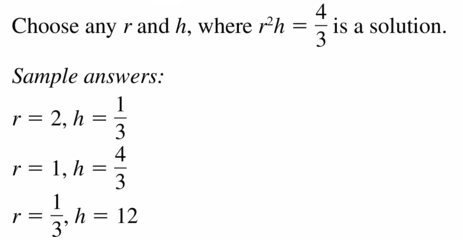
Question 46.
PROBLEM SOLVING
A spherical cap is a portion of a sphere cut off by a plane. The formula for the volume of a spherical cap is V = \(\frac{\pi h}{6}\) (3a2 + h2), where a is the radius of the base of the cap and h is the height of the cap. Use the diagram and given information to find the volume of each spherical cap.
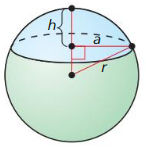
a. r = 5ft, a = 4ft
Answer:
V = πh/6 x (3a² +h²).
Where a = r = 5ft
h = 4ft
V = π(4)/6 x (3(5)² +(4)²)
= π(4)/6 x 91
= 4π/6 x 91
= 12.56/6 x 91 = 190.49 cu. ft
b. r = 34 cm, a = 30 cm
Answer:
V = π(30)/6 x (3(34)² +(30)²)
= π(30)/6 x (3(1156) + (900))
= π(30)/6 x 6,168
= 94.2/6 x 6,168
= 96,837.6 cu. cm
c. r = 13 m, h = 8 m
Answer:
V = π(8)/6 x (3(13)² +(8)²)
= 8π/6 x (3(169 + 64))
= 8π/6 x (699)
= 25.12/6 x 699
= 2,926.48 cu. cm
d. r=75 in., h = 54in.
Answer:
V = π(54)/6 x (3(75)² +(54)²)
= 54π/6 x (3(5,625 + 2,916)
= 54π/6 x (25,623)
= 169.56π/6 x 25,623
= 532.4184 x 25,623
= 13,642,156.66 cu. in
Question 47.
CRITICAL THINKING
A sphere with a radius of 2 inches is inscribed in a right cone with a height of 6 inches. Find the surface area and the volume of the cone.
Answer:

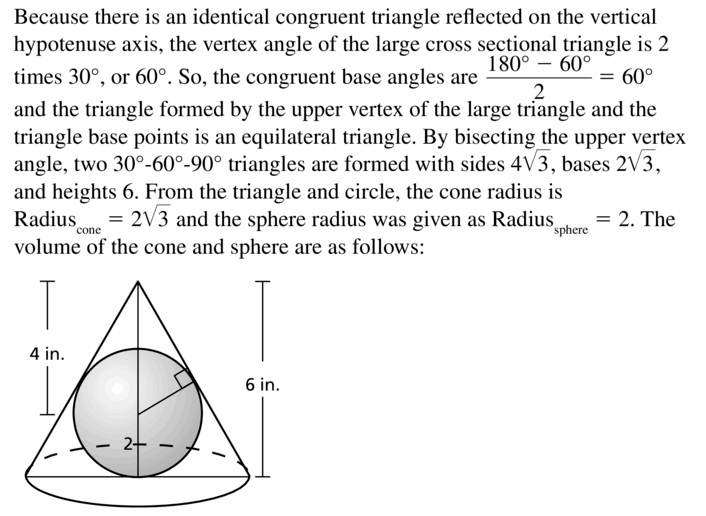
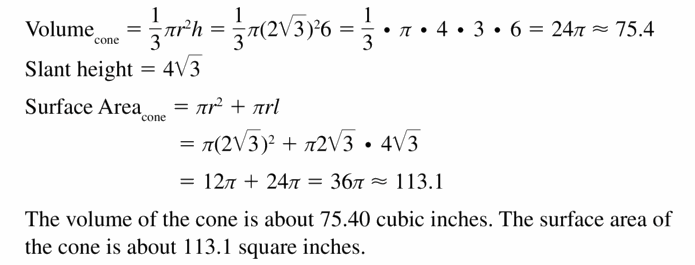
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
Solve the triangle. Round decimal answers to the nearest tenth.
Question 48.
A = 26°, C = 35°, b = 13
Answer:
B = 119°, a = 7.16, c = 9.5
Explanation:
Given,
A = 26°, C = 35°, b = 13
B = 180 – (A + C)
B = 180 – (26 + 35) = 119°
\(\frac { sin A }{ a } \) = \(\frac { sin B }{ b } \)
substitute the above values
\(\frac { sin 26 }{ a } \) = \(\frac { sin 119 }{ 13 } \)
By cross multiplying, we get
a = \(\frac { sin 26 . 13}{ sin119 } \)
Based on logarithm substitute the sin values.
a = 7.16
\(\frac { sin C }{ c } \) = \(\frac { sin B }{ b } \)
\(\frac { sin 35 }{ c } \) = \(\frac { sin 119 }{ 13 } \)
By cross multiplying, we get
c = \(\frac { sin 35 . 13}{ sin119 } \)
Based on logarithm substitute the sin values.
c = 9.5
Question 49.
B = 102°, C = 43°, b = 21
Answer:
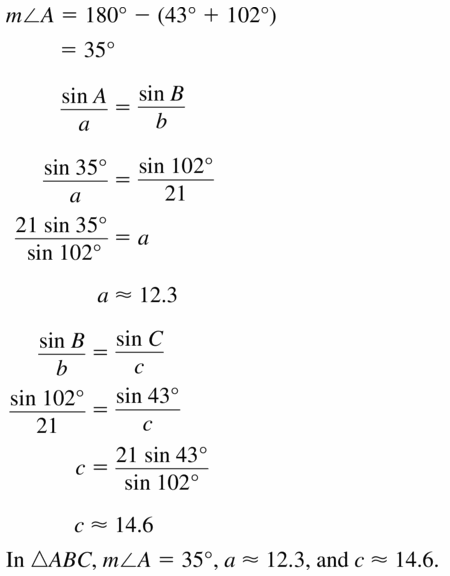
Question 50.
a = 23, b = 24, c = 20
Answer:
A = 62.2, B = 65.5, C = 49.4
Explanation:
Given,
a = 23, b = 24, c = 20
a² = b² + c² – 2bc cos A
23² = 24²+ 20² – 2(24 x 20) cos A
A = 62.2
\(\frac { sin 62.2 }{ 23 } \) = \(\frac { sin B }{ 24 } \)
By cross multiplying, we get
Based on logarithm substitute the sin values.
B = \(\frac { sin 62.2 . 24 }{ 23 } \)
B = 65.5
\(\frac { sin 62.2 }{ 23 } \) = \(\frac { sin C }{ 20 } \)
C = \(\frac { sin 62.2 . 20 }{ 23 } \)
C = 49.4
Question 51.
A = 103°, b = 15, c = 24
Answer:

Circumference, Area, and Volume Review
11.1 Circumference and Arc Length
Find the indicated measure.
Question 1.
diameter of ⊙P
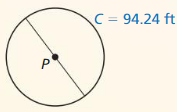
Answer:
Diameter of ⊙P is 29.99 ft.
Explanation:
Given,
Circumference = 94.24 ft
C = πd
94.24 = 3.141d
where π is 3.141 or 2/7
d = 94.24/3.141
d = 29.99 ft.
Question 2.
circumference of ⊙F
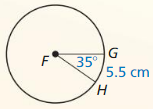
Answer:
circumference of ⊙F = 56.57 cm.
Explanation:
Given,
angle = 35 degrees, length of arc = 5.5 cm.
length of arc = 2 π r (θ/360°)
where as 2 π r = C
5.5 = \(\frac { 35 }{ 360 } \) x C
C = \(\frac { 1980 }{ 35 } \)
C = 56.57 cm
Question 3.
arc length of \(\widehat{A B}\)
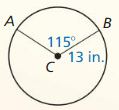
Answer:
arc length of \(\widehat{A B}\) = 26.10 in
Explanation:
Given,
angle = 115 degrees, radius = 13 in.
length of arc = 2 π r (θ/360°)
arc length of \(\widehat{A B}\) = \(\frac { 115 }{ 360 } \) . 2π(13)
where π is 3.141 or 2/7
s = \(\frac { 35 }{ 360 } \) 2 x \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 } \)x 13
s = \(\frac { 35 }{ 360 } \) 81.66
s = \(\frac { 65780 }{ 2520 } \)
= 26.10 in.
Question 4.
A mountain bike tire has a diameter of 26 inches. To the nearest foot, how far does the tire travel when it makes 32 revolutions?
Answer:
The tire travels 2613.80 inches.
Explanation:
Given,
D = 26 in
r = d/2
r = 26/2
r = 13 in
Circumference C = 2πr
2π(13) = 81.68
where πis 22/7 or 3.141
C = 2 x \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 } \) x 13
C = \(\frac { 572 }{ 7 } \)
C = 81.68
Number of revolutions = 32
Total distance travelled by the tire travels = 32 x 81.68
= 2613.80 in.
11.2 Areas of Circles and Sectors
Find the area of the blue shaded region.
Question 5.
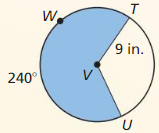
Answer:
Area = 169.64 sq in.
Explanation:
Given, angle = 240 degrees, radius = 9 in.
Area = (θ/360°) π(r)²
Area = \(\frac { 35 }{ 360 } \)π(r)²
A = \(\frac { 240 }{ 360 } \) . π(9)²
where π is 22/7 or 3.141
A = \(\frac { 240 }{ 360 } \) . π(9)²
A = \(\frac { 7168 }{ 48 } \)
= 169.64 sq in.
Question 6.
Answer:
Area of shaded region = 11.44 sq in.
Explanation:
Given,
diameter = 4 in.
r = d/2
r = 4/2
r = 2in
radius = 2in
Area of rectangle = 6 x 4 = 24
Area of semicircle = π(r)² = 4π
Area of shaded region = 24 – 4π
where π 22/7 or 3.141
4π = 4 x 3.141 = 12.56
Area of shaded region = 24 – 12.56
A = 11.44 sq in
Question 7.
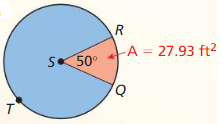
Answer:
Area of shaded region = 173.13 sq units.
Explanation:
Given,
angle = 50 degrees,
A = 27.93 sq ft.
Area = (θ/360°) π(r)²
Area = \(\frac { 50 }{ 360 } \) . πr²
27.93 = \(\frac { 50 }{ 360 } \) x \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 } \)
r² = \(\frac { 3519.18 }{ 55 } \)
r² = 63.98 or 64
r = 8
Area of the blue region = \(\frac { Total area – area of red region }{ 360 } \)
Area of the blue region = \(\frac { 360-50 }{ 360 } \)
Area of shaded region = \(\frac { 310 }{ 360 } \) . π(8)²
where π is 22/7 or 3.141
Area of the blue region = \(\frac { 31 }{ 36 } \) x \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 } \) 64
A = \(\frac { 43648 }{ 252 } \)
A = 173.13 3223 sq units.
11.3 Areas of Polygons
Find the area of the kite or rhombus.
Question 8.
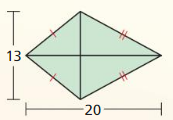
Answer:
Area = 65 sq units.
Explanation:
Given,
d₁ = 13, d₂ = 20
Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(d₁d₂)
A = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(13 x 20)
A = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)260
A = 65 sq units.
Question 9.
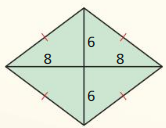
Answer:
Area = 48 sq units.
Explanation:
Given,
d₁ = 16, d₂ = 12
Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(d₁d₂)
A = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(16 x 12)
A = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)192
A = 48 sq units.
Question 10.
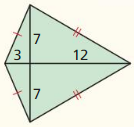
Answer:
Area = 52.5 sq units.
Explanation:
Given,
d₁ = 14, d₂ = 15
Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(d₁d₂)
A = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(14 x 15)
A = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)210
A = 52.5 sq units.
Find the area of the regular polygon.
Question 11.
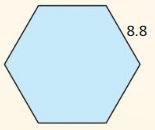
Answer:
A = 201.195 sq units.
Explanation:
Given,
A regular hexagon.
side length = 8.8
Area of hexagon = \(\frac { 3√3 }{ 2 } \)a²
A = \(\frac { 3√3 }{ 2 } \)(8.8)²
A = \(\frac { 3√3 }{ 2 } \)77.44
A= 3√3 x 38.72
A = 201.195 sq units.
Question 12.
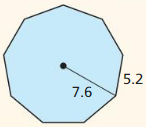
Answer:
A = 117.84 sq units.
Explanation:
Given,
a = 5.2, s = 7.6,
n = number of sides
Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(n . a . s)
A = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(9 . 5.2 . 7.6)
A = \(\frac { 355.68 }{ 2 } \)
A = 117.84 sq units.
Question 13.
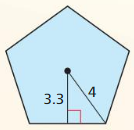
Answer:
A = 33 sq units.
Explanation:
Given,
a = 4, s = 3.3,
n = number of sides
Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(n . a . s)
A = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(5 . 4 . 3.3)
A = \(\frac { 66 }{ 2 } \)
A = 33
Question 14.
A platter is in the shape of a regular octagon with an apothem of 6 inches. Find the area of the platter.
Answer:
A = 16.97 sq units.
Explanation:
Given,
a = 6, s = sin 45,
n = number of sides
Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(n . a. s)
A = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(8 . 6 . sin 45)
A = \(\frac { 33.963 }{ 2 } \)
A = 16.97 sq units.
11.4 Three-Dimensional Figures
Sketch the solid produced by rotating the figure around the given axis. Then identify and describe the solid.
Question 15.
Answer:
Cone.

Explanation:
The solid produced by rotating the figure around the given axis is cone.
We know that a cone is flat and curved surface pointed towards the top.
It has 1 vertex, 1 edge, 1 face and 1 curved surface as shown in the above figure.
Question 16.
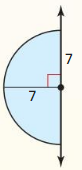
Answer:
Circle.
Explanation:
The solid produced by rotating the figure around the given axis is cone.
Because a circle is a flat, plane shape.
It does not form any edges or vertices.
Question 17.
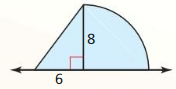
Answer:
Describe the cross section formed by the intersection of the plane and the solid.
Question 18.
Answer:
The cross section is a rectangle.
Explanation:
A cross section is the intersection of a figure in three-dimensional space with a plane as shown above.
It is the face obtain by making a slice through a solid object which is two-dimensional.
Therefore, the figure obtained from a cross section depends upon the angle of the plane doing the cutting.
So, the cross section formed by the intersection of the plane and the solid is rectangle.
Question 19.
Answer:
The cross-section is a square.
Explanation:
A cross section is the intersection of a figure in three-dimensional space with a plane as shown above.
It is the face obtain by making a slice through a solid object which is two-dimensional.
Therefore, the figure obtained from a cross section depends upon the angle of the plane doing the cutting.
So, the cross section formed by the intersection of the plane and the solid is square.
Question 20.
Answer:
The cross-section is a triangle.
Explanation:
A cross section is the intersection of a figure in three-dimensional space with a plane as shown above.
It is the face obtain by making a slice through a solid object which is two-dimensional.
Therefore, the figure obtained from a cross section depends upon the angle of the plane doing the cutting.
So, the cross section formed by the intersection of the plane and the solid is triangle.
11.5 Volumes of Prisms and Cylinders
Find the volume of the solid.
Question 21.
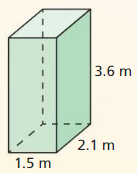
Answer:
V = 113.4 m³
Explanation:
Given,
l = 2.1m, b = 1.5m and h = 3.6m
Volume = lbh
V = 3.6 x 2.1 x 1.5
V = 113.4 m³
Question 22.
Answer:
V = 100.57 mm³
Explanation:
Given,
radius = 2mm, h = 8mm
Volume = πr²h
where π is 22/7 or 3.141
V = \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 } \) 4 x 8
V = \(\frac { 704 }{ 2 } \)
V = 100.57 mm³
Question 23.
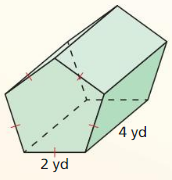
Answer:
V = 27.52 yd³
Explanation:
Given,
Pentagon area = 6.88 sq yd.
height = 4 yd
Volume = Area x height
V = 6.88 x 4 = 27.52 yd³
11.6 Volumes of Pyramids
Find the volume of the pyramid.
Question 24.
Answer:
V = 189 ft³
Explanation:
Base Area = 9² = 81 ft
height = 7 ft
Volume V = Base area x height/3
V = 81 x 7/3
V = 567/3
V = 189 ft³
Question 25.
Answer:
V = 400 yd³
Explanation:
Given,
Base Area = 4 x 15 = 60 yd
height = 20 yd
Volume V = Base area x height/3
V = 60 x 20/3
V = 1200/3
V = 400 yd³
Question 26.
Answer:
V = 300 m³
Explanation:
Given,
base area = 18 x 10 = 180m
height = 5m
Volume V = Base area x height/3
V = 180 x 5/3
V = 900/3
V = 300 m³
Question 27.
The volume of a square pyramid is 60 cubic inches and the height is 15 inches. Find the side length of the square base.
Answer:
The side length of the square base is 6 in.
Explanation:
Given,
The volume of a square pyramid is 60 cubic inches.
height = 15 in.
V = 60
V = s²h/3
s² x 15/3 = 60
5s² = 60
s² = 60/5
s² = 12
s = 6in.
Question 28.
The volume of a square pyramid is 1024 cubic inches. The base has a side length of 16 inches. Find the height of the pyramid
Answer:
h = 12 in.
Explanation:
Given,
The volume of a square pyramid is 1024 cubic inches.
side length of 16 inches.
V = s²h/3
1024 x 3 = 16²h
h = 3072/256
h = 12 in.
11.7 Surface Areas and Volumes of Cones
Find the surface area and the volume of the cone.
Question 29.
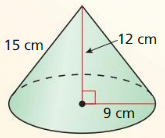
Answer:
Surface area is 678.85 cm²
volume is 1017.28 cm³
Explanation:
Given,
height = 12cm, radius = 9 cm, side length = 15 cm.
Surface area of cone S = πr² + πrl
where π= 22/7 or 3.141
S = π x 9² + π x 9 x 15
S = 254.57 + 424.28
S = 678.85 cm²
Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h)
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 9² x 12)
V = \(\frac { 21384 }{ 21 } \)
V = 1018.28 cm³
Question 30.
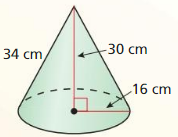
Answer:
Surface area is 2514.28 cm²
volume is 8045.71 cm³
Explanation:
Given,
height = 30cm, radius = 16 cm, side length = 34 cm.
Surface area of cone S = πr² + πrl
S = π x 16² + π x 16 x 34
where π= 22/7 or 3.141
S = 804.57 + 1709.71
S = 2514.28 cm²
Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h)
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 16² x 30)
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)( π x 256 x 30)
V = \(\frac { 168960 }{ 21 } \)
V = 8045.71cm³
Question 31.
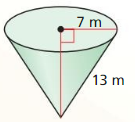
Answer:
Surface area is 440 m²
volume is 562.102 m³
Explanation:
Given,
height = 10.95 m, radius = 7 m, side length = 13 m.
Surface area of cone S = πr² + πrl
where π= 22/7 or 3.141
S = π x 7² + π x 7 x 13
S = 49π + 91π
S = 140π
S = 440m²
h = √13² – 7² = 10.95
Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h)
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 7² x 10.95)
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 49 x 10.95)
V = \(\frac { 11804.1 }{ 21 } \)
V = 562.102 m³
Question 32.
A cone with a diameter of 16 centimeters has a volume of 320π cubic centimeters. Find the height of the cone.
Answer:
The height of the cone = 15 cm.
Explanation:
Given,
r = 8
Volume V = 320π
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h)
320π = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 8² x h)
h = 960/64
h = 15 cm.
11.8 Surface Areas and Volumes of Spheres
Find the surface area and the volume of the sphere.
Question 33.
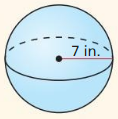
Answer:
The surface area is 616 in², volume is 1437.33 in³
Explanation:
Given,
radius = 7 m,
Surface area S = 4πr²
where π= 22/7 or 3.141
S = 4π x 7²
S = 4312/7
S = 616 in²
Volume V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³
V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 7³
V = \(\frac { 4312 }{ 3 } [/latex
V = 1437.33 in³
Question 34.
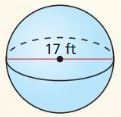
Answer:
The surface area is 908.2 ft², volume is 2573.47 ft³
Explanation:
Given,
d = 17 ft
r = d/2
r = 17/2
r = 8.5 ft
Surface area S = 4πr²
where π= 22/7 or 3.141
S = 4π x 8.5²
S = 6358/7
S = 908.2 ft²
Volume V = [latex]\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³
V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 8.5³
V = \(\frac { 54043 }{ 21 } \)
V = 2573.47 ft³
Question 35.
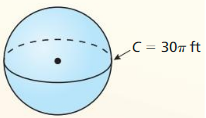
Answer:
The surface area is 2827.43 ft², volume is 14137.16 ft³
Explanation:
C = 30π
2πr = 30π
r = 15
Surface area S = 4πr²
S = 4π x 15²
where π= 22/7 or 3.141
S = 2827.43
Volume V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³
V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 15³
V = 14137.16
Question 36.
The shape of Mercury can be approximated by a sphere with a diameter of 4880 kilometers. Find the surface area and the volume of Mercury.
Answer:
The surface area and the volume of Mercury is 23814400π, 19369045330π
Explanation:
Given,
d = 4880 km
r = d/2
r = 4880/2
r = 2440 km
Surface area S = 4πr²
S = 4π x 2440²
S = 23814400π
Volume V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³
V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 2440³
V = 19369045330π
Question 37.
A solid is composed of a cube with a side length of 6 meters and a hemisphere with a diameter of 6 meters. Find the volume of the composite solid.
Answer:
Volume of the composite solid = 272.57 cu m.
Explanation:
Given,
Volume of cube = a³
a = 6³ = 216 m
Volume of hemisphere = \(\frac { 4 }{ 6 } \)πr³
V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 6 } \)π x 3³
V = 18π or 56.57
where π= 22/7 or 3.141
Volume of the composite solid = 216 + 56.57 = 272.57 cu m.
Circumference, Area, and Volume Test
Find the volume of the solid.
Question 1.
Answer:
Volume = 2577.29 m³
Explanation:
Given,
h = 15.5m, a = 8 m
Volume = \(\frac { 3√3 }{ 2 } \)a²h
V = \(\frac { 3√3 }{ 2 } \) x 8² x 15.5
V = \(\frac { 3√3 }{ 2 } \) x 992
V = 3√3 x 496
V = 2577.29 m³
Question 2.
Answer:
Volume is 17.157 ft³
Explanation:
Given,
d = 3.2 ft
r = d/2
r = 3.2/2
r = 1.6 ft
Volume V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³
V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 1.6³
where π= 22/7 or 3.141
V = \(\frac { 360.448 }{ 21 } \)
V = 17.164 ft³
Question 3.
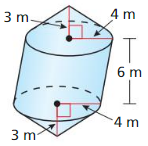
Answer:
Volume of sloid = 402.11 m³
Explanation:
Given,
r = 4m, h = 3m
Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)πr²h
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)π x 4² x 3
where π= 22/7 or 3.141
V = \(\frac { 1056 }{ 21 } \)
V = 50.28
Volume of cylinder = πr²h
V = π x 4² x 6
V = 301.71
Volume of sloid = 2(50.28) + 301.71
V = 100.56 + 301.71
V = 402.11m³
Question 4.
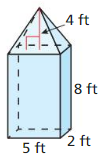
Answer:
Volume of solid = 106.66 cu ft.
Explanation:
Given,
l = 2 ft, b = 5 ft, h = 8 ft
Volume of rectangular box =lbh
V = 5 x 2 x 8 = 80 cu ft.
Volume of pyramid = lbh/3
V = (5 x 2 x 8)/3
V = 80/3 = 26.66 cu ft.
Volume of solid = Volume of rectangular box + volume of pyramid
80 + 26.66 = 106.66 cu. ft
Find the indicated measure.
Question 5.
circumference of ⊙F
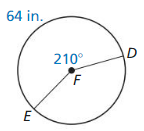
Answer:
circumference of ⊙F is 109.71 in.
Explanation:
Given,
angle = 210 degrees, arc length = 64 in.
length of arc = 2 π r (θ/360°)
s = \(\frac { 210 }{ 360 } \) • C
64 = \(\frac { 210 }{ 360 } \) • C
C = \(\frac { 2304 }{ 21 } \)
C = 109.7 in.
Question 6.
m\(\widehat{G H}\)
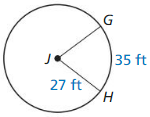
Answer:
m\(\widehat{G H}\) = 74.27 degrees.
Explanation:
Given,
radius = 27 ft, length of arc = 35 ft
length of arc = 2 π r (θ/360°)
35 = \(\frac { x }{ 360 } \) • 2π x 27
where π is 22/7 or 3.141
x = \(\frac { 88200 }{ 1188 } \)
x = 74.27 degrees.
Question 7.
area of shaded sector
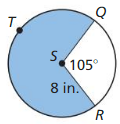
Answer:
Area is 142.41 in²
Explanation:
Given,
angle = 105 degrees, radius = 8 in.
length of arc = 2 π r (360 – θ/360°)
Area = \(\frac { 360 – 105 }{ 360 } \) • π x 8²
where π is 22/7 or 3.141
Area = \(\frac { 255 }{ 360 } \) 64π
A = \(\frac { 359040 }{ 2520 } \)
A = 142.41 in²
Question 8.
Sketch the composite solid produced by rotating the figure around the given axis. Then identify and describe the composite solid.
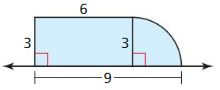
Answer:
The radius of the cylinder is 3
The height of the cylinder is 6.
The radius of the hemisphere is 3.
Question 9.
Find the surface area of a right cone with a diameter of 10 feet and a height of 12 feet.
Answer:
The surface area is 487.14 sq ft
Explanation:
Given,
diameter = 10 feet, height = 12 feet.
radius = d/2
r = 10/2
r = 5 ft.
l² = r² + h²
l² = 5² + 12²
l² = 25 + 144
l² = 169
l = 13 ft
Surface area S = πr² + 2πrl
where π is 22/7 or 3.141
S = π x 5² + 2π x 5 x 13
S = 25π + 130π
S = 155π
S = 487.14 sq ft.
Question 10.
You have a funnel with the dimensions shown.
a. Find the approximate volume of the funnel.
Answer:
V = 377.14 cu cm.
Explanation:
Given,
radius = 6 cm, height = 10 cm
Volume = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)πr²h
where π is 22/7 or 3.141
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)π x 6² x 10
V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \) 120π
V = \(\frac { 23760 }{ 21 } \)
V = 377.14 cu cm.
b. You use the funnel to put oil in a ear. Oil flows out of the funnel at a rate of 45 milliliters per second. How long will it take to empty the funnel when it is full of oil? (1 mL = 1 cm3)
Answer:
T = 376.8 ml/45 ml per sec
T = 8.373 sec
c. How long would it take to empty a funnel with a radius of 10 centimeters and a height of 6 centimeters if oil flows out of the funnel at a rate of 45 milliliters per second?
Answer:
V = 1/3 πr²h
= 1/3 (3.14 × 10² × 6)
= 1/3(1884)
= 628 cu. cm
T = 628 ml/45 ml per sec
T = 13.95 sec
d. Explain why you can claim that the time calculated in part (c) is greater than the time calculated in part (b) without doing any calculations.
Answer:
- In cone type shaped object if the radius is large then the volume of the cone increases.
- In the b part of the funnel, the radius is smaller than the height and in the c part, the radius is larger than the height of the cone.
- V = 1/3 πr²h
- It means if radius increase volume also increases with the same rate. So, the time is taken by the c part (13.95 sec) is larger than the b part.
Question 11.
A water bottle in the shape of a cylinder has a volume of 500 cubic centimeters. The diameter of a base is 7.5 centimeters. What is the height of the bottle? Justify your answer.
Answer:
The height of the bottle is 11.3 cm.
Explanation:
Given,
d = 7.5
r = d/2
r = 7.5/2
r = 3.75 cm
Volume of cylinder = 500 cubic centimeters.
V = πr²h
500 = π(3.75)²h
where π is 22/7 or 3.141
h = \(\frac { 3500 }{ 309.375 } \)
h = 11.3 cm
Question 12.
Find the area of a dodecagon (12 sides) with a side length of 9 inches.
Answer:
Area is 237.31 sq in.
Explanation:
Given,
dodecagon has 12 sides,
with a side length of 9 inches.
Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)πa²cot(π/n)
A = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)π x 9² x cot(π/12)
where π is 22/7 or 3.141
A = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)π x 81 x cot(π/12)
= 237.31 sq in.
Question 13.
In general, a cardboard fan with a greater area does a better job of moving air and cooling you. The fan shown is a sector of a cardboard circle. Another fan has a radius of 6 centimeters and an intercepted are of 150°. Which fan does a better job of cooling you?

Answer:
Area of sector for fan of radius 9 cm = 120/360 × 3.14 × 9 × 9
= 1/3 × 254.57
= 84.85 sq. cm
Circumference, Area, and Volume Cumulative Assessment
Question 1.
Identify the shape of the cross section formed by the intersection of the plane and the
solid.
a.
Answer:
The cross-section is a trapezoid.
Explanation:
A cross section is the intersection of a figure in three-dimensional space with a plane as shown above.
It is the face obtain by making a slice through a solid object which is two-dimensional.
Therefore, the figure obtained from a cross section depends upon the angle of the plane doing the cutting.
So, the cross section formed by the intersection of the plane and the solid is trapezoid.
b.
Answer:
The cross-section is a pentagon.
Explanation:
A cross section is the intersection of a figure in three-dimensional space with a plane as shown above.
It is the face obtain by making a slice through a solid object which is two-dimensional.
Therefore, the figure obtained from a cross section depends upon the angle of the plane doing the cutting.
So, the cross section formed by the intersection of the plane and the solid is rectangle.
c.
Answer:
The cross-section is a rectangle.
Explanation:
A cross section is the intersection of a figure in three-dimensional space with a plane as shown above.
It is the face obtain by making a slice through a solid object which is two-dimensional.
Therefore, the figure obtained from a cross section depends upon the angle of the plane doing the cutting.
So, the cross section formed by the intersection of the plane and the solid is rectangle.
Question 2.
In the diagram, ![]() is tangent to ⊙P at Q and \(\overline{P Q}\) is a radius of ⊙P? What must be true about
is tangent to ⊙P at Q and \(\overline{P Q}\) is a radius of ⊙P? What must be true about ![]() and \(\overline{PQ}\)? Select all that apply.
and \(\overline{PQ}\)? Select all that apply.
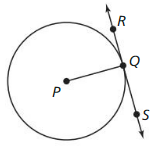
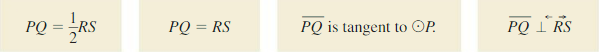
Answer:
PQ is perpendicular to RS.
Explanation:
In the given diagram, RS is tangent to circle ⊙P at Q and \(\overline{P Q}\) is a radius of ⊙P
PQ is perpendicular to must be true about ![]() and \(\overline{PQ}\)
and \(\overline{PQ}\)
Question 3.
A crayon can be approximated by a composite solid made from a cylinder and a cone.
A crayon box is a rectangular prism. The dimensions of a crayon and a crayon box containing 24 crayons are shown.
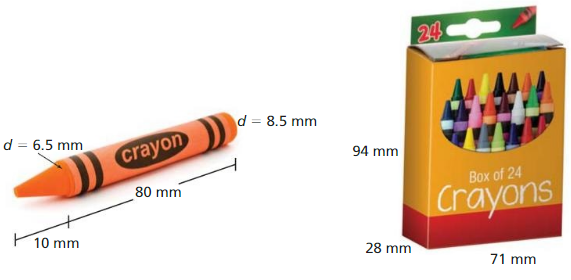
a. Find the volume of a crayon.
Answer:
V = = 4650.21 mm³
Explanation:
Given,
A crayon can be approximated by a composite solid made from a cylinder and a cone.
A crayon box is a rectangular prism.
The dimensions of a crayon and a crayon box containing 24 crayons are shown above,
diameter of cone = 6.5
r = d/2
r = 6.5/2
r = 3.25 mm
diameter of cylinder = 8.5
r = d/2
r = 8.5/2
r = 4.25 mm
The volume of a crayon = πr²h + \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)πr²h
V = π x 4.25² x 80 + \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)π x 3.25² x 10
V = 1445π + \(\frac { 105.625π }{ 3 } \)π x 3.25² x 10
V = 1445π + 35.20π
where πis 22/7 or 3.141
V = 4539.6 + 110.61
V = 4650.21 mm³
b. Find the amount of space within the crayon box not taken up by the crayons.
Answer:
75266.96 mm
Explanation:
Volume = lbh
Volume of box = 94 x 28 x 71
V = 186872 cu mm.
We know that the volume of a crayon = 4650.21 mm.
Number of crayons in a box = 24
24 x 4650.21 = 111605.04 mm.
Remaining space = 186872 -111605.04
= 75266.96 mm.
Question 4.
What is the equation of the line passing through the point (2, 5) that is parallel to the line x + \(\frac{1}{2}\)y = – 1?
(A) y = – 2x + 9
(B) y = 2x + 1
(C) y = \(\frac{1}{2}\)x + 4
(D) y = –\(\frac{1}{2}\)x + 6
Answer:
(A) y = – 2x + 9
Explanation:
Given that,
the equation of the line passing through the point (2, 5) that is parallel to the line x + \(\frac{1}{2}\)y = – 1
So, y = -2 – 2x
The slope of the line is -2
The equation of line is y – 5 = -2(x – 2)
y – 5 = -2x + 4
y = -2x + 9
Question 5.
The top of the Washington Monument in Washington, D.C., is a square pyramid, called a pyramidion. What is the volume of the pyramidion?

(A) 22,019.63 ft3
(B) 172,006.91 ft3
(C) 66,058.88 ft3
(D) 207,530.08 ft3
Answer:
(A) 22,019.63 ft3
Explanation:
Given,
h = 55.5 ft, a = 34.5 ft
Volume = a²\(\frac { h }{ 3 } \)
V = 34.5² x \(\frac { 55.5 }{ 3 } \)
V = 1190.25 x 18.5
V = 22019.62 ft3
Question 6.
Prove or disprove that the point (1, √3 ) lies on the circle centered at the origin and containing the point (0, 2).
Answer:
We consider the circle centered at the origin containing the point (0, 2).
Therefor, radius is 2 and points be (0, 0), (1, √3)
distance = √(1 – 0)² + (√3 – 0)² = 2
As radius and distance are same.
The point B(1, √3) lies on the circle.
Question 7.
Your friend claims that the house shown can be described as a composite solid made from a rectangular prism and a triangular prism. Do you support your friend’s claim? Explain your reasoning.

Answer:
Yes
Explanation:
With reference to the given figure,
the sides are rectangular, the bases are equilateral and sides are squares.
We know that a triangular prism consists of two triangles and three rectangles.
The triangles are the bases of the prism and the rectangles are the lateral faces.
So, the house shown is described as a composite solid made from a rectangular prism and a triangular prism.
Question 8.
The diagram shows a square pyramid and a cone. Both solids have the same height, h, and the base of the cone has radius r. According to Cavalieri’s Principle, the solids will have the same volume if the square base has sides of length ______ .
Answer:
length = 2r/√2
Explanation:
Given,
Square diagonal = √2a
radius = √2a/2
Volume of square pyramid = a²\(\frac { h }{ 3 } \)
Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)πr²h
Question 9.
About 19,400 people live in a region with a 5-mile radius. Find the population density in people per square mile.

Answer:
The number of people per square mile is 247
Explanation:
Given,
About 19,400 people live in a region with a 5-mile radius.
S = πr²
S = π x 5²
where π is 22/7 or 3.141
S = 78.5
Number of people per square mile = 19400/78.5 = 247 sq mi.