The division is one of the four basic arithmetic operations that help to split into equal parts. Dividing by 2 digit number means a large quantity of data is distributing into equal groups. Here, students can know the definition of division by two-digit numbers. Also, find a detailed explanation to solve the division by two digit numbers problems along with the solutions.
Also, Check:
- Division of Four-Digit by a One-Digit Numbers
- Dividing Numbers
- Problem Solving on Division
- Worksheet on Divide by 2-Digit Divisors
Division by Two-Digit Numbers
Division by Two-digit numbers means the divisor should be a two-digit number and dividend can be a two-digit or more than a two-digit number. Every two-digit number has ten’s place and one’s place in it. Get the instructions and simple steps to compute the division of a number by a two-digit number in the below-included sections of this page.
How to Divide a Number by Two-Digit Numbers?
Make use of various division methods to divide by two-digit numbers from the following sections.
Method 1:
- Take the first 3 digits of the dividend if it is less than the divisor. Otherwise, take the first 2 digits of the dividend.
- Write the quotient on the top of the dividend and the product below the dividend.
- Subtract dividend from the product.
- Bring down the next number of the dividend.
- Repeat the process.
Method 2:
- Write the dividend inside the division symbol and the divisor outside the division symbol.
- Write the quotient on the top and multiply the quotient by the hundredth number.
- Write that product below the dividend and subtract it from the dividend
- Repeat the process.
2-Digit Division Examples with Answers
Example 1:
Divide 768 by 12 using 1st method.
Solution:
Given that,
768 ÷ 12
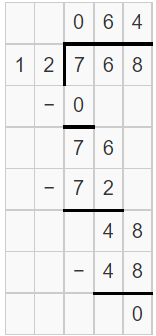
76 > 12. So, take the first two digits of the dividend.
Let us check 12 x 6 = 72 and 76 > 72
Subtract 72 from 76 i.e 76 – 72 = 4
Write 6 in the place of quotient
Bring down the next digit of the dividend i.e 8
It makes 48
Let us check 12 x 4 = 48
Subtract 48 from 48 i.e 48 – 48 = 0
Write 4 at the quotient after 6.
Write 0 as the remainder.
The quotient will be 64.
Therefore, 768 ÷ 12 = 64
Example 2:
Divide 1378 by 26 using the 2nd method.
Solution:
Given that,
1378 ÷ 26
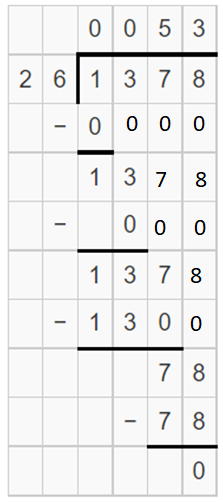
1 < 13. So, consider the first two digits of the dividend
13 < 26. So, consider the first three digits of the dividend
137 > 26
26 x 50 = 1300
1378 – 1300 = 78
26 x 3 = 78
78 – 78= 0
The quotient will be 50 + 3 = 53
Therefore, 1378 ÷ 26 = 53
Example 3:
Divide 47320 by 35 and verify the quotient.
Solution:
Given that,
47320 ÷ 35
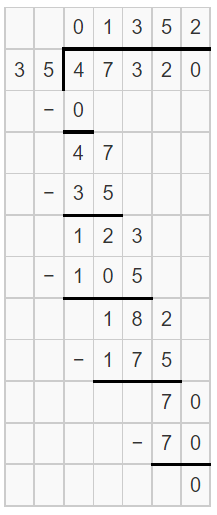
47 > 35
Consider the first two digits of the dividend for the division.
35 x 1 = 35
35 x 2 = 70
So, add 1 at the quotient part
Subtract 35 from 47
47 – 35 = 12
Bring down the next digit of the dividend i.e 3.
It becomes 123
35 x 5 = 175
So, add 5 after 13 at the quotient
Subtract 175 from 182
182 – 175 = 7
Bring down the next digit of the dividend i.e 0.
It becomes 70
35 x 2 = 70
Subtract 70 from 70
70 – 70 = 0
Therefore, quotient is 1352
Verification:
Dividend = Divisor x quotient + remainder
= 35 x 1352 + 0
= 47320
Therefore, 47320 ÷ 35 = 1352.