Engage NY Eureka Math Algebra 1 Module 1 Lesson 11 Answer Key
Eureka Math Algebra 1 Module 1 Lesson 11 Example Answer Key
Example 1.
Consider the equation, x2 =3x+4, where x represents a real number.
a. Are the expressions x2 and 3x+4 algebraically equivalent?
Answer:
No.
→ Then, we cannot guarantee there will be any real value of x that will make the equation true.
b. The following table shows how we might “sift” through various values to assign to the variable symbol x in the hunt for values that would make the equation true.
Answer:
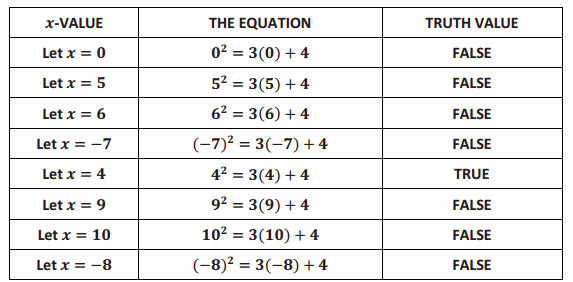
→ Of course, we should sift through ALL the real numbers if we are seeking all values that make the equation x2 =3x+4 true. (This makes for quite a large table!) So far, we have found that setting x equal to 4 yields a true statement.
→ Look at the image in your student materials. Can you see what is happening here and how it relates to what we have been discussing?
→ The numbers are going down the road and being accepted into the solution set or rejected based on whether or not the equation is true.
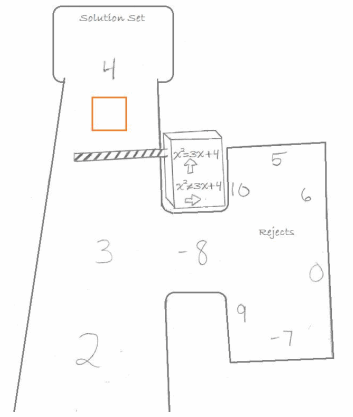
→ There happens to be just one more value we can assign to x that makes x2 =3x+4 a true statement. Would you like to continue the search to find it?
→ x=-1
Example 2.
Consider the equation 7+p=12.

Answer:
→ Here is a table that could be used to hunt for the value(s) of p that make the equation true:
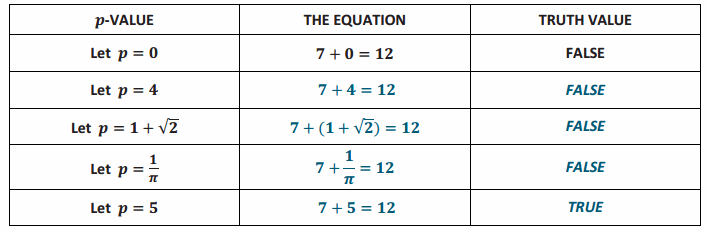
→ But is a table necessary for this question? Is it obvious what value(s) we could assign to p to make the equation true?
Example 3.
Solve for a: a2 =25.
Answer:
We know that setting a=5 or setting a=-5 makes a2 =25 a true statement. And a little thought shows that these are the only two values we can assign to make this so. The solution set is just the set containing the numbers 5 and -5. (And since the question made no mention of restricting the domain of values we should consider, we shall assume both these values are admissible solutions for this question.)
Example 4.
Solve \(\frac{x}{x}\)=1 for x, over the set of positive real numbers. Depict the solution set in words, in set notation, and graphically.
Answer:
→ The question statement indicates that we are to consider assigning values to x only from the set of positive real numbers. Let’s create a table to get a feel for the problem. (It might actually be helpful this time.)
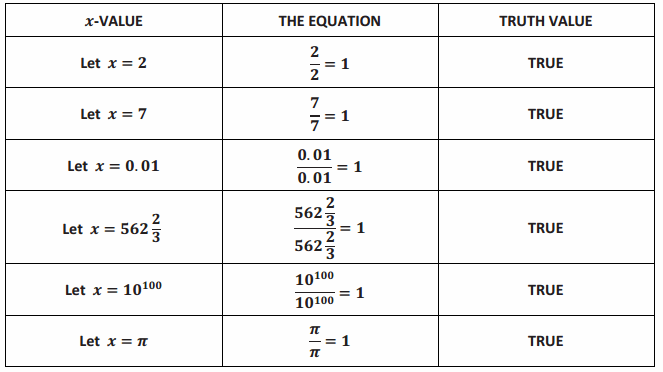
It seems that each and every positive real number is a solution to this equation.
IN WORDS: The solution set is the set of all positive real numbers.
IN SET NOTATION: This is {x real | x>0}.
IN A GRAPHICAL REPRESENTATION:
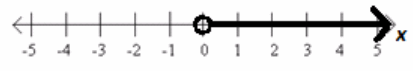
Example 5.
Solve for x: x(3+x)=3x+x2 .
Answer:
→ Since it is not specified otherwise, we should again assume that we are considering solutions from the set of all real numbers.
→ In drawing a table to sift for possible solutions, students might come to suspect that every real value for x is a solution to this equation.
→ The distributive property states that, for all real numbers a, b, and c, the expressions a(b+c) and ab+ac are sure to have the same numerical value. The commutative property for multiplication states that, for all real numbers d and e, the expressions de and ed have the same numerical value.
→ Consequently, we can say, for any value we assign to x:
x(3+x)=x∙3+x2 ,
that is, x(3+x)=3x+x2 is sure to be a true numerical statement. This proves that the solution set to this equation is the set of all real numbers.
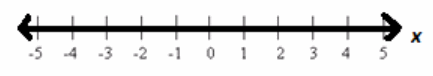
→ It is awkward to express the set of all real numbers in set notation. We simply write the “blackboard script” ![]() for the set of all real numbers. (By hand, one usually just draws a double vertical bar in the capital letter: .)
for the set of all real numbers. (By hand, one usually just draws a double vertical bar in the capital letter: .)
Example 6
Solve for w: w+2>4.
In discussing this problem, have students realize
→ An inequality between two numerical expressions also has a well-defined truth value: true or false.
→ Just as for equations, one can “sift” through real values of the variable in an inequality to find those values that make the inequality a true statement. The solution set of an inequality is the set of all real values that make the inequality true.
Have students describe the solution set to w+ 2>4 in words, in set notation, and in graphical representation.
Answer:
IN WORDS: w must be greater than 2.
IN SET NOTATION: {w real | w>2}
IN GRAPHICAL REPRESENTATION:
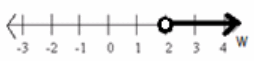
Eureka Math Algebra 1 Module 1 Lesson 11 Exercise Answer Key
Exercise 1.
Solve for a: a2 =-25. Present the solution set in words, in set notation, and graphically.
Answer:
IN WORDS: The solution set to this equation is the empty set. There are no real values to assign to a to make the equation true.
IN SET NOTATION: The solution set is { } (the empty set).
IN A GRAPHICAL REPRESENTATION: The solution set is
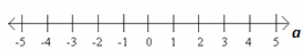
Exercise 2.
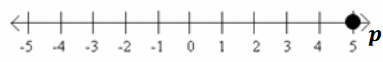
Depict the solution set of 7+p=12 in words, in set notation, and graphically.
Answer:
IN WORDS: 7+p=12 has the solution p=5.
IN SET NOTATION: The solution set is {5}.
IN A GRAPHICAL REPRESENTATION:
Exercise 3.
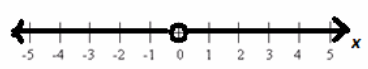
Solve \(\frac{x}{x}\)=1 for x over the set of all nonzero real numbers. Describe the solution set in words, in set notation, and graphically.
Answer:
IN WORDS: The solution set is the set of all nonzero real numbers.
IN SET NOTATION: {x real | x≠0}
IN A GRAPHICAL REPRESENTATION:
Exercise 4
Solve for α: α+α2 =α(α+1). Describe carefully the reasoning that justifies your solution. Describe the solution set in words, in set notation, and graphically.
Answer:
IN WORDS: By the distributive property, we have α+α2 =α(1+α). This is a true numerical statement no matter what value we assign to α. By the commutative property of addition, we have α+α2 =α(α+1), which is a true numerical statement no matter what real value we assign to α.
The solution set is the set of all real numbers.
IN SET NOTATION: The solution set is ![]()
IN GRAPHICAL REPRESENTATION:
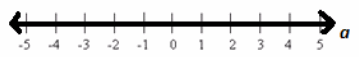
Exercise 5.
Identify the properties of arithmetic that justify why each of the following equations has a solution set of all real numbers.
a. 2x2 +4x=2(x2 +2x)
b. 2x2 +4x=4x+2x2
c. 2x2 +4x=2x(2+x)
Answer:
(a) Distributive property; (b) commutative property of addition; (c) multiple properties: distributive property, commutative property of addition, and maybe even associative property of multiplication if we analyze the interpretation of 2x2 with extreme care.
Exercise 6.
Create an expression for the right side of each equation such that the solution set for the equation will be all real numbers. (There is more than one possibility for each expression. Feel free to write several answers for each one.)
a. 2x-5= ___
b. x2 +x= ___
c. 4•x•y•z= ___
d. (x+2)2 = __
Answer:
Sample answers:
(a) -5+2x or 2(x-\(\frac{5}{2}\))
(b) x+x2 or x(x+1) or x(1+x)
(c) Any rearranging of the factors
(d) (2+x)2 or x2 +4x+4
Review their answers, and then have them complete Exercise 7.
Exercise 7
a. Solve for B: B2 ≥9. Describe the solution set using a number line.
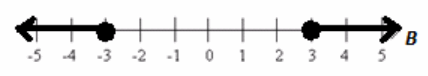
b. What is the solution set to the statement: “Sticks of lengths 2 yards, 2 yards, and L yards make an isosceles triangle”? Describe the solution set in words and on a number line.
Answer:
L must be greater than 0 yards and less than 4 yards.
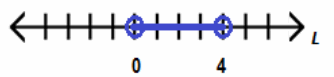
Eureka Math Algebra 1 Module 1 Lesson 11 Problem Set Answer Key
For each solution set graphed below, (a) describe the solution set in words, (b) describe the solution set in set notation, and (c) write an equation or an inequality that has the given solution set.
Question 1.
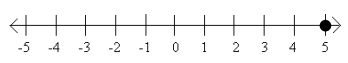
Answer:
a. The set of all real numbers equal to 5
b. {5}
c. x+2=7
Question 2.
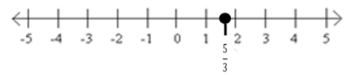
Answer:
a. The set of all real numbers equal to \(\frac{5}{3}\)
b. {\(\frac{5}{3}\)}
c. 3x=5
Question 3.
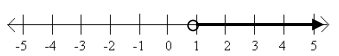
Answer:
a. The set of all real numbers greater than 1
b. {x real | x > 1}
c. x-1>0
Question 4.
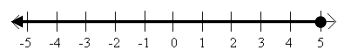
Answer:
a. The set of all real numbers less or equal to 5
a. The set of all real numbers not equal to 2
b. {x real | x ≤ 5}
c. 2x≤10
Question 5.
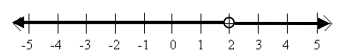
Answer:
a. The set of all real numbers not equal to 4
b. {x real | x≠2}
c. \(\frac{x-2}{x-2}\)=1
Question 6.
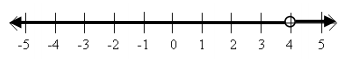
Answer:
a. The set of all real numbers
b. { x real} or x≠4
c. x-1<3 or x-1>3
Question 7.
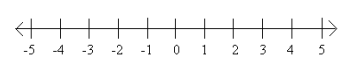
Answer:
a. The null set
b. {} or ɸ
c. c2 = -4
Question 8.
Answer:
a. The set of all real numbers
b.![]()
c. 2x – 8 = 2(x – 4)
Fill in the chart below.
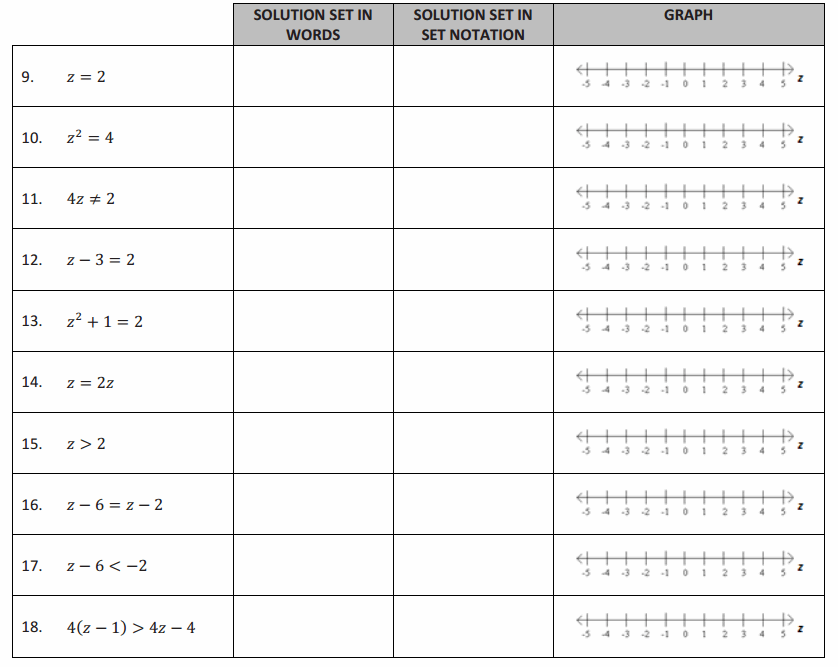
Answer:
For Problems 19–24, answer the following: Are the two expressions algebraically equivalent? If so, state the property (or properties) displayed. If not, state why (the solution set may suffice as a reason), and change the equation, ever so slightly (e.g., touch it up), to create an equation whose solution set is all real numbers.
Question 19.
x(4-x2)=(-x2 +4)x
Answer:
Yes. Commutative.
Question 20.
\(\frac{2 x}{2 x}\)=1
Answer:
No. The solution set is {x real | x≠0}. If we changed it to \(\frac{2x}{1}\)=2x, it would have a solution set of all real numbers.
Question 21.
(x-1)(x+2)+(x-1)(x-5)=(x-1)(2x-3)
Answer;
Yes. Distributive.
Question 22.
\(\frac{x}{5}\)+\(\frac{x}{3}\)=\(\frac{2x}{8}\)
Answer:
No. The solution set is {0}. If we changed it to \(\frac{x}{5}\)+\(\frac{x}{3}\)=8x/15, it would have a solution set of all real numbers.
Question 23.
x2 +2x3+3x4=6x9
Answer:
No. Neither the coefficients nor the exponents are added correctly. One way it could have a solution set of all real numbers would be x2 +2x3+3x4=x2 (1+2x+3x2).
Question 24.
x3+4x2 +4x=x(x+2)2
Answer:
Yes. Distributive.
Question 25.
Solve for w: \(\frac{6 w+1}{5}\)≠2. Describe the solution set in set notation.
Answer:
{w real | w≠1\(\frac{1}{2}\)}
Question 26.
Edwina has two sticks: one 2 yards long and the other 2 meters long. She is going to use them, with a third stick of some positive length, to make a triangle. She has decided to measure the length of the third stick in units of feet.
a. What is the solution set to the statement: “Sticks of lengths 2 yards, 2 meters, and L feet make a triangle”? Describe the solution set in words and through a graphical representation.
Answer:
One meter is equivalent, to two decimal places, to 3.28 feet. We have that L must be a positive length greater than 0.56 feet and less than 12.56 feet. Within these values, the sum of any two sides will be greater than the third side.
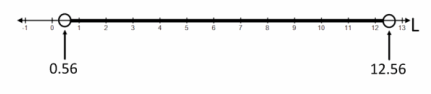
b. What is the solution set to the statement: “Sticks of lengths 2 yards, 2 meters, and L feet make an isosceles triangle”? Describe the solution set in words and through a graphical representation.
Answer:
L=6 feet or L=6.56 feet
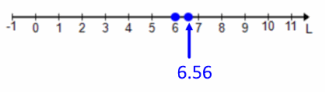
c. What is the solution set to the statement: “Sticks of lengths 2 yards, 2 meters, and L feet make an equilateral triangle”? Describe the solution set in words and through a graphical representation.
Answer:
The solution set is the empty set.
![]()
Eureka Math Algebra 1 Module 1 Lesson 11 Exit Ticket Answer Key
Question 1.
Here is the graphical representation of a set of real numbers:
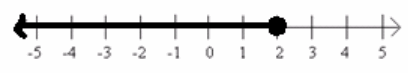
a. Describe this set of real numbers in words.
Answer:
The set of all real numbers less than or equal to two.
b. Describe this set of real numbers in set notation.
Answer:
{r real | r≤2} (Students might use any variable.)
c. Write an equation or an inequality that has the set above as its solution set.
Answer:
w-7≤-5 (Answers will vary. Students might use any variable.)
Question 2.
Indicate whether each of the following equations is sure to have a solution set of all real numbers. Explain your answers for each.
a. 3(x+1)=3x+1
Answer:
No. The two algebraic expressions are not equivalent.
b. x+2=2+x
Answer:
Yes. The two expressions are algebraically equivalent by application of the commutative property.
c. 4x(x+1)=4x+4x2
Answer:
Yes. The two expressions are algebraically equivalent by application of the distributive property and the commutative property.
d. 3x(4x)(2x)=72x3
Answer:
No. The two algebraic expressions are not equivalent.