Engage NY Eureka Math Grade 6 Module 5 Lesson 9 Answer Key
Eureka Math Grade 6 Module 5 Lesson 9 Example Answer Key
Example 1
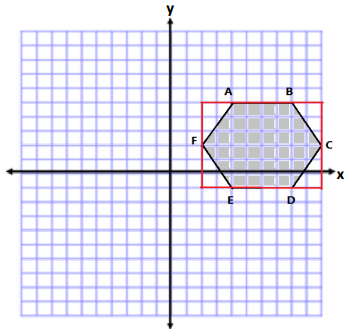
Jasjeet has made a scale drawing of a vegetable garden she plans to make in her backyard. She needs to determine the perimeter and area to know how much fencing and dirt to purchase. Determine both the perimeter and area.
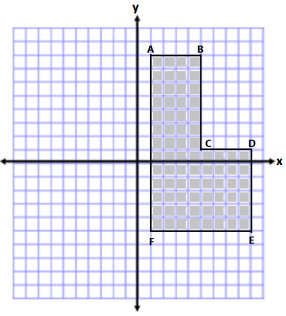
Answer:
AB = 4 units BC = 7 units CD = 4 units
DE = 6 units EF = 8 units AF = 13 units
Perimeter = 4 units + 7 units + 4 units + 6 units + 8 units + 13 units
Perimeter = 42 units
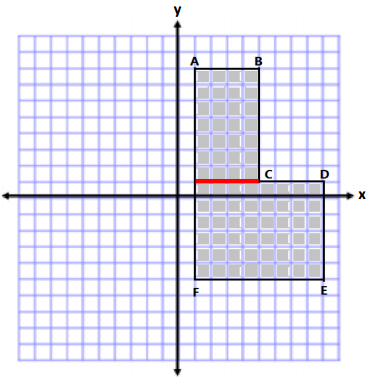
The area is determined by making a horizontal cut from (1, 1) to point C.
Area of Top
A = lw
A = (4 units)(7 units)
A = 28 units2
Area of Bottom
A = lw
A = (8 units) (6 units)
A = 48 units2
Total Area = 28 units2 + 48 units2
Total Area = 76 units2
Example 2:
Calculate the area of the polygon using two different methods. Write two expressions to represent the two methods, and compare the structure of the expressions.
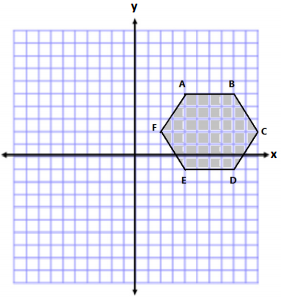
Answer:
Answers will vary. The following are two possible methods. However, students could also break the shape into two
triangles and a rectangle or use another correct method.
Method one:
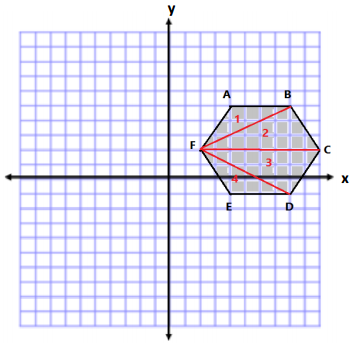
Method Two:
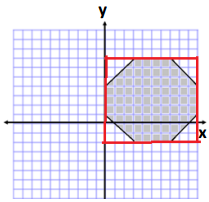
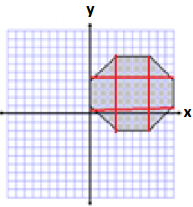
Area of Triangle 1 and 4
A = \(\frac{1}{2}\) bh
A = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (4 units)(3 units)
A = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (12 units2)
A = 6 units2
Since there are 2, we have a total area of 12 units2.
Area of Triangle 2 and 3
A = \(\frac{1}{2}\) bh
A = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (8 units)(3 units)
A = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (24 units2)
A = 12 units2
Since there are 2, we have a total area of 24 units2.
A = lw
A = (8 units) (6 units)
A = 48 units2
A = \(\frac{1}{2}\) bh
A = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (2 units)(3 units)
A = 3 units2
There are 4 triangles of equivalent base and height.
4(3 units2) = 12 units2
Total Area = 48 units2 – 12 units2
Total area = 36 units2
Total Area = 12 units2 + 24 units2 = 36 units2
Total area = 36 units2
Expressions:
2(\(\frac{1}{2}\)(4)(3)) + 2(\(\frac{1}{2}\)(8)(3)) or (8)(6) – 4(\(\frac{1}{2}\)(2)(3))
The first expression shows terms being added together because I separated the hexagon into smaller pieces and had to add their areas back together.
The second expression shows terms being subtracted because I made a larger outside shape and then had to take away the extra pieces.
Eureka Math Grade 6 Module 5 Lesson 9 Exercise Answer Key
Question 1.
Determine the area of the following shapes.
a. 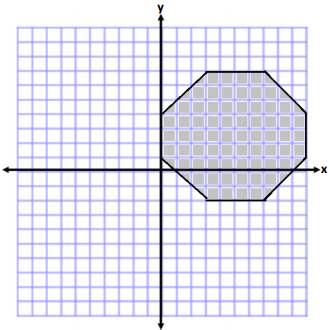
Answer:
Area of rectangle = lw
A = (10 units) (9 units)
A = 90 units 2
Area of Triangle
A = \(\frac{1}{2}\) bh
A = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (3 units) (3 units)
A = 4.5 units 2
4 triangles with equivalent base and height
4 (4.5 units 2) = 18 units2
Area = 90 units2 – 18 units2
Area = 72 units2
Please note the students may also choose to solve by decomposing. Here is another option.
b. 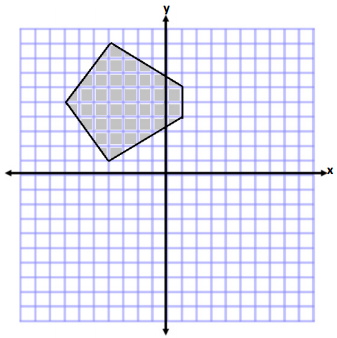
Answer:
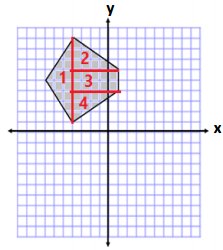
Area of Triangle 1
A = \(\frac{1}{2}\) bh
A = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (8 units)(3 units)
A = (4 units)(3 units)
A = 12 units2
Area of Triangles 2 and 4
A = \(\frac{1}{2}\) bh
A = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (5 units)(3 units)
A = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (15 units2)
A = 7.5 units2
Since triangles 2 and 4 have the same base and height measurements, the combined area is 15 units.
Area of Rectangle 3
A = bh
A = (5 units)(2 units)
A = 10 units2
Total Area = 12 units2 + 15 units2 + 10 units2
Total Area = 37 units2
Another correct solution might start with the following diagram:
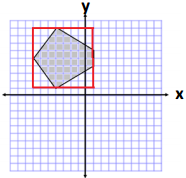
Question 2.
Determine the area and perimeter of the following shapes.
a. 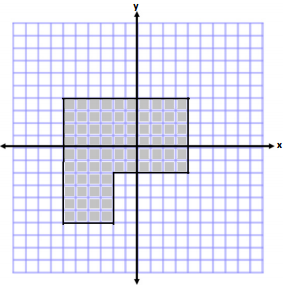
Answer:
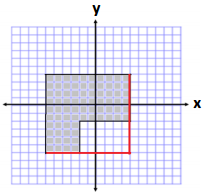
Area of Large Square
A = s2
A = (10 units)2
A = 100units2
Removed Piece
A = bh
A = (6 units)(4 units)
A = 24 units2
Area = 100 units2 – 24 units2
Area = 76 units2
Perimeter = 10 units + 6 units + 6 units + 4 units + 4 units + 10 units
Perimeter = 40 units
Other correct solutions might start with the following diagrams:
b. 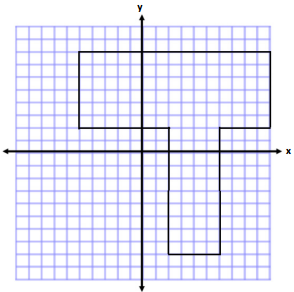
Answer:
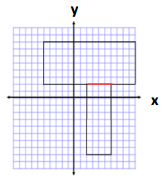
Area:
Horizontal Area
A = bh
A = (15 units) (6 units)
A = 90 units2
Vertical Area
A = bh
A = (10 units) (4 units)
A = 40 units2
Total Area = 90 units2 + 40 units2
Total Area = 130 units2
Perimeter = 15 units + 6 units + 4 units + 10 units + 4 units + 10 units + 7 units + 6 units
Perimeter = 62 units
Other correct solutions might start with the following diagrams:
Eureka Math Grade 6 Module 5 Lesson 9 Problem Set Answer Key
Question 1.
Determine the area of polygon.
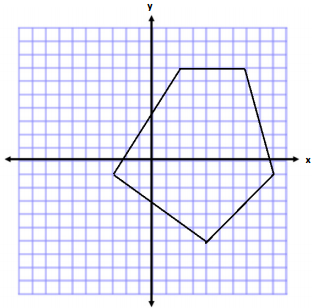
Answer:
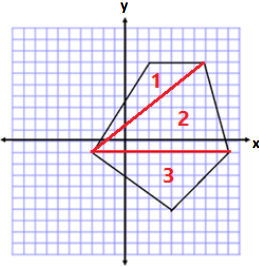
Area of Triange 1
A = \(\frac{1}{2}\) bh
A = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (5 units)(8 units)
A = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (40 units2)
A = 20 units2
Area of Triangle 2
A = \(\frac{1}{2}\) bh
A = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (12 units)(8 units)
A = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (96 units2)
A = 48 units2
Area of Tnangle 3
A = \(\frac{1}{2}\) bh
A = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (12 units)( 5 units)
A = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (60 units2)
A = 30 units2
Total Area = 20 units2 + 48 units2 + 30 units2
Total Area = 98 units2
Question 2.
Determine the area and perimeter of the polygon.
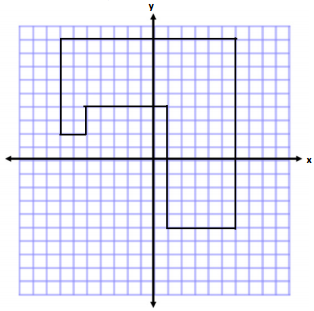
Answer:
Area:
Horizontal Rectangle
A = bh
A = (13 units) (5 units)
A = 65 units2
Vertical Rectangle
A = bh
A = (5 units) (9 units)
A = 45 units2
Square
A = S2
A = (2 units)2
A = 4 units2
Total Area = 65 units2 + 45 units2 +4 units2
Total Area = 114 units2
Perimeter:
Perimeter = 2 units + 2 units + 7 units + 13 units + 14 units + 5 units + 9 units + 6 units
Perimeter = 58 units
Question 3.
Determine the area of the polygon. Then, write an expression that could be used to determine the area.
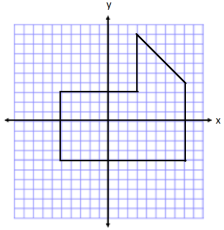
Answer:
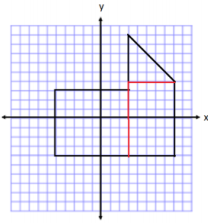
Area of Rectangle on Left
A = lw
A = (8 units) (7 units)
A = 56 units2
Area of Rectangle on Right
A = lw
A = (5 units) (8 units)
A = 40 units2
Area of Triangle on Top
A = \(\frac{1}{2}\) bh
A = \(\frac{1}{2}\) (5 units)(5 units)
A = 12.5 units2
Total Area = 56 units2 + 40 units2 + 12.5 units2 = 108.5 units2
Expression: (8)(7) + (5)(8) + \(\frac{1}{2}\) (5)(5)
Question 4.
If the length of each square was worth 2 instead of 1, how would the area in Problem 3 change? How would your expression change to represent this area?
Answer:
If each length is twice as long, when they are multiplied, 2l × 2w = 41w. Therefore, the area will be four times larger when the side lengths are doubled.
I could multiply my entire expression by 4 to make it 4 times as big. 4 [(8)(7) + (5)(8) + \(\frac{1}{2}\) (5)(5)]
Question 5.
Determine the area of the polygon. Then, write an expression that represents the area.
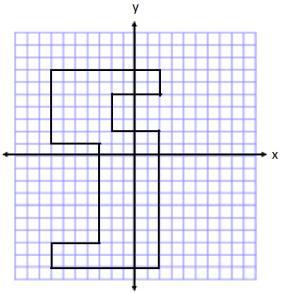
Answer:
Area of Outside Rectangle
A = lw
A = (9 units) (16 units)
A = 144 units2
Area of Rectangle on Left
A = lw
A = (4 units) (8 units)
A = 32 units2
Area of Rectangle on Right
A = lw
A = (4 units) (3 units)
A = 12 units2
Total Area = 144 units2 – 32 units2 – 12 units2
Total Area = 100 units2
Expression: (9)(16) – (4)(8) – (4)(3)
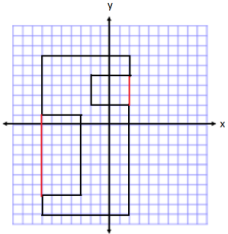
Question 6.
Describe another method you could use to find the area of the polygon in Problem 5. Then, state how the expression for the area would be different than the expression you wrote.
Answer:
I could have broken up the large shape into many smaller rectangles. Then I would need to add all the areas of these rectangles together to determine the total area.
My expression showed subtraction because I created o rectangle that was larger than the original polygon, and then I had to subtract the extra oreos. If I break the shape into pieces, I would need to add the terms together instead of subtracting them to get the total area.
Question 7.
Write one of the letters from your name using rectangles on the coordinate plane. Then, determine the area and perimeter. (For help see Exercise 2(b). This irregular polygon looks sort of like a T.)
Answer:
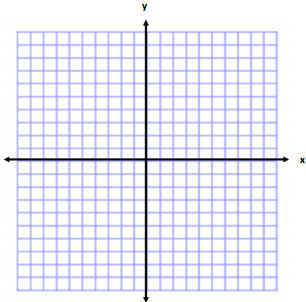
Answers will vary.
Eureka Math Grade 6 Module 5 Lesson 9 Exit Ticket Answer Key
Question 1.
Determine the area and perimeter of the figure below. Note that each square unit is 1 unit in length.
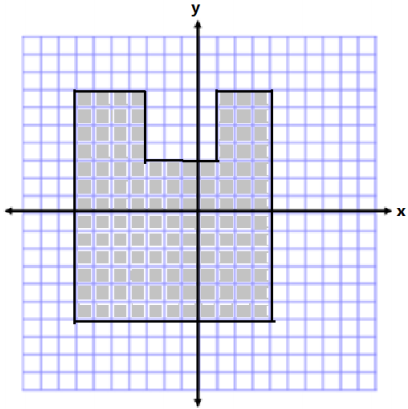
Answer:
Area:
Area of Large Rectangle
A = bh
A = (11 units)(13 units)
A = 143 units2
Area of Small Square
A = s2
A = (4units)2
A = 16 units2
Area of Irregular Shape
A = 143 units2 – 16 units2
A = 127 units2
Perimeter = 13 units + 4 units + 4 units + 4 units + 4 units + 3 units + 13 units + 11 units
Perimeter = 56 units
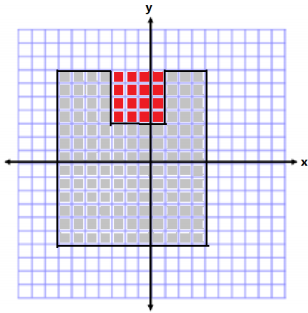
Other correct solutions might start with the following diagrams:
Eureka Math Grade 6 Module 5 Lesson 9 Addition and Subtraction Equations Answer Key
Addition and Subtraction Equations – Round 1:
Directions: Find the value of m in each equation.

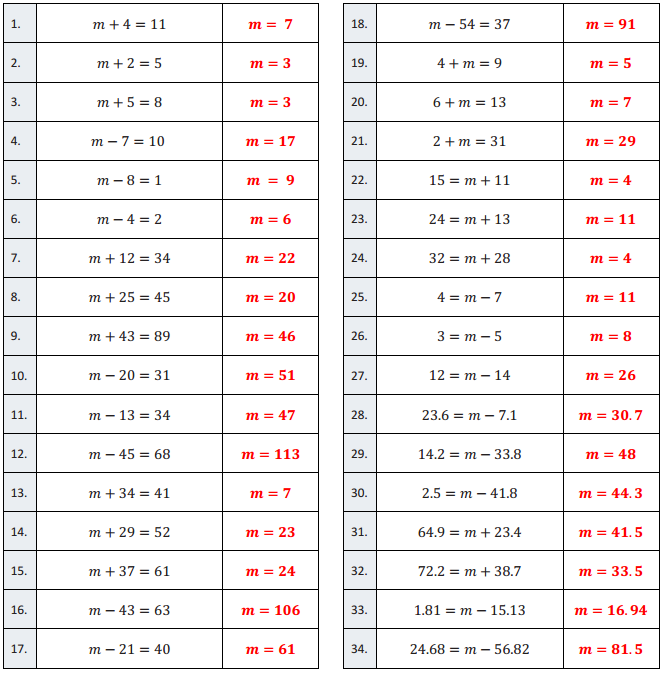
Question 1.
m + 4 = 11
Answer:
m = 7
Question 2.
m + 2 = 5
Answer:
m = 3
Question 3.
m + 5 = 8
Answer:
m = 3
Question 4.
m – 7 = 10
Answer:
m = 17
Question 5.
m – 8 = 1
Answer:
m = 9
Question 6.
m – 4 = 2
Answer:
m = 6
Question 7.
m + 12 = 34
Answer:
m = 22
Question 8.
m + 25 = 45
Answer:
m = 20
Question 9.
m + 43 = 89
Answer:
m = 46
Question 10.
m – 20 = 31
Answer:
m = 51
Question 11.
m – 13 = 34
Answer:
m = 47
Question 12.
m – 45 = 68
Answer:
m = 113
Question 13.
m + 34 = 41
Answer:
m = 7
Question 14.
m + 29 = 52
Answer:
m = 23
Question 15.
m + 37 = 61
Answer:
m = 24
Question 16.
m – 43 = 63
Answer:
m = 106
Question 17.
m – 21 = 40
Answer:
m = 61
Question 18.
m – 54 = 37
Answer:
m = 91
Question 19.
4 + m = 9
Answer:
m = 5
Question 20.
6 + m = 13
Answer:
m = 7
Question 21.
2 + m = 31
Answer:
m = 29
Question 22.
15 = m + 11
Answer:
m = 4
Question 23.
24 = m + 13
Answer:
m = 11
Question 24.
32 = m + 28
Answer:
m = 4
Question 25.
4 = m – 7
Answer:
m = 11
Question 26.
3 = m – 5
Answer:
m = 8
Question 27.
12 = m – 14
Answer:
m = 26
Question 28.
23.6 = m – 7.1
Answer:
m = 30.7
Question 29.
14.2 = m – 33.8
Answer:
m = 48
Question 30.
2.5 = m – 41.8
Answer:
m = 44.3
Question 31.
64.9 = m + 23.4
Answer:
m = 41.5
Question 32.
72.2 = m + 38.7
Answer:
m = 33.5
Question 33.
1.81 = m – 15.13
Answer:
m = 16.94
Question 34.
24.68 = m – 56.82
Answer:
m = 81.5
Addition and Subtraction Equations – Round 1:
Directions: Find the value of m in each equation.
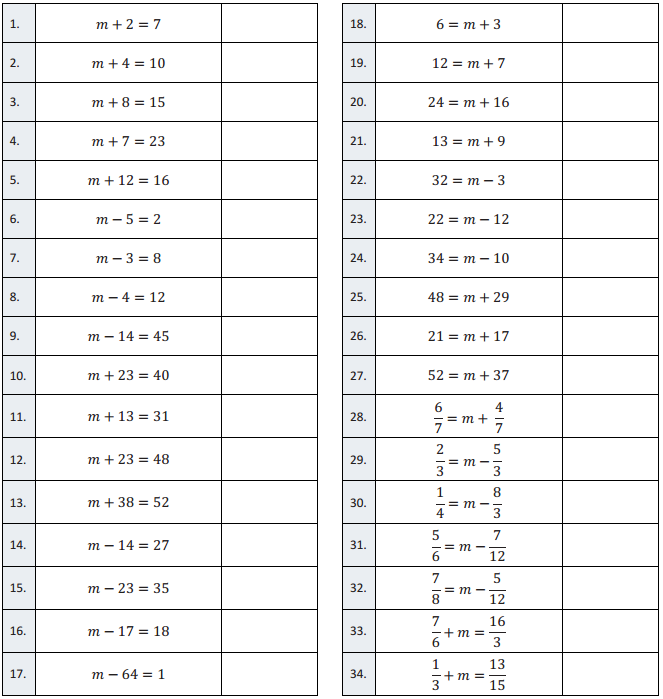
Question 1.
m + 2 = 7
Answer:
m = 5
Question 2.
m + 4 = 10
Answer:
m = 6
Question 3.
m + 8 = 15
Answer:
m = 7
Question 4.
m + 7 = 23
Answer:
m = 16
Question 5.
m + 12 = 16
Answer:
m = 4
Question 6.
m – 5 = 2
Answer:
m = 7
Question 7.
m – 3 = 8
Answer:
m = 11
Question 8.
m – 4 = 12
Answer:
m = 16
Question 9.
m – 14 = 45
Answer:
m = 59
Question 10.
m + 23 = 40
Answer:
m = 17
Question 11.
m + 13 = 31
Answer:
m = 18
Question 12.
m + 23 = 48
Answer: 25
m =
Question 13.
m + 38 = 52
Answer:
m = 14
Question 14.
m – 14 = 27
Answer:
m = 13
Question 15.
m – 23 = 35
Answer:
m = 12
Question 16.
m – 17 = 18
Answer:
m = 35
Question 17.
m – 64 = 1
Answer:
m = 65
Question 18.
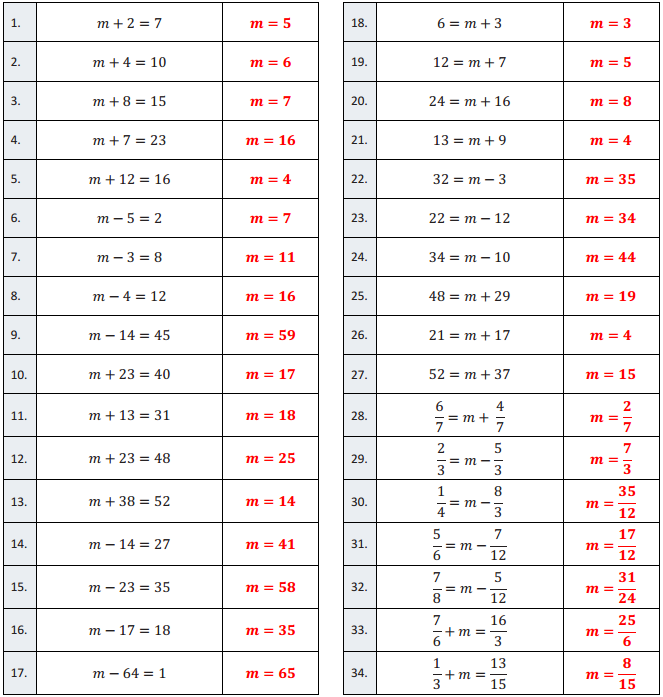
6 = m + 3
Answer:
m = 3
Question 19.
12 = m + 7
Answer:
m = 5
Question 20.
24 = m + 16
Answer:
m = 8
Question 21.
13 = m + 9
Answer:
m = 4
Question 21.
32 = m – 3
Answer:
m = 35
Question 23.
22 = m – 12
Answer:
m = 34
Question 24.
34 = m – 10
Answer:
m = 44
Question 25.
48 = m + 29
Answer: 19
Question 26.
21 = m + 17
Answer:
m = 4
Question 27.
52 = m + 37
Answer:
m = 15
Question 28.
\(\frac{6}{7}\) = m + \(\frac{4}{7}\)
Answer:
m = \(\frac{2}{7}\)
Question 29.
\(\frac{2}{3}\) = m – \(\frac{5}{3}\)
Answer:
m = \(\frac{7}{3}\)
Question 30.
\(\frac{1}{4}\) = m – \(\frac{8}{3}\)
Answer:
m = \(\frac{35}{12}\)
Question 31.
\(\frac{5}{6}\) = m – \(\frac{7}{12}\)
Answer:
m = \(\frac{17}{12}\)
Question 32.
\(\frac{7}{8}\) = m – \(\frac{5}{12}\)
Answer:
m = \(\frac{31}{24}\)
Question 33.
\(\frac{7}{6}\) + m = \(\frac{16}{3}\)
Answer:
m = \(\frac{25}{6}\)
Question 34.
\(\frac{1}{3}\) + m = \(\frac{13}{15}\)
Answer:
m = \(\frac{8}{15}\)