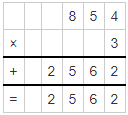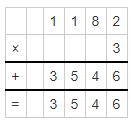A multiple is the product of one number with another number. Also, we can define a multiple as the result that is obtained by multiplying a number by an integer. But it is not a function. The multiples of the whole numbers are found by doing the product of the counting numbers and that of whole numbers. For example, multiples of 5 can be obtained when we multiply 5 by 1, 5 by 2, 5 by 3, and so on.
Example 1: Find the multiples of whole number 4?
Firstly, do the multiplication of 4 with other numbers to get multiples of 4.
Multiplication: 4 x 1, 4 x 2, 4 x 3, 4 x 4, 4 x 5, 4 x 6, 4 x 7, 4 x 8
Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32
Solution: The multiples of 4 are 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32,……
Example 2: Find the multiples of whole number 6?
Firstly, do the multiplication of 6 with other numbers to get multiples of 6.
Multiplication: 6 x 1, 6 x 2, 6 x 3, 6 x 4, 6 x 5, 6 x 6, 6 x 7, 6 x 8
Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48.
Solution: The multiples of 6 are 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48,……
Also, Check: Common Multiples
Properties of Multiples
Here we have given some important Properties of Multiples. Check out the properties and get a grip on them to make your learning easy.
(i) Every number is a multiple of itself.
For example, the first multiple of 5 is 5 because 5 × 1 = 5.
(ii) The multiples of a number are infinite.
We know that numbers are infinite. Therefore, the multiples of a number also infinite. If you take the example of multiples of 2, we begin with 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14,…. and so on.
(iii) The multiple of a number is greater than or equal to the number itself.
For example, if we take the multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, .… and so on. We can see that: The 1st multiple of 3 is equal to 3: 3 × 1 = 3. The 2nd multiple, the 3rd multiple, and the following multiples of 3 are all greater than 3 (6 > 3, 9 > 3, ….)
(iv) 0 is a multiple of every number.
Common Multiples
Multiples that are common to any given two numbers are known as common multiples of those numbers. Check out the example for better understanding.
Consider two numbers– 2 and 3. Multiples of 2 and 3 are –
Multiples of 2 = 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, ….
Multiples of 3 = 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18,……….
We observe that 6 and 12 are the first two common multiples of 2 and 3. But what can be the real-life use of common multiples?
Suppose Arun and Anil are cycling on a circular track. They start from the same point but Arun takes 30 seconds to cover a lap while Anil takes 45 seconds to cover the lap. So when will be the first time they meet again at the starting point?
This can be deduced from the list of common multiples. Arun and Anil will meet again after 90 minutes.
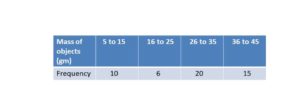
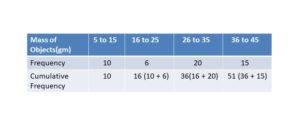
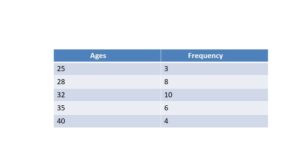
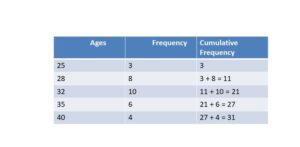
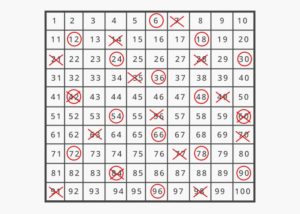
First Ten Multiples of the Numbers
Find out the first ten multiples of the numbers from the below figure.
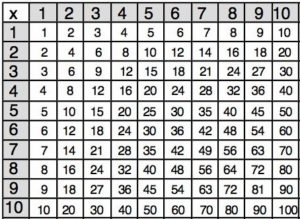
Multiples of Different Numbers
When two numbers are multiplied the result is called the product of the multiple of given numbers. If the number 6 is multiplied with other numbers, then you get different multiples. Also, if the number 7 is multiplied with other numbers, then you get different multiples.
Solved Examples on Multiples
1. Find the first three multiples of 7.
Solution:
The given number is 7.
To find the first three multiples of 7, you need to multiply 7 with 1, 2, 3.
7 × 1 = 7
7 × 2 = 14
7 × 3 = 21
So, 7, 14, 21 are the first 3 multiples of 7.
2. Four friends Alex, Ram, Vijay, and Venu decided to pluck flowers from the garden in the order of the first four multiples of 5. Can you list the number of flowers that each of them plucked as a series of the first four multiples of 5?
Solution:
Given that four friends Alex, Ram, Vijay, and Venu decided to pluck flowers from the garden in the order of the first four multiples of 5.
To find the first four multiples of 5, you need to multiply 5 with 1, 2, 3, and 4.
5 × 1 = 5
5 × 2 = 10
5 × 3 = 15
5 × 4 = 20
The first four multiples of 5 are (5 × 1) = 5, (5 × 2) =10, (5 × 3) = 15, and (5 × 4) = 20.
Hence, Alex plucked 5 flowers, Ram plucked 10 flowers, Vijay plucked 15 flowers and Venu plucked 20 flowers.
3. Sam loves watering plants. Her mom asked her to water the pots which were marked in the order of the multiples of 8. However, she missed a few pots. Can you help her identify the pots that she missed in the following list: 8, 16, __, 32, __, 48, 56, 64, __?
Solution:
Given that Sam’s mom asked her to water the pots which were marked in the order of the multiples of 8.
Let us start counting the multiplication table of 8: 8 × 1 = 8, 8 × 2 = 16, 8 × 3 = 24, 8 × 4 = 32, 8 × 5 = 40, 8 × 6 = 48, 8 × 7 = 56, 8 × 8 = 64, 8 × 9 = 72.
The missed pots are 24, 40, and 72.