Engage NY Eureka Math Geometry Module 5 Lesson 7 Answer Key
Eureka Math Geometry Module 5 Lesson 7 Example Answer Key
Example
What if we started with an angle inscribed in the minor arc between A and C?
Answer:
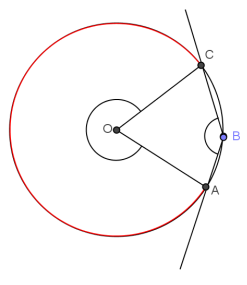
→ Draw a point B on the minor arc between A and C.
Students draw point B.
→ Draw the arc intercepted by ∠ABC. Make it red in your diagram.
Students draw the arc and color it red.
→ In your diagram, do you think the measure of an arc between A and C is half of the measure of the inscribed angle? Why or why not?
The phrasing and explanations can vary. However, there is one answer; the measure of the inscribed arc is twice the measure of the inscribed angle.
→ Using your protractor, measure ∠ABC. Write your answer on your diagram.
Answers will vary.
Now measure the arc in degrees.
→ We could measure ∠AOC and then subtract that measure from 360°.
→ Yes, the measure of the inscribed angle is half the measure of its intercepted arc.
Eureka Math Geometry Module 5 Lesson 7 Exercise Answer Key
Opening Exercise
If the measure of ∠GBF is 17°, name three other angles that have the same measure and explain why.
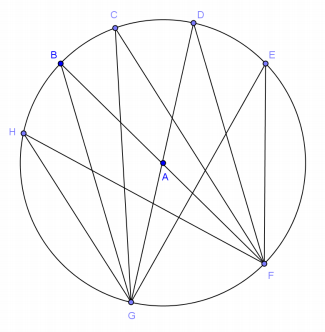
Answer:
Answers will vary. ∠GHF, ∠GCF, ∠GDF, ∠GEF all have the same measure because they are inscribed in the same arc.
What is the measure of ∠GAF? Explain.
Answer:
34°; it is the central angle with an inscribed arc of 17°. The measure of the central angle is double the measure of the inscribed angle of the same arc.
Can you find the measure of ∠BAD? Explain.
Answer:
34°; ∠BAD and ∠GAF are vertical angles and are congruent.
Exercises
Exercise 1.
In circle A, \(m \widehat{B C}\) : \(m \widehat{C E}\) : \(m \widehat{E D}\) : \(m \widehat{B D}\) = 1 : 2 : 3 : 4. Find the following angles of measure.
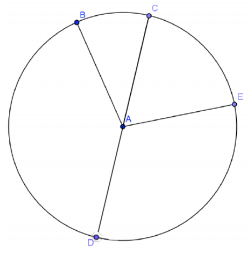
a. m∠BAC
Answer:
36°
b. m∠DAE
Answer:
108°
c. \(m \widehat{B D}\)
Answer:144°
d. \(m \widehat{C E D}\)
Answer:
180°
Exercise 2.
In circle B, AB = CD. Find the following angles of measure.
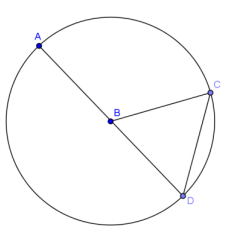
a. \(m \widehat{C D}\)
Answer:
60°
b. \(m \widehat{C A D}\)
Answer:
300°
c. \(m \widehat{A C D}\)
Answer:
180°
Exercise 3.
In circle A, \(\overline{B C}\) is a diameter and m∠DAC = 100°. If \(m \widehat{E C}\) = 2\(m \widehat{B D}\), find the following angles of measure.
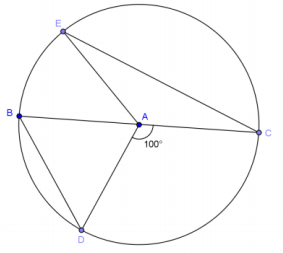
a. m∠BAE
Answer:
20°
b. \(m \widehat{E C}\)
Answer:
160°
c. \(m \widehat{D E C}\)
Answer:
260°
Exercise 4.
Given circle A with m∠CAD = 37°, find the following angles of measure.
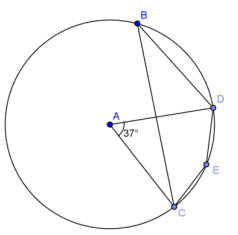
a. \(m \widehat{C B D}\)
Answer:
323°
b. m∠CBD
Answer:
18.5°
c. m∠CED
Answer:
161.5°
Eureka Math Geometry Module 5 Lesson 7 Problem Set Answer Key
Question 1.
Given circle A with m∠CAD = 50°,
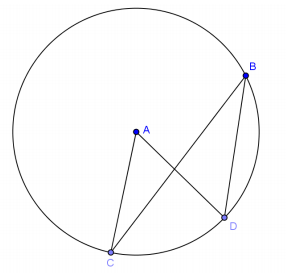
a. Name a central angle.
Answer:
∠CAD
b. Name an inscribed angle.
Answer:
∠CBD
c. Name a chord.
Answer:
Answers will vary. \(\overline{B D}\)
d. Name a minor arc.
Answer:
Answers will vary. \(\widehat{C D}\)
e. Name a major arc.
Answer:
\(\widehat{C B D}\)
f. Find \(m \widehat{C D}\)
Answer:
50°
g. Find \(m \widehat{C B D}\).
Answer:
310°
h. Find m∠CBD.
Answer:
25°
Question 2.
Given circle A, find the measure of each minor arc.
Answer:
\(m \widehat{B E}\) = 64°
\(m \widehat{C D}\) = 64°
\(m \widehat{C E}\) = 116°
\(m \widehat{B D}\) = 116°
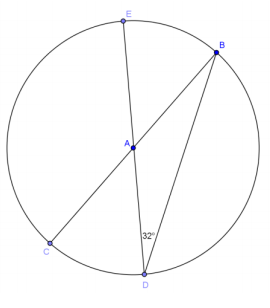
Question 3.
Given circle A, find the following measure.
a. m∠BAD
Answer:
100°
b. m∠CAB
Answer:
80°
c. \(m \widehat{B C}\)
Answer:
80°
d. \(m \widehat{B D}\)
Answer:
100°
e. \(m \widehat{B C D}\)
Answer:
260°
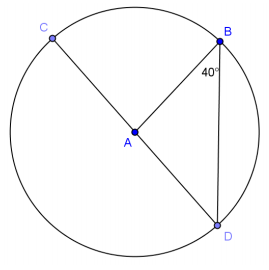
Question 4.
Find the measure of angle x.
Answer:
33°
Question 5.
In the figure, m∠BAC = 126° and m∠BED = 32°. Find m∠DEC.
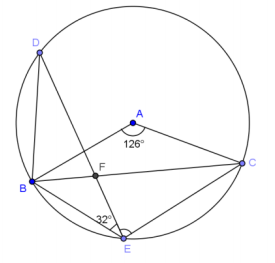
Answer:
85°
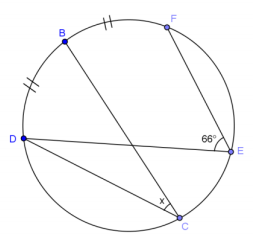
Question 6.
In the figure, m∠BCD = 74° and m∠BDC = 42°. K is the midpoint of \(\widehat{C B}\), and J is the midpoint of \(\widehat{B D}\). Find m∠KBD and m∠CKJ.
Solution: Join BK, KC, KD, KJ, JC, and JD.
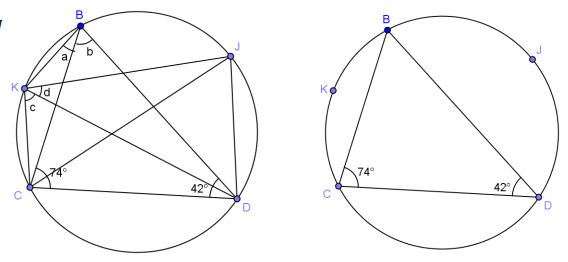
\(m \widehat{B K}\) = \(m \widehat{K C}\)
m∠KDC = \(\frac{42^{\circ}}{2}\) = 21˚
a = _________________________________
In △BCD, b = _________________________________
c = _________________________________
\(m \widehat{B J}\) = \(m \widehat{J D}\)
m∠JCD = _________________________________
d = _______________ _________________________________
m∠KBD = a + b = _________________________________
m∠CKJ = c + d = _________________________________
Answer:
\(m \widehat{B K}\) = \(m \widehat{K C}\) Midpoint forms arcs of equal measure
m∠KDC = \(\frac{42^{\circ}}{2}\) = 21° Angle bisector
a =
21°
Congruent angles inscribed in same arc
In △BCD, b = 64° Sum of angles of triangle is 180°
c = 64° Congruent angles inscribed in same arc
\(m \widehat{B J}\) = \(m \widehat{J D}\) Midpoint forms arcs of equal measure
m∠JCD = 37° Angle bisector
d = 37° Congruent angles inscribed in same arc
m∠KBD = a + b = 85°
m∠CKJ = c + d = 101°
Eureka Math Geometry Module 5 Lesson 7 Exit Ticket Answer Key
Question 1.
Given circle A with diameters \(\overline{B C}\) and \(\overline{D E}\) and \(m \widehat{C D}\) = 56°.
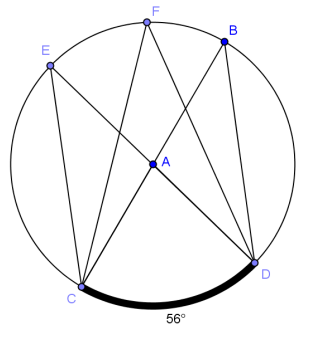
a. Name a central angle.
Answer:
∠CAD
b. Name an inscribed angle.
Answer:
Answers will vary. ∠CED
c. Name a chord that is not a diameter.
Answer:
Answers will vary. \(\overline{C E}\)
d. What is the measure of ∠CAD?
Answer:
56°
e. What is the measure of ∠CBD?
Answer:
28°
f. Name 3 angles of equal measure.
Answer:
m∠CED = m∠CFD = m∠CBD
g. What is the degree measure of \(\widehat{C D B}\)?
Answer:
180°