Engage NY Eureka Math 7th Grade Module 6 Lesson 7 Answer Key
Eureka Math Grade 7 Module 6 Lesson 7 Example Answer Key
Example 1.
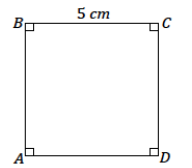
Use what you know about drawing parallel lines with a setsquare to draw rectangle ABCD with dimensions of your choice. State the steps you used to draw your rectangle, and compare those steps to those of a partner.
Answer:
Possible steps: Draw \(\overline{A B}\) first. Align the setsquare so that one leg aligns with \(\overline{A B}\), and place the ruler against the other leg of the setsquare; mark a point X, ___ cm away from \(\overline{A B}\). Draw a line parallel to \(\overline{A B}\) through X. Realign the setsquare with \(\overline{A B}\) situate the ruler so that it passes through A, and draw a segment with a length of ___ cm. Mark the intersection of the line through A and the parallel line to \(\overline{A B}\) as D. \(\overline{A D}\) is now drawn perpendicular to \(\overline{A B}\). Repeat the steps to determine C.
Example 2.
Use what you know about drawing parallel lines with a setsquare to draw rectangle ABCD with AB = 3 cm and BC = 5 cm. Write a plan for the steps you will take to draw ABCD.
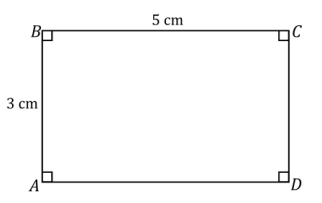
Answer:
Draw \(\overline{A D}\) first. Align the setsquare so that one leg aligns with \(\overline{A D}\), and place the ruler against the other leg of the setsquare; mark a point X 5 cm away from \(\overline{A D}\). Slide the setsquare along the ruler until it aligns with X. Draw a line parallel to \(\overline{A D}\) through X. To create the right angle at A, align the setsquare so that the leg of the setsquare aligns with \(\overline{A D}\), situate the ruler so that the outer edge of the ruler passes through A, and draw a line through A. Mark the intersection of the line through A and the parallel line to \(\overline{A D}\) as D. Repeat the steps to determine C.
Example 3.
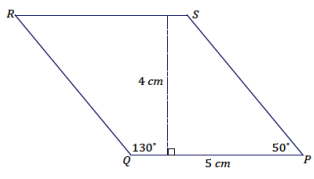
Use a setsquare, ruler, and protractor to draw parallelogram PQRS so that the measurement of ∠P is 50°, PQ = 5 cm, the measurement of ∠Q is 130°, and the length of the altitude to \(\overline{P Q}\) is 4 cm.
Answer:
Steps to draw the figure: Draw \(\overline{P Q}\) first. Align the setsquare and ruler so one leg of the setsquare aligns with \(\overline{P Q}\), and mark a point X 4 cm from \(\overline{P Q}\). Slide the setsquare along the ruler so that one side of the setsquare passes through X, and draw a line through X; this line is parallel to \(\overline{P Q}\). Using \(\overline{P Q}\) as one ray of ∠P, draw ∠P so that the measurement of ∠P is 50° and that the ray PS intersects with the line parallel to \(\overline{P Q}\) (the intersection is S). Draw ∠Q so that the measurement of ∠Q is 130°; the ray QR should be drawn to intersect with the line parallel to \(\overline{P Q}\)(the intersection is R).
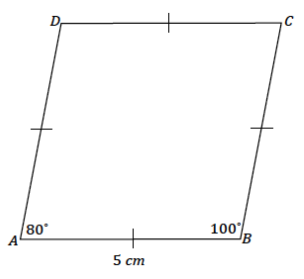
Example 4.
Use a setsquare, ruler, and protractor to draw rhombus ABCD so that the measurement of ∠A = 80°, the measurement of ∠B = 100°, and each side of the rhombus measures 5 cm.
Answer:
Steps to draw the figure: Draw \(\overline{A B}\) first. Using \(\overline{A B}\) as one ray of ∠A, draw ∠A so that the measurement of ∠A is 80°. The other ray, or the to-be side of the rhombus, AD, should be 5 cm in length; label the endpoint of the segment as D. Align the setsquare and ruler so one leg of the setsquare aligns with \(\overline{A B}\) and the edge of the ruler passes through D. Slide the setsquare along the ruler so that the edge of the setsquare passes through D, and draw a line along the edge of the setsquare. This line is parallel to \(\overline{A B}\).
Now align the setsquare and ruler so one leg of the setsquare aligns with \(\overline{A D}\) and the edge of the ruler passes through B. Slide the setsquare along the ruler so that the edge of the setsquare passes through B, and draw a line along the edge of the setsquare. This line is parallel to \(\overline{A D}\). Along this line, measure a segment 5 cm with B as one endpoint, and label the other endpoint C. Join C to D.
Eureka Math Grade 7 Module 6 Lesson 7 Exercise Answer Key
Exercise 1.
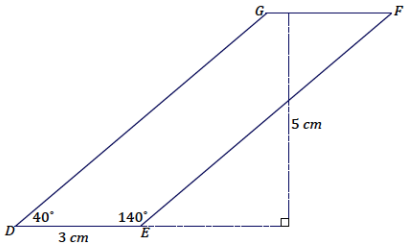
Use a setsquare, ruler, and protractor to draw parallelogram DEFG so that the measurement of ∠D is 40°, DE = 3 cm, the measurement of ∠E is 140°, and the length of the altitude to \(\overline{D E}\) is 5 cm.
Answer:
Steps to draw the figure: Draw \(\overline{D E}\) first. Align the setsquare and ruler so one leg of the setsquare aligns with \(\overline{D E}\) , and mark a point X 5 cm from \(\overline{D E}\) . Slide the setsquare along the ruler so that one side of the setsquare passes through X, and draw a line through X; this line is parallel to \(\overline{D E}\). Using \(\overline{D E}\) as one ray of ∠D, draw ∠D so that the measurement of ∠D is 40° and that the ray DG intersects with the line parallel to \(\overline{D E}\) (the intersection is G). Draw ∠E so that the measurement of ∠E is 140°; the ray EF should be drawn to intersect with the line parallel to \(\overline{D E}\) (the intersection is F).
Eureka Math Grade 7 Module 6 Lesson 7 Problem Set Answer Key
Question 1.
Draw rectangle ABCD with AB = 5 cm and BC = 7 cm.
Answer:
Steps to draw the figure: Draw \(\overline{A B}\) first. Align the setsquare so that one leg aligns with \(\overline{A B}\), and place the ruler against the other leg of the setsquare; mark a point X 7 cm away from \(\overline{A B}\). Draw a line parallel to \(\overline{A B}\) through X. To create the right angle at A, align the setsquare so that its leg aligns with \(\overline{A B}\), situate the ruler so that the outer edge of the ruler passes through A, and draw a line through A. Mark the intersection of the line through A and the parallel line to \(\overline{A B}\) as D. Repeat the steps to determine C.
Question 2.
Use a setsquare, ruler, and protractor to draw parallelogram PQRS so that the measurement of ∠P is 65°, PQ = 8 cm, the measurement of ∠Q is 115°, and the length of the altitude to \(\overline{P Q}\) is 3 cm.
Answer:
Steps to draw the figure: Draw \(\overline{P Q}\) first. Align the setsquare and ruler so one leg of the setsquare aligns with \(\overline{P Q}\), and mark a point X 3 cm from \(\overline{P Q}\). Slide the setsquare along the ruler so that one side of the setsquare passes through X, and draw a line through X; this line is parallel to \(\overline{P Q}\). Using \(\overline{P Q}\) as one ray of ∠P, draw ∠P so that the measurement of ∠P is 65° and that the ray PS intersects with the line parallel to \(\overline{P Q}\) (the intersection is S). Draw ∠Q so that the measurement of ∠Q is 115°; the ray QR should be drawn to intersect with the line parallel to \(\overline{P Q}\) (the intersection is R).
Question 3.
Use a setsquare, ruler, and protractor to draw rhombus ABCD so that the measurement of ∠A is 60°, and each side of the rhombus measures 5 cm.
Answer:
Steps to draw the figure: Draw \(\overline{A B}\) first. Using \(\overline{A B}\) as one ray of ∠A, draw ∠A so that the measurement of
∠A is 60°. The other ray, or to-be side of the rhombus, AD, should be 5 cm in length; label the endpoint of the segment as D. Align the setsquare and ruler so one leg of the setsquare aligns with \(\overline{A B}\) and the edge of the ruler passes through D. Slide the setsquare along the ruler so that the edge of the setsquare passes through D, and draw a line along the edge of the setsquare.
This line is parallel to\(\overline{A B}\). Now, align the setsquare and ruler so one leg of the setsquare aligns with \(\overline{A D}\) and the edge of the ruler passes through B. Slide the setsquare along the ruler so that the edge of the setsquare passes through B, and draw a line along the edge of the setsquare. This line is parallel to \(\overline{A D}\). Along this line, measure a segment 5 cm with B as one endpoint, and label the other endpoint C. Join C to D.
The following table contains partial information for parallelogram ABCD. Using no tools, make a sketch of the parallelogram. Then, use a ruler, protractor, and setsquare to draw an accurate picture. Finally, complete the table with the unknown lengths.
Two of the sketches are provided.
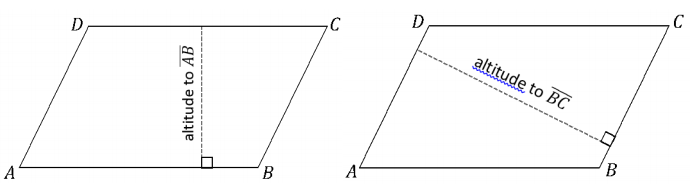
The following table contains partial information for parallelogram ABCD. Using no tools, make a sketch of the parallelogram. Then, use a ruler, protractor, and setsquare to draw an accurate picture. Finally, complete the table with the unknown lengths.
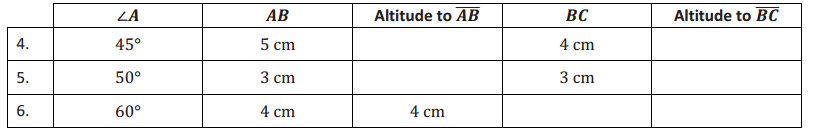
Answer:
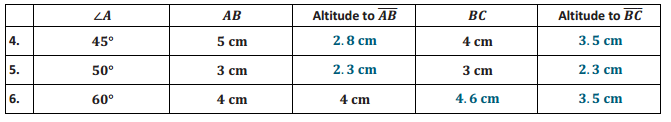
Question 7.
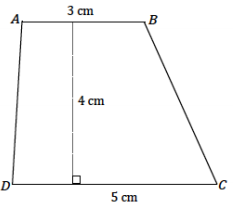
Use what you know about drawing parallel lines with a setsquare to draw trapezoid ABCD with parallel sides \(\overline{A B}\) and \(\overline{C D}\). The length of \(\overline{A B}\) is 3 cm, and the length of \(\overline{C D}\) is 5 cm; the height between the parallel sides is 4 cm. Write a plan for the steps you will take to draw ABCD.
Answer:
Draw \(\overline{A B}\) (or \(\overline{C D}\)) first. Align the setsquare and ruler so that one leg of the
setsquare aligns with \(\overline{A B}\); mark a point X 4 cm away from \(\overline{A B}\). Draw a line parallel to \(\overline{A B}\) through X. Once a line parallel to \(\overline{A B}\) has been drawn through X, measure a portion of the line to be 3 cm, and label the endpoint on the right as C and the other endpoint D. Join D to A and C to B.
Question 8.
Use the appropriate tools to draw rectangle FIND with FI = 5 cm and IN = 10 cm.
Answer:
Draw \(\overline{F I}\) first. Align the setsquare so that one leg aligns with \(\overline{F I}\), and place the ruler against the other leg of the
setsquare; mark a point X 10 cm away from \(\overline{F I}\). Draw a line parallel to \(\overline{F I}\) through X. To create the right angle at F, align the setsquare so that its leg aligns with \(\overline{F I}\), and situate the ruler so that its outer edge passes through F, and then draw a line through F. Mark the intersection of the line through F and the parallel line to \(\overline{F I}\) as D. Repeat the steps to determine N.
Question 9.
Challenge: Determine the area of the largest rectangle that will fit inside an equilateral triangle with side length 5 cm.
Answer:
Students will quickly discover that rectangles of different dimensions can be drawn; finding the largest rectangle may take multiple efforts. The maximum possible area is 5.4 cm2.
Eureka Math Grade 7 Module 6 Lesson 7 Exit Ticket Answer Key
Use what you know about drawing parallel lines with a setsquare to draw square ABCD with AB = 5 cm. Explain how you created your drawing.
Answer:
Draw \(\overline{A B}\)(any side will do here) first. Align the setsquare and ruler so that one leg of the setsquare aligns with \(\overline{A B}\); mark a point X 5 cm away from \(\overline{A B}\). Draw a line parallel to \(\overline{A B}\) through X. To create the right angle at A, align the setsquare so that the leg of the setsquare aligns with \(\overline{A B}\), situate the ruler so that the outer edge of the ruler passes through A, and draw a line through A. Mark the intersection of the line through A and the parallel line to \(\overline{A B}\) as D; join A and D. Repeat the steps to determine C, and join B and C.