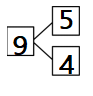
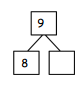
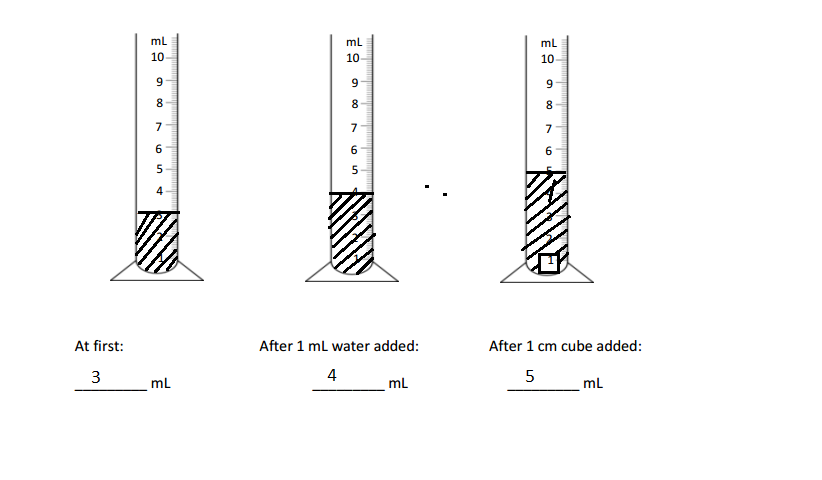
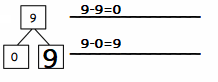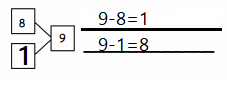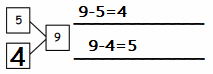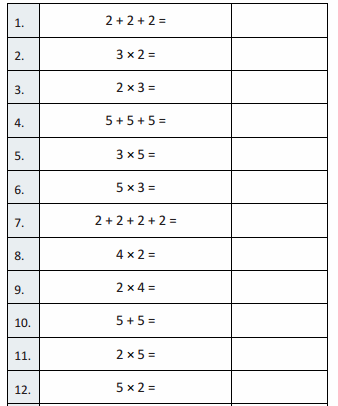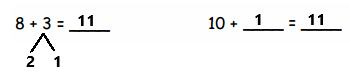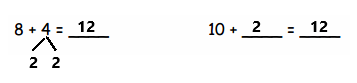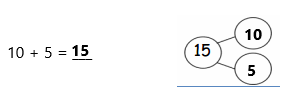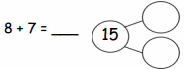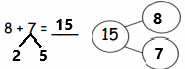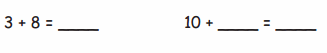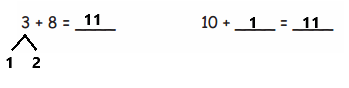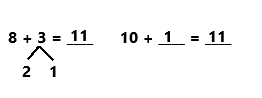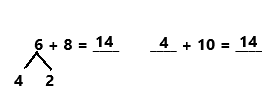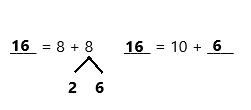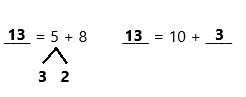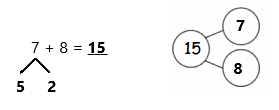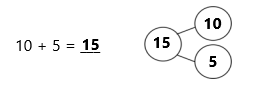Engage NY Eureka Math 3rd Grade Module 1 Lesson 4 Answer Key
Eureka Math Grade 3 Module 1 Answer Key
Eureka Math Grade 3 Module 1 Lesson 4 Sprint Answer Key
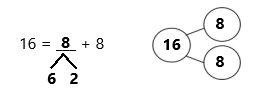
A
Repeated Addition as Multiplication

Answer:
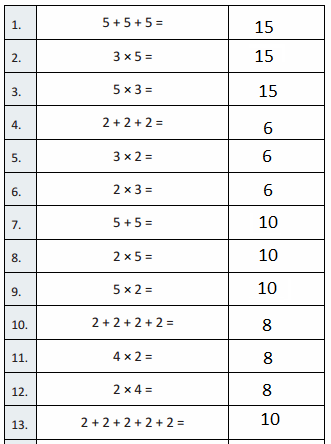
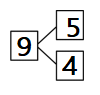
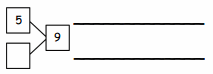
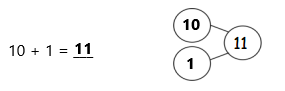
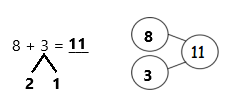
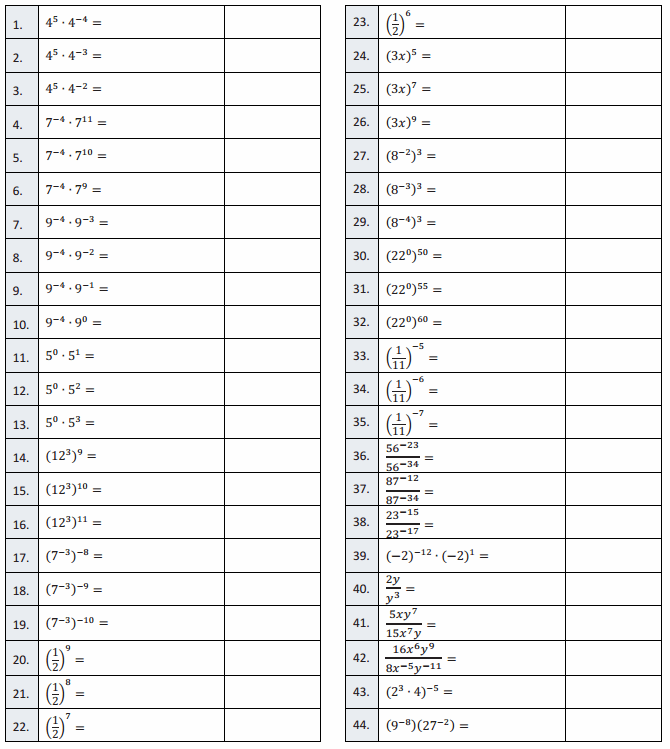
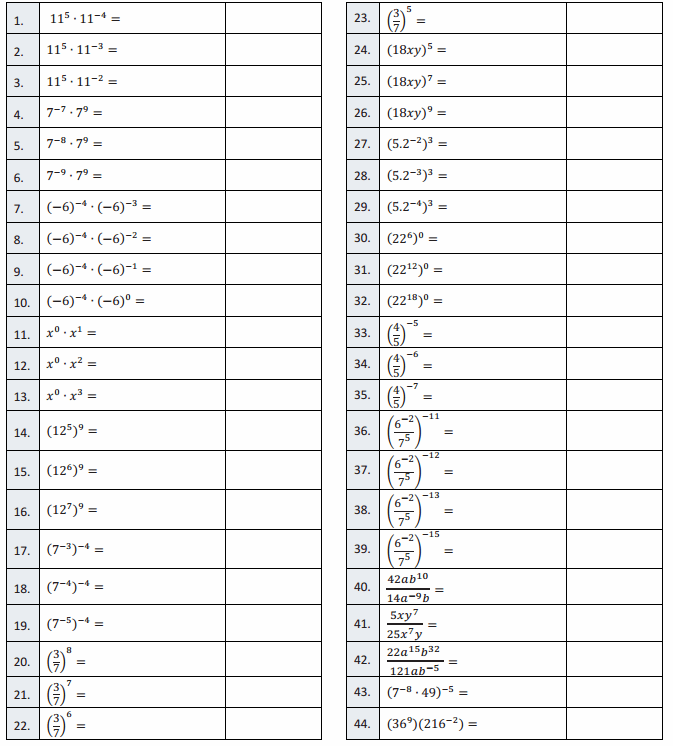
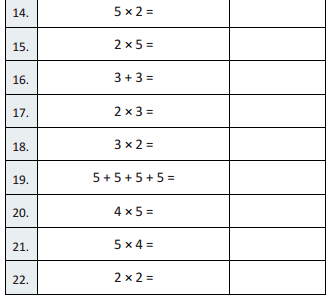
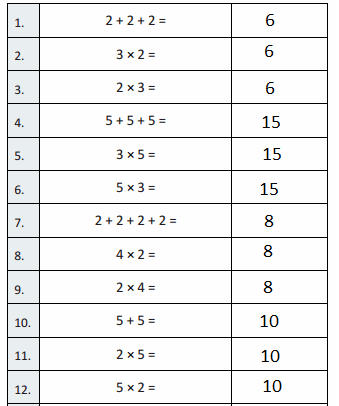
Question 1.
5 + 5 + 5 =
Answer:
5 + 5 + 5 = 15,
Explanation:
Given 5 + 5 + 5 we add 5 by 3 times
we get 15, So 5 + 5 + 5 = 15.
Question 2.
3 × 5 =
Answer:
3 × 5 = 15,
Explanation:
Given 3 × 5 we multiply 3 with 5,
we get 15 as 3 × 5 = 15.
Question 3.
5 × 3 =
Answer:
5 × 3 = 15,
Explanation:
Given 5 × 3 we multiply 5 with 3,
we get 15 as 5 × 3 = 15.
Question 4.
2 + 2 + 2 =
Answer:
2 + 2 + 2 = 6,
Explanation:
Given 2 + 2 + 2 we add 2 by 3 times
we get 6, So 2 + 2 + 2 = 6.
Question 5.
3 × 2 =
Answer:
3 × 2 = 6,
Explanation:
Given 3 × 2 we multiply 3 with 2,
we get 6 as 3 × 2 = 6.
Question 6.
2 × 3 =
Answer:
2 × 3 = 6,
Explanation:
Given 2 × 3 we multiply 2 with 3,
we get 6 as 2 × 3 = 6.
Question 7.
5 + 5 =
Answer:
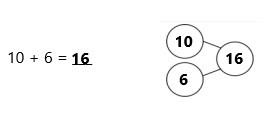
5 + 5 = 10,
Explanation:
Given 5 + 5 we add 5 by 2 times
we get 10, So 5 + 5 = 10.
Question 8.
2 × 5 =
Answer:
2 X 5 = 10,
Explanation:
Given 2 × 5 we multiply 2 with 5,
we get 10 as 2 × 5 = 10.
Question 9.
5 × 2 =
Answer:
5 × 2 = 10,
Explanation:
Given 5 × 2 we multiply 5 with 2,
we get 10 as 5 × 2 = 10.
Question 10.
2 + 2 + 2 + 2 =
Answer:
2 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 8,
Explanation:
Given 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 we add 2 by 4 times
we get 8, So 2 + 2 + 2 + 2= 8.
Question 11.
4 × 2 =
Answer:
4 × 2 = 8,
Explanation:
Given 4 × 2 we multiply 4 with 2,
we get 8 as 4 × 2 = 8.
Question 12.
2 × 4 =
Answer:
2 × 4 = 8,
Explanation:
Given 2 × 4 we multiply 2 with 4,
we get 8 as 2 × 4 = 8.
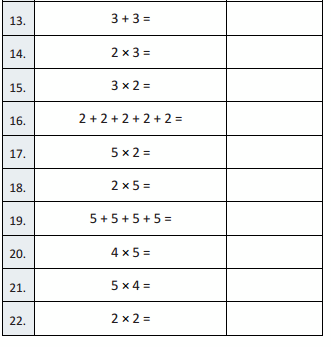
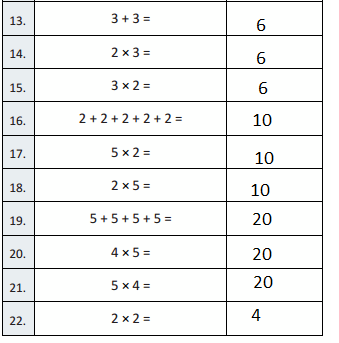
Question 13.
2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 =
Answer:
2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 10,
Explanation:
Given 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 we add 2 by 5 times
we get 10, So 2+ 2 + 2 + 2 + 2= 10.
Question 14.
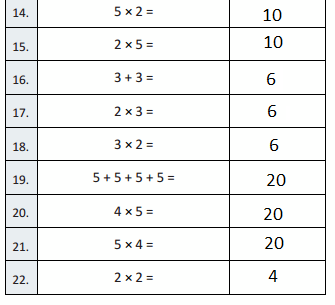
5 × 2 =
Answer:
5 × 2 = 10,
Explanation:
Given 5 × 2 we multiply 5 with 2,
we get 10 as 5 × 2 = 10.
Question 15.
2 × 5 =
Answer:
2 × 5 = 10,
Explanation:
Given 2 × 5 we multiply 2 with 5,
we get 10 as 2 × 5 = 10.
Question 16.
3 + 3 =
Answer:
3 + 3 = 6,
Explanation:
Given 3 + 3 we add 3 by 2 times
we get 6, So 3 + 3 = 6.
Question 17.
2 × 3 =
Answer:
2 × 3 = 6,
Explanation:
Given 2 × 3 we multiply 2 with 3,
we get 6 as 2 × 3 = 6.
Question 18.
3 × 2 =
Answer:
3 × 2 = 6,
Explanation:
Given 3 × 2 we multiply 3 with 2,
we get 6 as 3 × 2 = 6.
Question 19.
5 + 5 + 5+ 5 =
Answer:
5 + 5 + 5 + 5 = 20,
Explanation:
Given 5 + 5 + 5 + 5 we add 5 by 4 times
we get 20, So 5 + 5 + 5 + 5 = 20.
Question 20.
4 × 5 =
Answer:
4 × 5 = 20,
Explanation:
Given 4 × 5 we multiply 4 with 5,
we get 20 as 4 × 5 = 20.
Question 21.
5 × 4 =
Answer:
5 × 4 = 20,
Explanation:
Given 5 × 4 we multiply 5 with 4,
we get 20 as 5 × 4 = 20.
Question 22.
2 × 2 =
Answer:
2 × 2 = 4,
Explanation:
Given 2 × 2 we multiply 2 with 2,
we get 4 as 2 × 2 = 4.
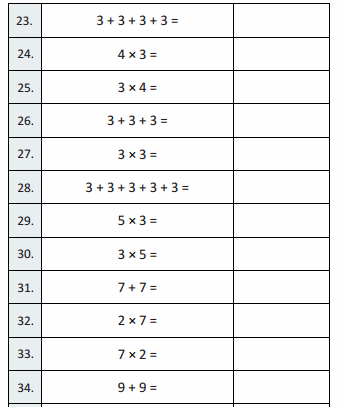
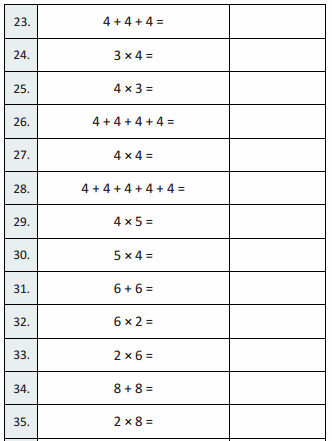
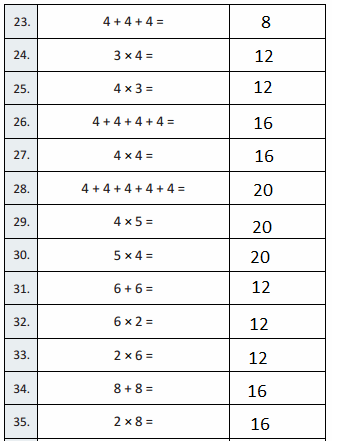
Question 23.
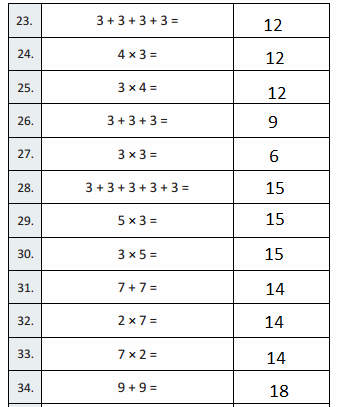
3 + 3 + 3 + 3 =
Answer:
3 + 3 + 3 + 3 = 12,
Explanation:
Given 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 we add 3 by 4 times
we get 12, So 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 = 12.
Question 24.
4 × 3 =
Answer:
4 × 3 = 12,
Explanation:
Given 4 × 3 we multiply 4 with 3,
we get 12 as 4 × 3 = 12.
Question 25.
3 × 4 =
Answer:
3 × 4 = 12,
Explanation:
Given 3 × 4 we multiply 3 with 4,
we get 12 as 3 × 4 = 12.
Question 26.
3 + 3 + 3 =
Answer:
3 + 3 + 3 = 9,
Explanation:
Given 3 + 3 + 3 we add 3 by 3 times
we get 9, So 3 + 3 + 3 = 9.
Question 27.
3 × 3 =
Answer:
3 × 3 = 9,
Explanation:
Given 3 × 3 we multiply 3 with 3,
we get 9 as 3 × 3 = 9.
Question 28.
3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 =
Answer:
3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 = 15,
Explanation:
Given 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 we add 3 by 5 times
we get 15, So 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 = 15.
Question 29.
5 × 3 =
Answer:
5 × 3 = 15,
Explanation:
Given 5 × 3 we multiply 5 with 3,
we get 15 as 5 × 3 = 15.
Question 30.
3 × 5 =
Answer:
3 × 5 = 15,
Explanation:
Given 3 × 5 we multiply 3 with 5,
we get 15 as 3 × 5 = 15.
Question 31.
7 + 7 =
Answer:
7 + 7 = 14,
Explanation:
Given 7 + 7 we add 7 by 2 times
we get 14, So 7 + 7 = 14.
Question 32.
2 × 7 =
Answer:
2 × 7 = 14,
Explanation:
Given 2 × 7 we multiply 2 with 7,
we get 14 as 2 × 7 = 14.
Question 33.
7 × 2 =
Answer:
7 × 2 = 14,
Explanation:
Given 7 × 2 we multiply 7 with 2,
we get 14 as 7 × 2 = 14.
Question 34.
9 + 9 =
Answer:
9 + 9 = 18,
Explanation:
Given 9 + 9 we add 9 by 2 times
we get 18, So 9 + 9 = 18.
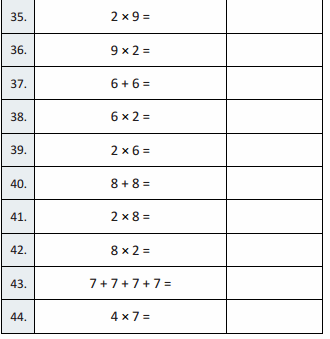
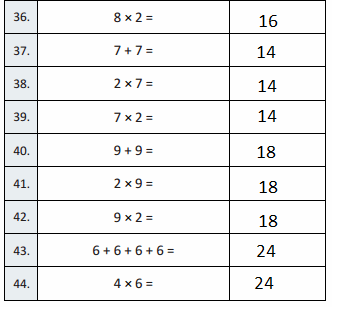
Question 35.
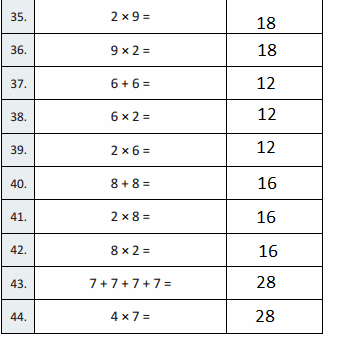
2 × 9 =
Answer:
2 × 9 = 18,
Explanation:
Given 2 × 9 we multiply 2 with 9,
we get 18 as 2 × 9 = 18.
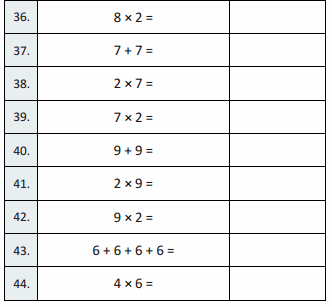
Question 36.
9 × 2 =
Answer:
9 × 2 = 18,
Explanation:
Given 9 × 2 we multiply 9 with 2,
we get 18 as 9 × 2 = 18.
Question 37.
6 + 6 =
Answer:
6 + 6 = 12,
Explanation:
Given 6 + 6 we add 6 by 2 times
we get 12, So 6 + 6 = 12.
Question 38.
6 × 2 =
Answer:
6 × 2 = 12,
Explanation:
Given 6 × 2 we multiply 6 with 2,
we get 12 as 6 × 2 = 12.
Question 39.
2 × 6 =
Answer:
2 × 6 = 12,
Explanation:
Given 2 × 6 we multiply 2 with 6,
we get 12 as 2 × 6 = 12.
Question 40.
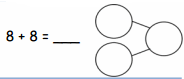
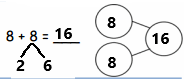
8 + 8 =
Answer:
8 + 8 = 16,
Explanation:
Given 8 + 8 we add 8 by 2 times
we get 16, So 8 + 8 = 16.
Question 41.
2 × 8 =
Answer:
2 × 8 = 16,
Explanation:
Given 2 × 8 we multiply 2 with 8,
we get 16 as 2 × 8 = 16.
Question 42.
8 × 2 =
Answer:
8 × 2 = 16,
Explanation:
Given 8 × 2 we multiply 8 with 2,
we get 16 as 8 X 2 = 16.
Question 43.
7 + 7 + 7 + 7 =
Answer:
7 + 7 + 7 + 7 = 28,
Explanation:
Given 7 + 7 + 7 + 7 we add 7 by 4 times
we get 28, So 7 + 7 + 7 + 7 = 28.
Question 44.
4 × 7 =
Answer:
4 × 7 = 28,
Explanation:
Given 4 × 7 we multiply 4 with 7,
we get 28 as 4 × 7 = 28.
B
Repeated Addition as Multiplication
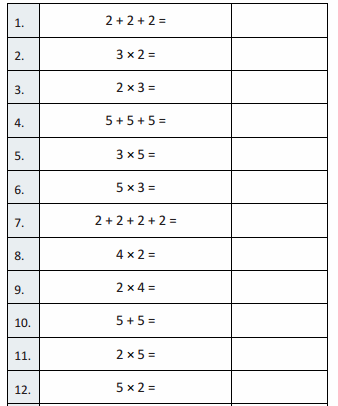
Answer:
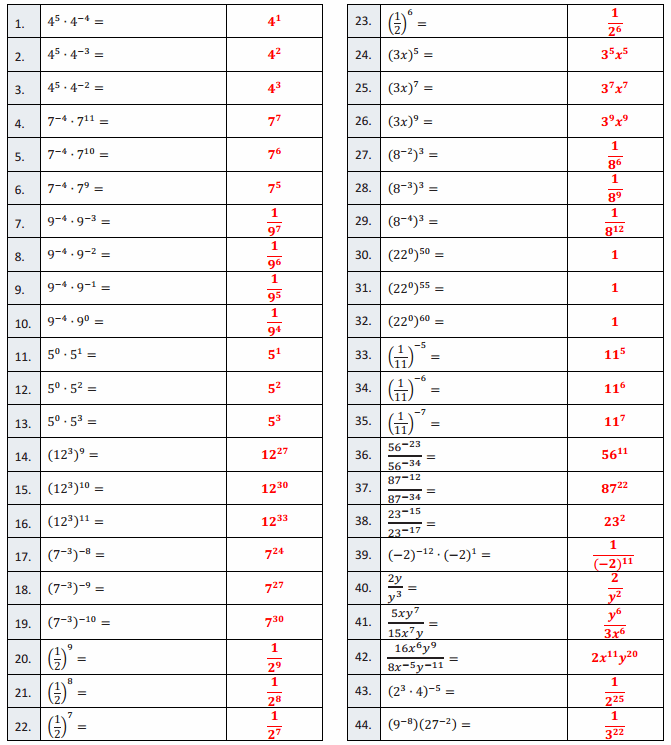
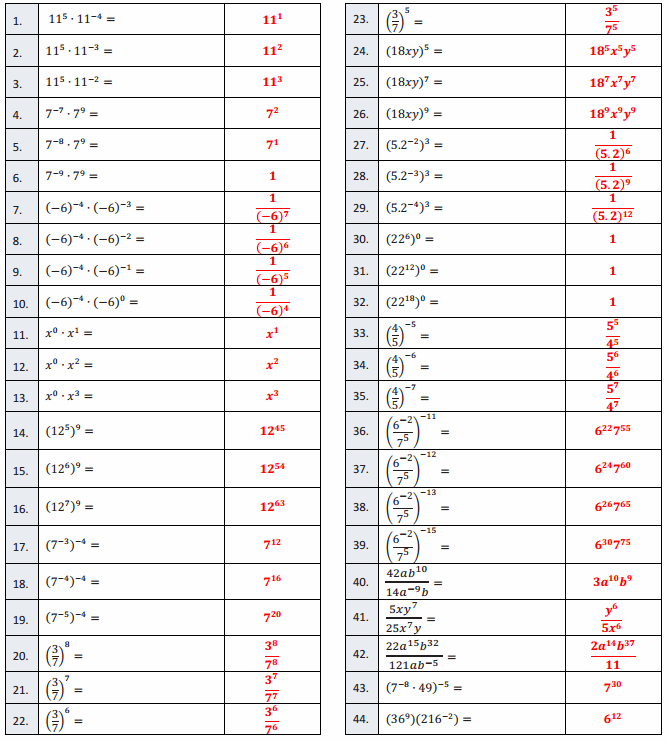
Question 1.
2 + 2 + 2 =
Answer:
2 + 2 + 2 = 6,
Explanation:
Given 2 + 2 + 2 we add 2 by 3 times
we get 6, So 2 + 2 + 2 = 6.
Question 2.
3 × 2 =
Answer:
3 × 2 = 6,
Explanation:
Given 3 × 2 we multiply 3 with 2,
we get 6 as 3 × 2 = 6.
Question 3.
2 × 3 =
Answer:
2 × 3 = 6,
Explanation:
Given 2 × 3 we multiply 2 with 3,
we get 6 as 2 × 3 = 6.
Question 4.
5 + 5 + 5 =
Answer:
5 + 5 + 5 = 15,
Explanation:
Given 5 + 5 + 5 we add 5 by 3 times
we get 15, So 5 + 5 + 5 = 15.
Question 5.
3 × 5 =
Answer:
3 × 5 = 15,
Explanation:
Given 3 × 5 we multiply 3 with 5,
we get 15 as 3 × 5 = 15.
Question 6.
5 × 3 =
Answer:
5 × 3 = 15,
Explanation:
Given 5 × 3 we multiply 5 with 3,
we get 15 as 5 × 3 = 15.
Question 7.
2 + 2 + 2 + 2 =
Answer:
2 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 8,
Explanation:
Given 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 we add 2 by 4 times
we get 8, So 2 + 2 + 2 + 2= 8.
Question 8.
4 × 2 =
Answer:
4 × 2 = 8,
Explanation:
Given 4 × 2 we multiply 4 with 2,
we get 8 as 4 × 2 = 8.
Question 9.
2 × 4 =
Answer:
2 X 4 = 8,
Explanation:
Given 2 × 4 we multiply 2 with 4,
we get 8 as 2 × 4 = 8.
Question 10.
5 + 5 =
Answer:
5 + 5 = 10,
Explanation:
Given 5 + 5 we add 5 by 2 times
we get 10, So 5 + 5 = 10.
Question 11.
2 × 5 =
Answer:
2 × 5 = 10,
Explanation:
Given 2 × 5 we multiply 2 with 5,
we get 10 as 2 × 5 = 10.
Question 12.
5 × 2 =
Answer:
5 × 2 = 10,
Explanation:
Given 5 × 2 we multiply 5 with 2,
we get 10 as 5 × 2 = 10.
Question 13.
3 + 3 =
Answer:
3 + 3 = 6,
Explanation:
Given 3 + 3 we add 3 by 2 times
we get 6, So 3 + 3 = 6.
Question 14.
2 × 3 =
Answer:
2 X 3 = 6,
Explanation:
Given 2 × 3 we multiply 2 with 3,
we get 6 as 2 × 3 = 6.
Question 15.
3 × 2 =
Answer:
3 × 2 = 6,
Explanation:
Given 3 × 2 we multiply 3 with 2,
we get 6 as 3 × 2 = 6.
Question 16.
2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 =
Answer:
2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 10,
Explanation:
Given 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 we add 2 by 5 times
we get 10, So 2+ 2 + 2 + 2 + 2= 10.
Question 17.
5 × 2 =
Answer:
5 × 2 = 10,
Explanation:
Given 5 × 2 we multiply 5 with 2,
we get 10 as 5 × 2 = 10.
Question 18.
2 × 5 =
Answer:
2 × 5 = 10,
Explanation:
Given 2 × 5 we multiply 2 with 5,
we get 10 as 2 × 5 = 10.
Question 19.
5 + 5 + 5 + 5 =
Answer:
5 + 5 + 5 + 5 = 20,
Explanation:
Given 5 + 5 + 5 + 5 we add 5 by 4 times
we get 20, So 5 + 5 + 5 + 5 = 20.
Question 20.
4 × 5 =
Answer:
4 × 5 = 20,
Explanation:
Given 4 × 5 we multiply 4 with 5,
we get 20 as 4 × 5 = 20.
Question 21.
5 × 4 =
Answer:
5 × 4 = 20,
Explanation:
Given 5 × 4 we multiply 5 with 4,
we get 20 as 5 × 4 = 20.
Question 22.
2 × 2 =
Answer:
2 X 2 = 4,
Explanation:
Given 2 × 2 we multiply 2 with 2,
we get 4 as 2 × 2 = 4.
Question 23.
4 + 4 + 4 =
Answer:
4 + 4 + 4 = 12,
Explanation:
Given 4 + 4 + 4 we add 4 by 3 times
we get 12, So 4 + 4 + 4 = 12.
Question 24.
3 × 4 =
Answer:
3 × 4 = 12,
Explanation:
Given 3 × 4 we multiply 3 with 4,
we get 12 as 3 × 4 = 12.
Question 25.
4 × 3 =
Answer:
4 × 3 = 12,
Explanation:
Given 4 × 3 we multiply 4 with 3,
we get 12 as 4 × 3 = 12.
Question 26.
4 + 4 + 4 + 4 =
Answer:
4 + 4 + 4 + 4 = 16,
Explanation:
Given 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 we add 4 by 4 times
we get 16, So 4 + 4 + 4 +4 = 16.
Question 27.
4 × 4 =
Answer:
4 × 4 = 16,
Explanation:
Given 4 × 4 we multiply 4 with 4,
we get 14 as 4 × 4 = 16.
Question 28.
4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 =
Answer:
4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 = 20,
Explanation:
Given 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 we add 4 by 5 times
we get 20, So 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 = 20.
Question 29.
4 × 5 =
Answer:
4 × 5 = 20,
Explanation:
Given 4 × 5 we multiply 4 with 5,
we get 20 as 4 × 5 = 20.
Question 30.
5 × 4 =
Answer:
5 × 4 = 20,
Explanation:
Given 5 × 4 we multiply 5 with 4,
we get 20 as 5 × 4 = 20.
Question 31.
6 + 6 =
Answer:
6 + 6 = 12,
Explanation:
Given 6 + 6 we add 6 by 2 times
we get 12, So 6 + 6 = 12.
Question 32.
6 × 2 =
Answer:
6 × 2 = 12,
Explanation:
Given 6 × 2 we multiply 6 with 2,
we get 12 as 6 × 2 = 12.
Question 33.
2 × 6 =
Answer:
2 × 6 = 12,
Explanation:
Given 2 × 6 we multiply 2 with 6,
we get 12 as 2 × 6 = 12.
Question 34.
8 + 8 =
Answer:
8 + 8 = 16,
Explanation:
Given 8 + 8 we add 8 by 2 times
we get 16, So 8 + 8 = 16.
Question 35.
2 × 8 =
Answer:
2 × 8 = 16,
Explanation:
Given 2 × 8 we multiply 2 with 8,
we get 16 as 2 × 8 = 16.
Question 36.
8 × 2 =
Answer:
8 × 2 = 16,
Explanation:
Given 8 × 2 we multiply 8 with 2,
we get 16 as 8 × 2 = 16.
Question 37.
7 + 7 =
Answer:
7 + 7 = 14,
Explanation:
Given 7 + 7 we add 7 by 2 times
we get 14, So 7 + 7 = 14.
Question 38.
2 × 7 =
Answer:
2 × 7 = 14,
Explanation:
Given 2 × 7 we multiply 2 with 7,
we get 14 as 2 X 7 = 14.
Question 39.
7 × 2 =
Answer:
7 × 2 = 14,
Explanation:
Given 7 × 2 we multiply 7 with 2,
we get 14 as 7 × 2 = 14.
Question 40.
9 + 9 =
Answer:
9 + 9 = 18,
Explanation:
Given 9 + 9 we add 9 by 2 times
we get 18, So 9 + 9 = 18.
Question 41.
2 × 9 =
Answer:
2 × 9 = 18,
Explanation:
Given 2 × 9 we multiply 2 with 9,
we get 18 as 2 × 9 = 18.
Question 42.
9 × 2 =
Answer:
9 × 2 = 18,
Explanation:
Given 9 × 2 we multiply 9 with 2,
we get 18 as 9 × 2 = 18.
Question 43.
6 + 6 + 6 + 6 =
Answer:
6 + 6 + 6 + 6 = 24,
Explanation:
Given 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 we add 6 by 4 times
we get 24, So 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 = 24.
Question 44.
4 × 6 =
Answer:
4 × 6 = 24,
Explanation:
Given 4 × 6 we multiply 4 with 6,
we get 24 as 4 × 6 = 24.
Eureka Math Grade 3 Module 1 Lesson 4 Problem Set Answer Key
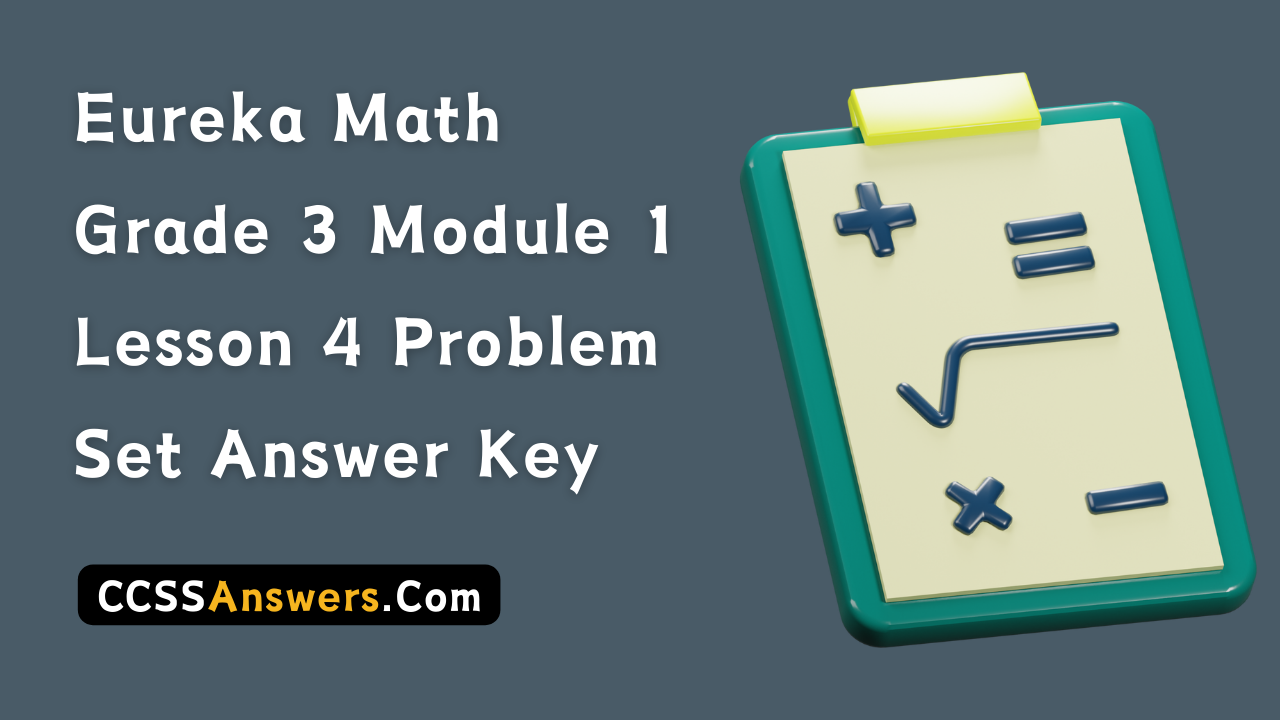
Question 1.
14 flowers are divided into 2 equal groups.
There are ____7_____ flowers in each group.
Answer:
There are 7 flowers in each group,
Explanation:
Given 14 flowers are divided into 2 equal groups,
So there are 14 ÷ 2 = 7 flowers in 2 equal groups.
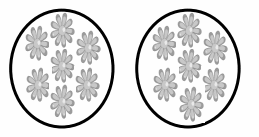
Question 2.
28 books are divided into 4 equal groups.
There are _____7____ books in each group.
Answer:
There are 7 books in each group.
Explanation:
Given 28 books are divided into 4 equal groups,
So there are 28 ÷ 4 = 7 books in 4 equal groups.
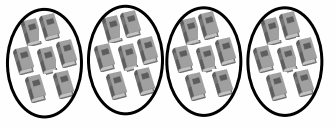
Question 3.
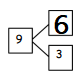
30 apples are divided into ___3___ equal groups.
There are ____10_____ apples in each group.
Answer:
30 apples are divided into 3 equal groups.
There are 10 apples in each group.
Explanation:
Given in the picture there are30 apples divided into
3 equal groups. So there are 30 ÷ 3 = 10 apples
in each group.
Question 4.
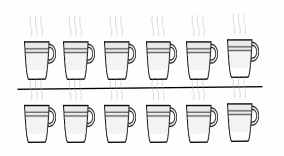
___12____ cups are divided into ___2____ equal groups.
There are ____6_____ cups in each group.
12 ÷ 2 = ___6______
Answer:
12 cups are divided into 2 equal groups.
There are 6 cups in each group. 12 ÷ 2 = 6 cups,
Explanation:
As given in the picture there are 12 cups divided
into 2 equal groups, There are 6 cups in each group
as 12 ÷ 2 = 6 cups.
Question 5.
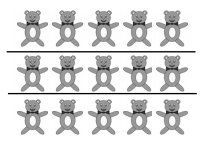
There are ____15_____ toys in each group.
15 ÷ 3 = ____5_____
There are ____15_____ toys in each group,
Explanation:
As given in the picture there are 15 toys divided
as 15 ÷ 3 = 5 toys in each group, So, there are
15 toys in 3 equal groups.
Question 6.
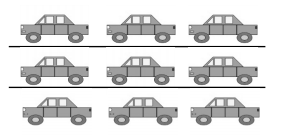
9 ÷ 3 = ____3______
Answer:
There are 3 cars in each group,
Explanation:
As given in the picture there are 9 cars divided as 9 ÷ 3 = 3 cars in each group.
So, there are 3 cars in 3 equal groups.
Question 7.
Audrina has 24 colored pencils. She puts them in 4 equal groups. How many colored pencils are in each group?
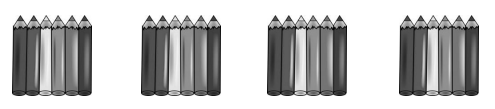
There are ___6____ colored pencils in each group.
24 ÷ 4 = ___6____
Answer:
There are 6 colored pencils in each group,
Explanation:
Given Audrina has 24 colored pencils. She puts them in 4 equal groups. So number of colored pencils in each group are 24 ÷ 4 = 6 pencils in 4 equal groups.
Question 8.
Charlie picks 20 apples. He divides them equally between 5 baskets. Draw the apples in each basket.
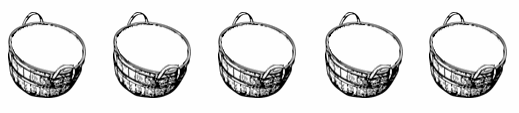
There are _____4______ apples in each basket.
20 ÷ ____5____ = ____4______

Answer:
There are 4 apples in each basket,
Explanation:
Given Charlie picks 20 apples. He divides them equally between 5 baskets. Drawn the apples in each basket as 20 ÷ 5 = 4 apples in 5 equal groups.
Question 9.
Chelsea collects butterfly stickers. The picture shows how she placed them in her book. Write a division sentence to show how she equally grouped her stickers.
There are ______3______ butterflies in each row.
____15______ ÷ _____5_____ = ____3______
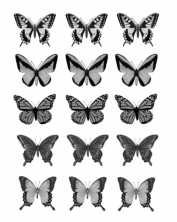
Answer:
Division sentence : 15 ÷ 5 = 3, Chelsea equally grouped 3 butterflies in her stickers.
Explanation:
Given Chelsea collects butterfly stickers.
The picture is showing 15 butterflies she placed them in her book. Wrote a division sentence as 15 ÷ 5 = 3 butterflies to show how she equally grouped 3 butterflies in her stickers.
Eureka Math Grade 3 Module 1 Lesson 4 Exit Ticket Answer Key
Question 1.
There are 16 glue sticks for the class. The teacher divides them into 4 equal groups. Draw the number of glue sticks in each group.
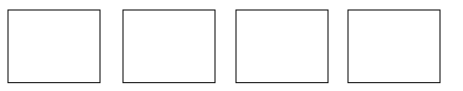
There are _____16______ glue sticks in each group.
16 ÷ ___4_____ = ____4______

Answer:
There are 16 glue sticks in each group.
Explanation:
Given there are 16 glue sticks for the class. The teacher divides them into 4 equal groups.
Drawn the number of glue sticks in each group as 16 ÷ 4 = 4 glue sticks in 4 equal groups.
Question 2.
Draw a picture to show 15 ÷ 3. Then, fill in the blank to make a true division sentence.
15 ÷ 3 = ____5______
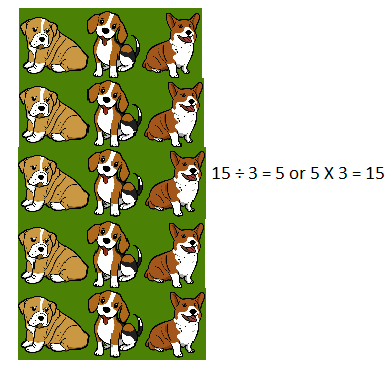
Drawn a picture to show division sentence as
15 ÷ 3 = 5,
Filled in the blank to make a true division sentence as
15 ÷ 3 = ____5____,
Explanation:
Drawn 15 dogs and wrote division sentence as 15 ÷ 3 = 5 as shown above and filled in the blank to make a true division sentence as 15 ÷ 3 = ____5__ or 5 × 3 = 15.
Eureka Math Grade 3 Module 1 Lesson 4 Homework Answer Key

Question 1.
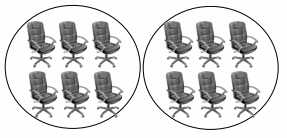
12 chairs are divided into 2 equal groups.
There are ____6_____ chairs in each group.
Answer:
There are 6 chairs in each group,
Explanation:
As given in the picture there are 12 chairs divided as 12 ÷ 2 = 6 chairs in each group, So, there are 6 chairs in 2 equal groups.
Question 2.
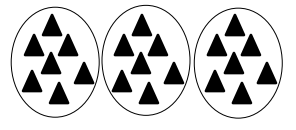
21 triangles are divided into 3 equal groups.
There are ____7_____ triangles in each group.
Answer:
There are 7 triangles in each group,
Explanation:
As given in the picture there are 21 triangles divided as 21 ÷ 3 =7 triangles in each group, So, there are 7 triangles in 3 equal groups.
Question 3.
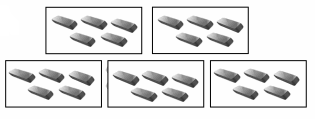
25 erasers are divided into ___5___ equal groups.
There are ____5_____ erasers in each group.
Answer:
25 erasers are divided into 5 equal groups.
There are 5 erasers in each group as 25 ÷ 5 = 5 erasers,
Explanation:
As given in the picture there are 25 erasers divided into 5 equal groups.
There are 5 erasers in each group as 25 ÷ 5 = 25 erasers.
Question 4.
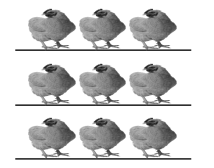
___9____ chickens are divided into ___3____ equal groups.
There are ____3_____ chickens in each group.
9 ÷ 3 = ____3______
Answer:
9 chickens are divided into 3 equal groups.
There are 3 chickens in each group as 9 ÷ 3 = 3 chickens,
Explanation:
As given in the picture there are 9 chickens divided into 3 equal groups, There are 3 chickens in each group as 9 ÷ 3 = 3 chickens.
Question 5.

There are ____3_____ buckets in each group.
12 ÷ 4 = ____3____
Answer:
12 buckets are divided into 4 equal groups.
There are 3 buckets in each group as 12 ÷ 4 = 3 buckets,
Explanation:
As given in the picture there are 12 buckets divided into 4 equal groups, There are 3 buckets in each group as 12 ÷ 4 = 3 buckets.
Question 6.
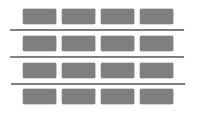
16 ÷ 4 = _4_
Answer:
16 bricks are divided into 4 equal groups.
There are 4 bricks in each group as 16 ÷ 4 = 4 bricks,
Explanation:
As given in the picture there are 16 bricks divided into 4 equal groups, There are 4 bricks in each group as 16 ÷ 4 = 4 bricks.
Question 7.
Andrew has 21 keys. He puts them in 3 equal groups.
How many keys are in each group?
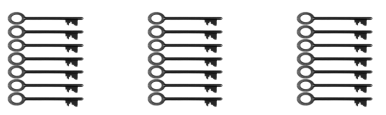
There are ___7____ keys in each group.
21 ÷ 3 = ____7______
Answer:
21 keys are divided into 3 equal groups.
There are 7 keys in each group.
Explanation:
Given Andrew has 21 keys. He puts them in 3 equal groups. So, number of keys in each group are 7 keys as 21 ÷ 3 = 7 keys in each group.
Question 8.
Mr. Doyle has 20 pencils. He divides them equally between 4 tables. Draw the pencils on each table.
There are _____5_____ pencils on each table.
20 ÷ ___4_____ = ____5______
Answer:
There are 5 pencils on each table,
Explanation:
Given Mr. Doyle has 20 pencils and he divides them equally between 4 tables. Drawn the pencils on each table as 20 ÷ 4= 5 pencils on each table as shown above.
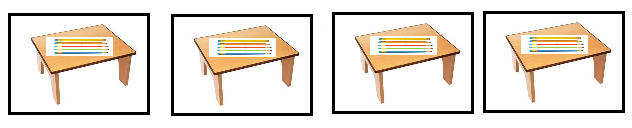
Question 9.
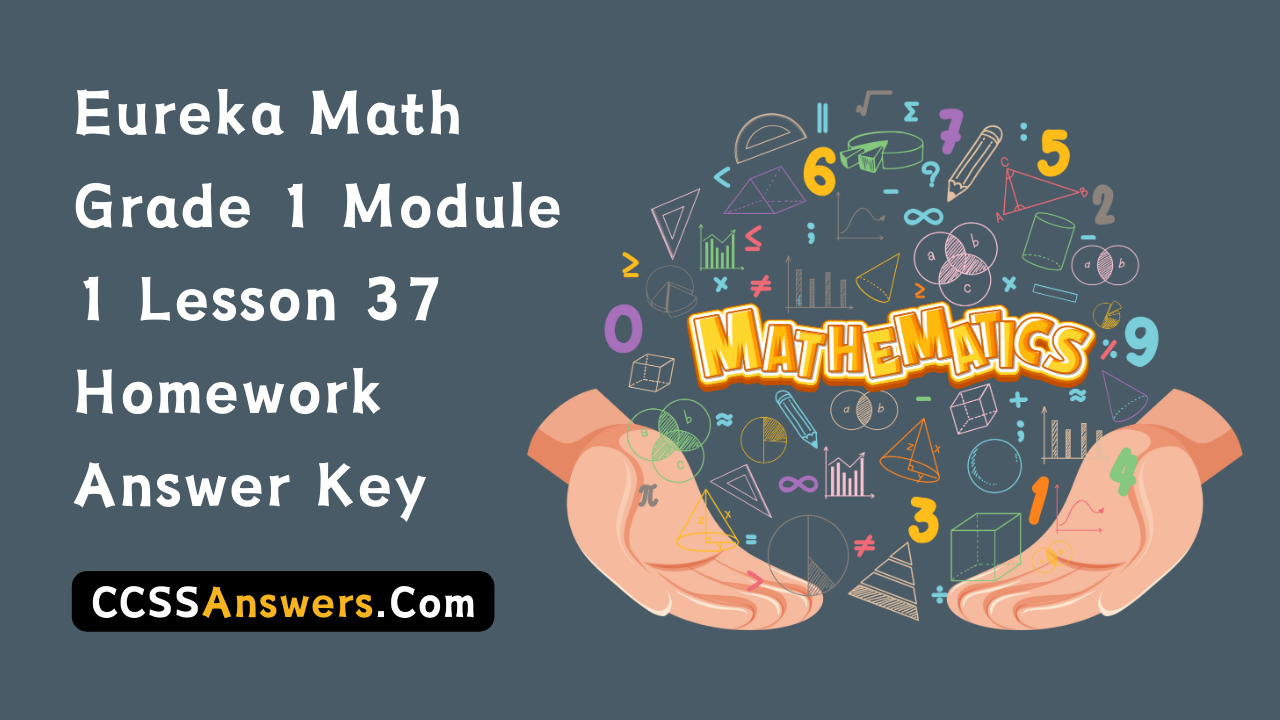
Jenna has markers. The picture shows how she placed them on her desk. Write a division sentence to represent how she equally grouped her markers.
There are ______4______ markers in each row.
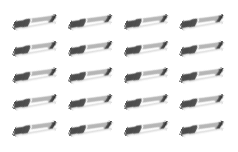
____20______ ÷ ___5_______ = ____4____
Answer:
Division sentence to represent Jenna is 20 ÷ 5 = 4 markers equally grouped in each row,
Explanation:
Given Jenna has markers and the picture shows how she placed them on her desk. Wrote a division sentence 20 ÷ 5 = 4 markers to represent how Jenna equally grouped 4 markers in each row.